Detoxification method of wood fiber hydrolyzed sugar liquid
A technology for hydrolyzing sugar liquid and wood fiber, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as poor performance, and achieve the effects of improving fermentation performance, sugar utilization rate, and utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Organic modification of bentonite with cationic surfactant.
[0026] Organic modification of bentonite: Use cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as a modifier to organically modify sodium-based bentonite to prepare organic bentonite——CTAB-bentonite, as follows:
[0027] 1. Weigh 2-4g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and fully dissolve it in 100ml of distilled water to prepare a 2%-4% cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution.
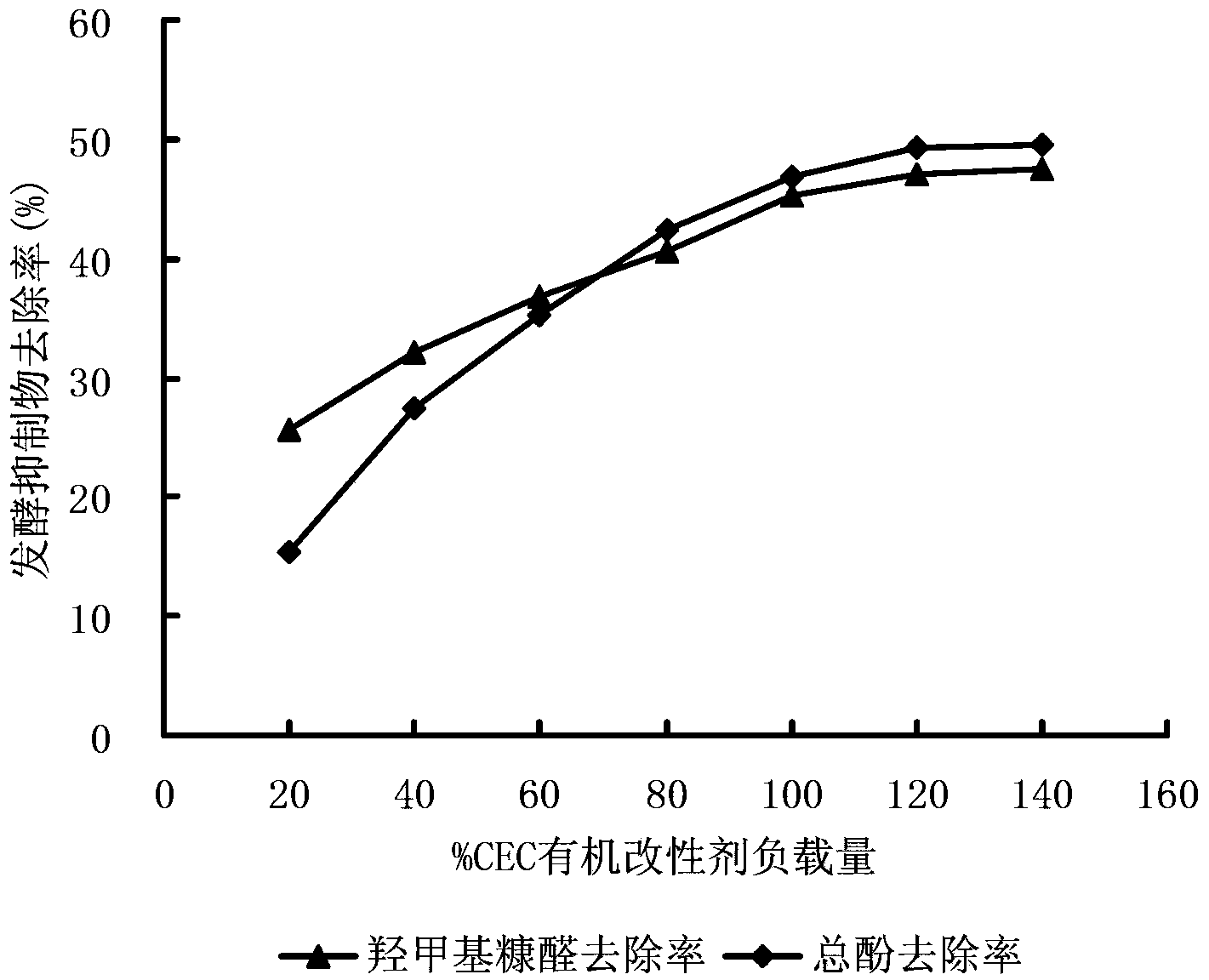
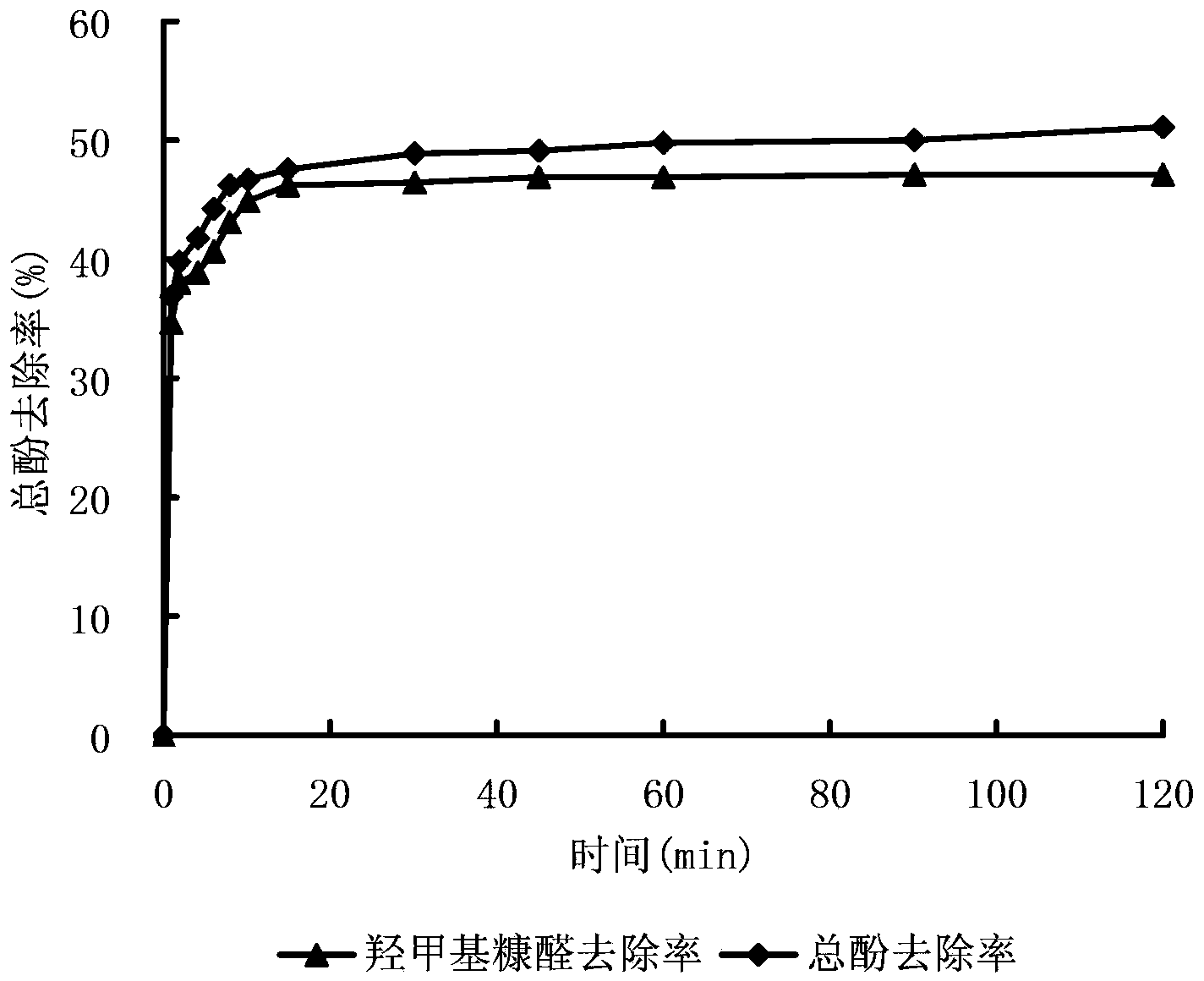
[0028] 2. Add 10g of sodium bentonite to the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution above to prepare a 10% suspension, and heat it in a water bath at 70°C for 2 hours with stirring. The dosage ratio of sodium bentonite and organic modifier is determined according to the cation exchange capacity of bentonite.
[0029] 3. After heating, centrifuge and discard the supernatant.
[0030] 4. Wash the bentonite obtained by the above centrifugation repeatedly, then dry it at 80° C., activate it at 105° C. for 1 hour, and grind it through a ...
Embodiment 2
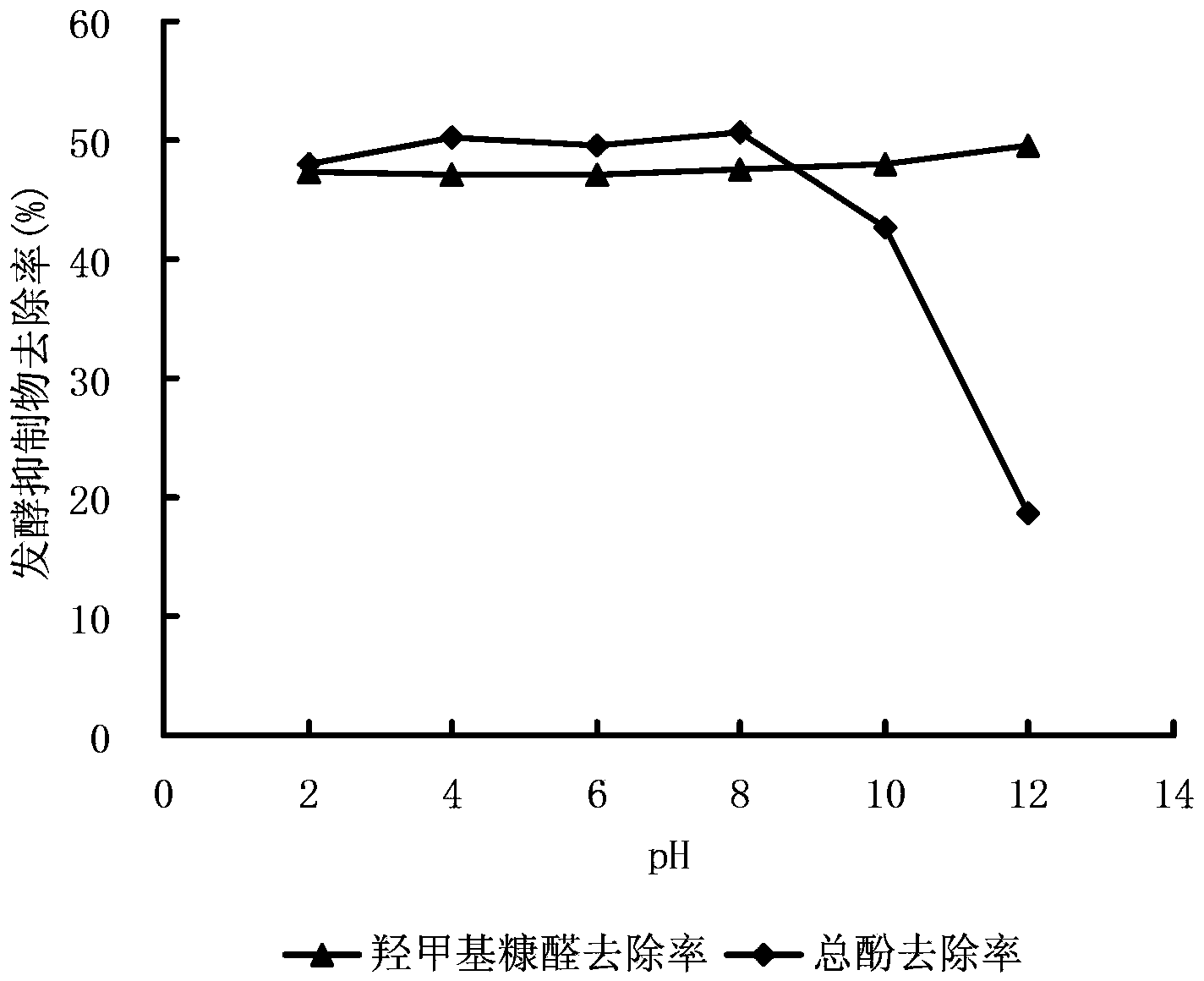
[0031] Determination of cation exchange capacity: Wash the soluble salts in bentonite with 50% ethanol solution, then add 0.1mol / L ammonium chloride-50% absolute ethanol extract to fully carry out the exchange reaction; collect the exchange liquid, and add 35% neutral formaldehyde, make it condense with the residual ammonium ion in the exchange liquid to generate formic acid, then immediately titrate with 0.1mol / L sodium hydroxide standard solution, the amount of ammonium ion consumed in the exchange liquid is is the corresponding amount of exchangeable cations. The cation exchange capacity refers to the amount of K adsorbed at a pH of 7 + 、Na + , Ca 2+ , Mg 2+ The total amount of cations, referred to as CEC. The cation exchange capacity of bentonite is the main basis for judging the quality of bentonite. The larger the CEC value, the greater the negative charge, and the stronger its hydration, expansion and dispersion capabilities; otherwise, the worse its hydration, expa...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Organic modification of bentonite with cationic surfactant.
[0038] Organic modification of bentonite: Use dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide as a modifier to organically modify sodium-based bentonite, as follows:
[0039] 1. Weigh 2-4g of dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide and fully dissolve it in 100ml of distilled water to prepare a 2%-4% cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution.
[0040] 2. Add 10g of sodium bentonite to the above dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide solution to prepare a 10% suspension, and heat it in a water bath at 70°C for 3 hours with stirring. The dosage ratio of sodium bentonite and organic modifier is determined according to the cation exchange capacity of bentonite.
[0041] 3. After heating, centrifuge and discard the supernatant.
[0042] 4. Repeatedly washing the bentonite obtained by the above centrifugation, drying at 70°C, activating at 105°C for 2 hours, and grinding through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com