Infrared sensor
An infrared sensor and infrared technology, applied in the direction of instruments, scientific instruments, electric radiation detectors, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the distance of heat-sensitive elements, high thermal conductivity of resin films, and high prices, so as to improve thermal responsiveness and detection sensitivity , high sensitivity, compact and well-made effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] Below, reference Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 The first embodiment of the infrared sensor according to the present invention will be described. In addition, in each drawing used in the following description, in order to make each component a recognizable or easily recognizable size, the scale is appropriately changed.
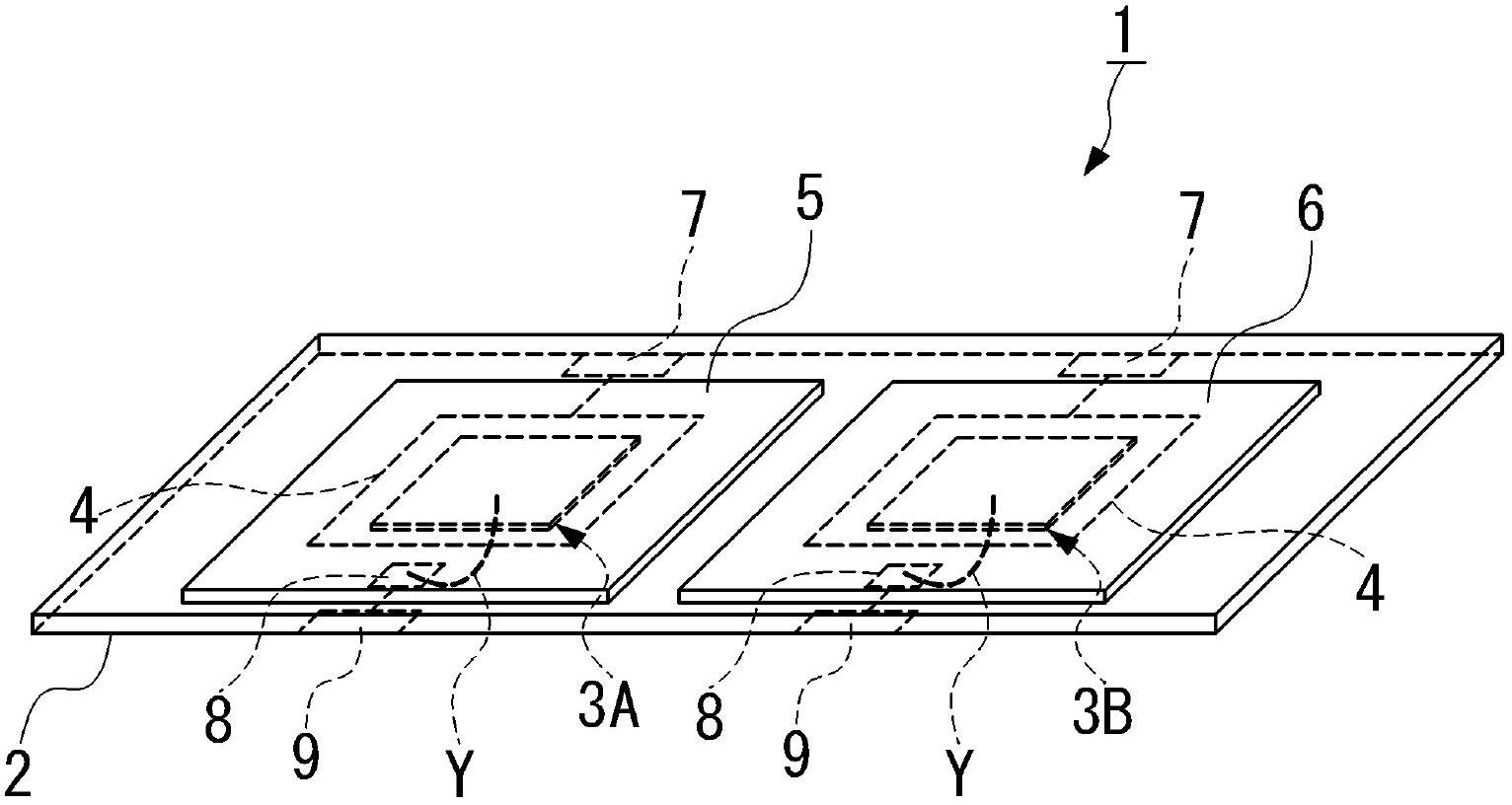
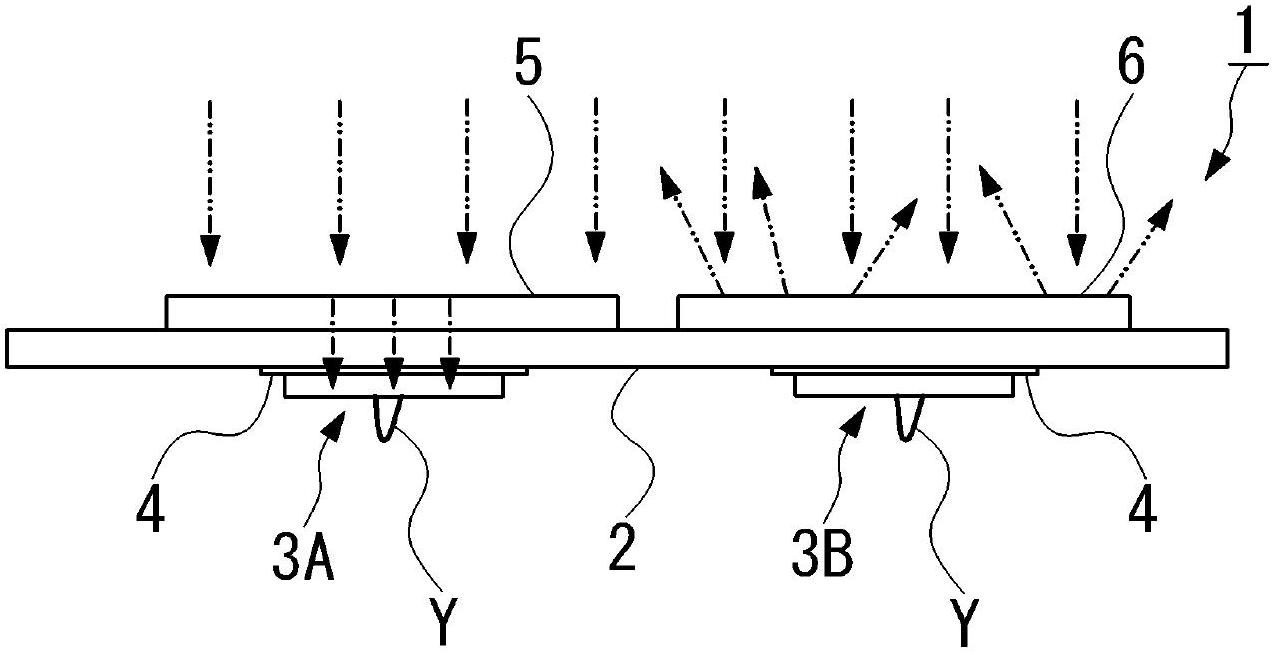
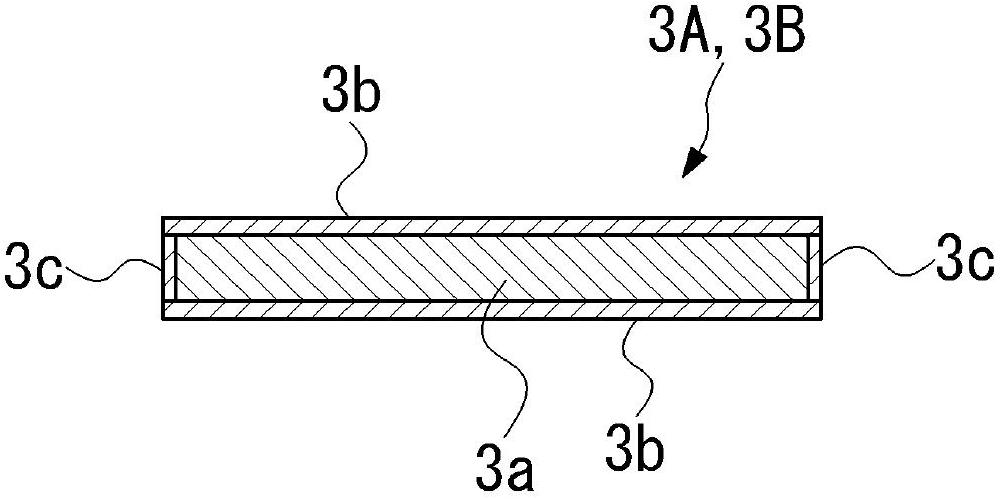
[0035] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the infrared sensor 1 of the present embodiment includes: an insulating film 2; a first thermal element 3A and a second thermal element 3B, which are spaced apart from each other on one surface (lower surface) of the insulating film 2; For the bonding electrode 4, the insulating film 2 is patterned with copper foil or the like on one side, and the first heat-sensitive element 3A and the second heat-sensitive element 3B; the infrared absorption film 5 and the first heat-sensitive element 3A are bonded respectively Opposite and provided on the other side (upper surface) of the insulating film 2; and the infrared reflec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com