Rapid identification method for homology of bacterial strains
A homology, bacterial strain technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problem of inability to identify the best strain, and achieve the effect of low cost and safe experimental process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
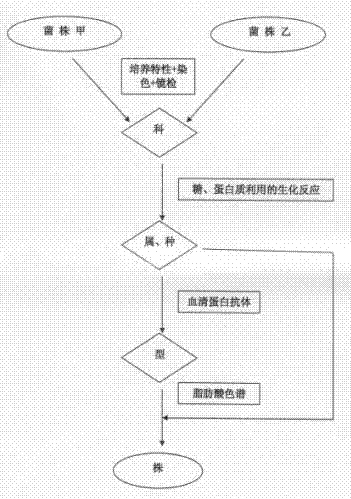
[0025] Such as figure 1 Shown, the homologous rapid identification method of a kind of bacterial strain of the present invention comprises the steps:
[0026] Ⅰ. Preliminary identification is carried out according to the morphology, staining and culture characteristics of bacteria. This method can identify bacteria into families.
[0027] Ⅱ. Use the biochemical reaction of bacteria to sugar and protein to identify. This method can identify bacteria to genus or species.
[0028] Ⅲ. Serological identification: Use antibodies containing known specific proteins to detect unknown bacteria. This method can identify bacteria into species or types.
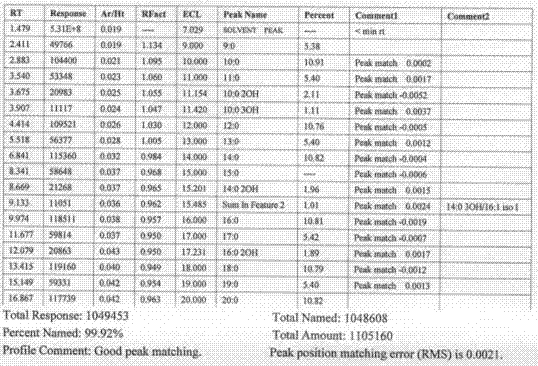
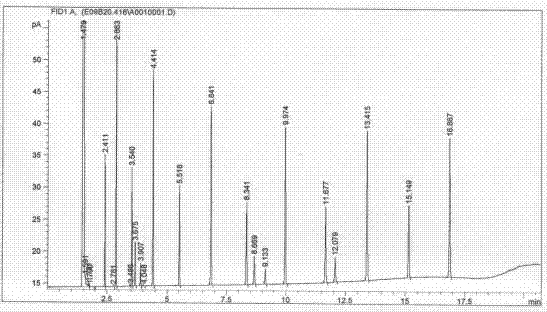
[0029] Ⅳ. Inoculate the bacteria to be tested on a lipid-free medium for culture, collect colonies, and transfer bacterial fatty acids from the aqueous phase to the organic phase through saponification, methylation, extraction, and washing processes. Specifically include the following processes:
[0030] 1. Colony acquisition: Inoculat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com