On-line testing structure for polycrystalline silicon material residual stress
A technology of residual stress and online testing, which is applied in the fields of material resistance, force/torque/power measuring instrument, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, etc. The effect of simple signal loading and measurement, simple method, and low requirements for test equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
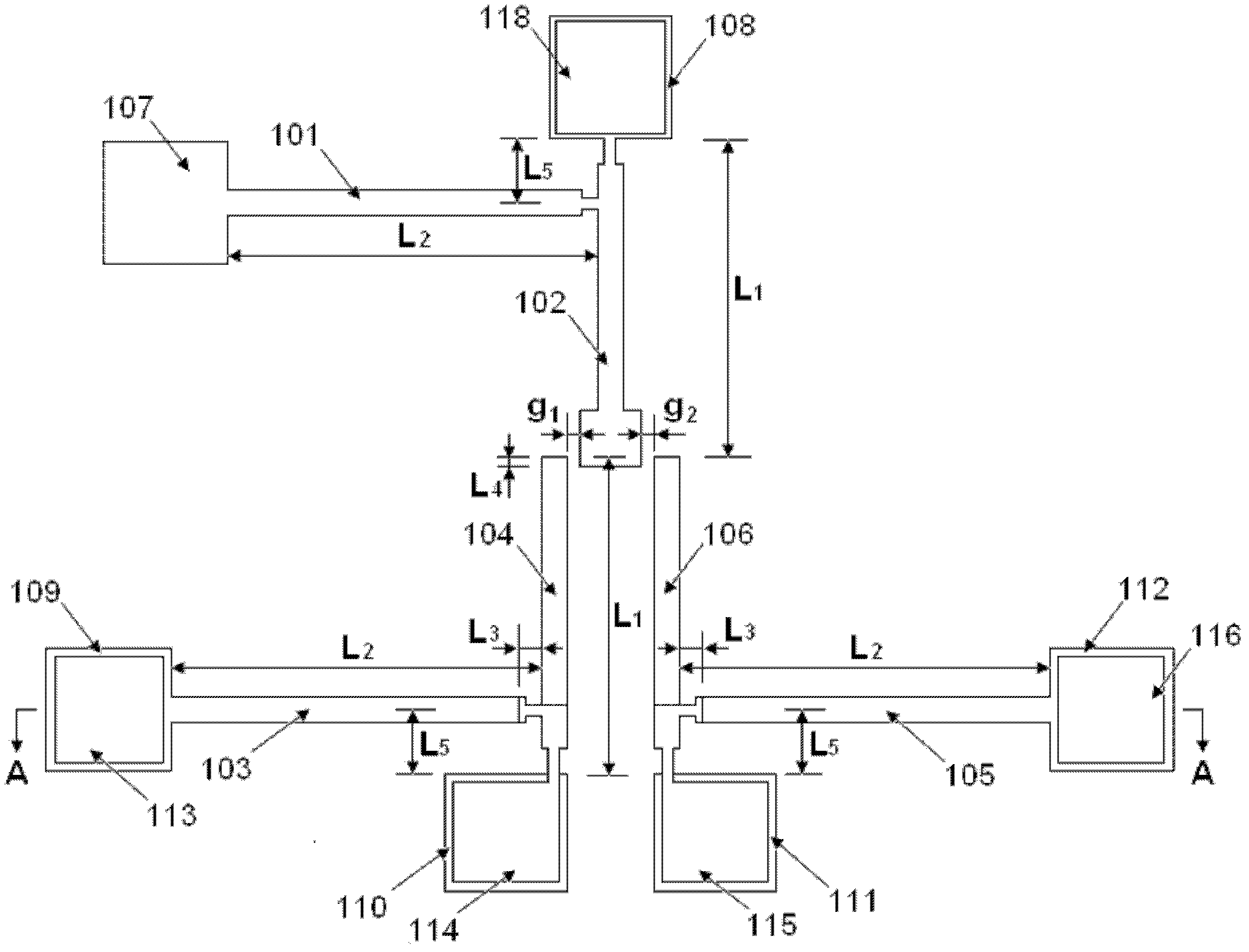
[0012] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
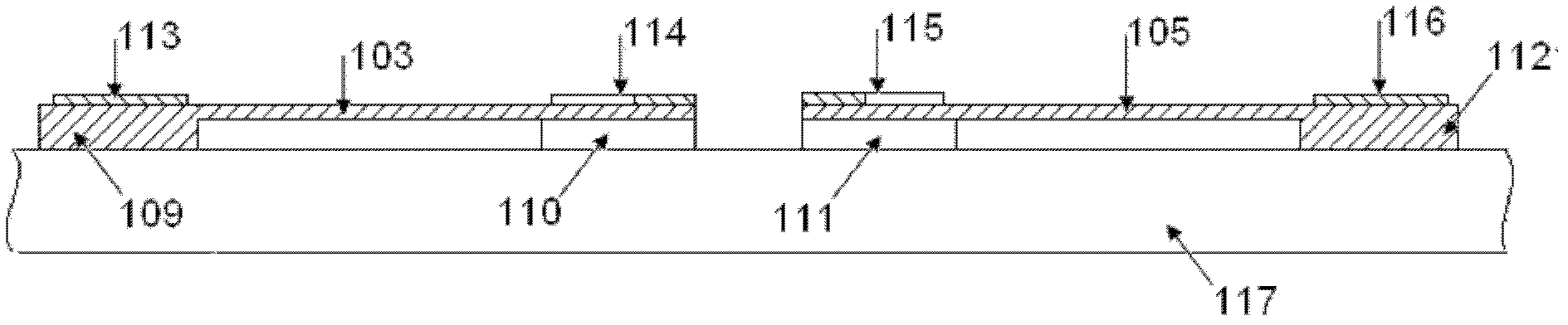
[0013] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the polysilicon material residual stress on-line testing structure of the present invention includes three deflection pointers with the same basic structure, and each deflection pointer includes a horizontal driving beam 101, 103, 105, and a vertical driving beam 101, 103, 105. pointers 102, 104, 106 and two anchor regions fixed on the substrate, and the two anchor regions respectively fix one end of the driving beam 101, 103, 105 and one end of the pointer 102, 104, 106. The main body of the test structure is fabricated from polysilicon material.
[0014] The three polysilicon deflection pointers are placed in the shape of "pin", and the pointers 102, 104, and 106 all point to the center; the upper polysilicon deflection pointer includes the driving beam 101, the pointer 102, the anchor areas 107, 108 and the metal ele...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com