Optical fiber end structures for improved multi-mode bandwidth, and related systems and methods
A multi-mode optical fiber and optical fiber technology, applied in transmission systems, multi-mode transmission, optical fiber transmission, etc., can solve the problem of clock frequency reducing link transmission data rate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] Referring now to the embodiments in detail, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings, in which some, but not all, are shown. The concepts may, of course, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limiting herein; rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will satisfy applicable legal requirements. Wherever possible, the same reference numerals will be used to refer to the same components or parts.
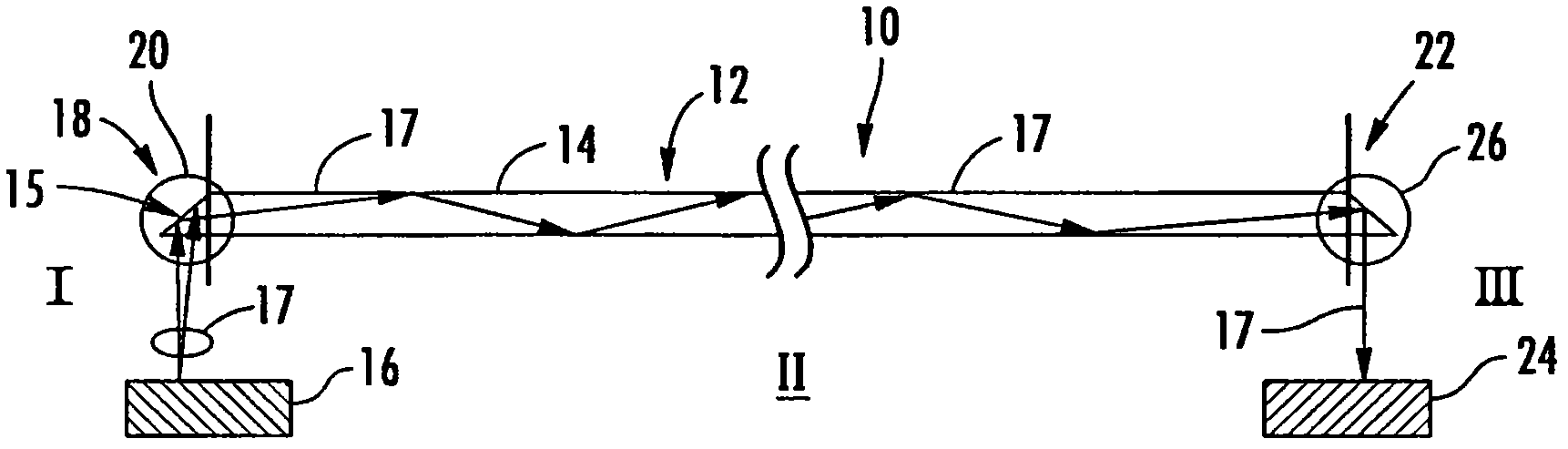
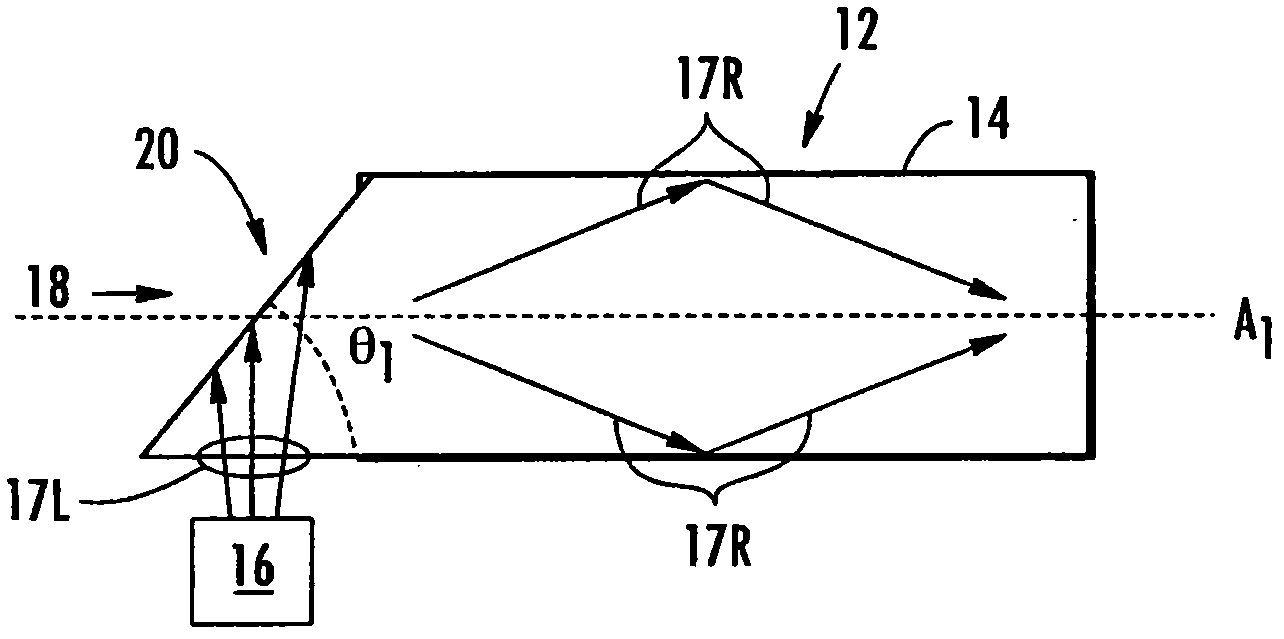
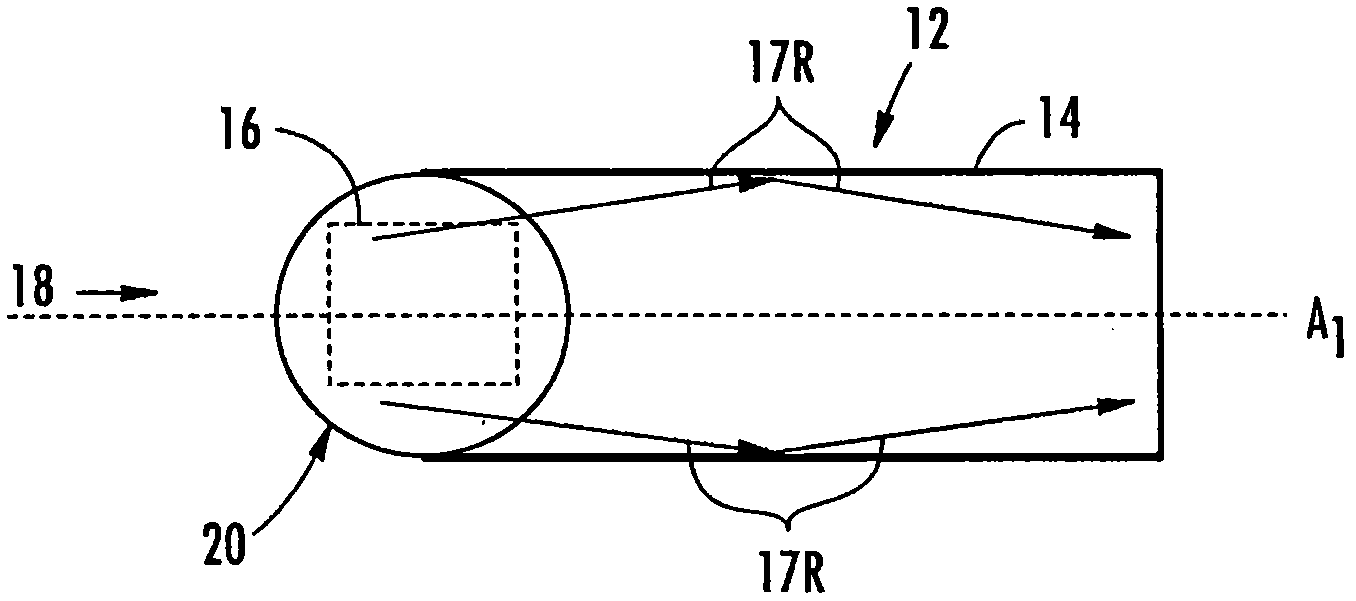
[0026] Embodiments disclosed in this detailed description include multimode fiber optic equipment, multimode fiber optics, and related methods for improving the bandwidth of fiber optic links. One or more end structures may be placed at the fiber end of a multimode fiber to improve link bandwidth by reducing and / or eliminating modal dispersion. Modal dispersion can result from fiber launch conditions that excite a set of modes or groups of modes in the fiber that have group velocities that differ significan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com