Method and system for data migration in peer-to-peer network
A peer-to-peer network and data technology, applied in the network field, can solve the problems of long time required for node joining or load balancing, slow network connection speed, long transmission time, etc., to reduce transmission volume, improve speed and reliability, and ensure The effect of normal operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
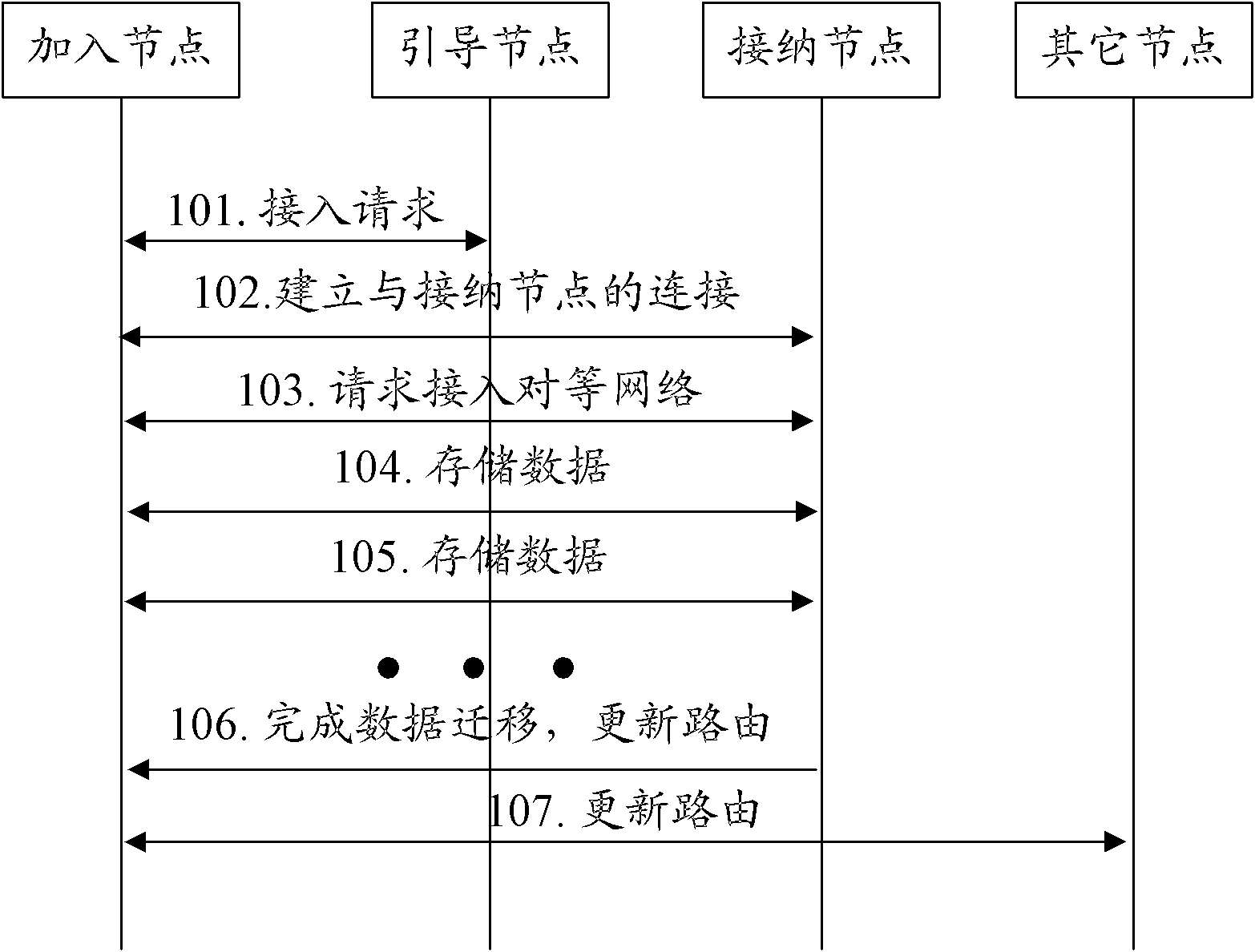
[0058] The application scenario of this embodiment is: a node joining process. In the following description, a node that requests to join is called a joining node, and a node that is currently responsible for storing the data acquired by the joining node is called an accepting node. This embodiment implements the method of data migration, such as image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0059] Step 301: The joining node wishes to join the P2P network, sends an access request to the bootstrap node, and establishes a connection with the bootstrap node.
[0060] Step 302: Under the guidance of the guide node, the joining node establishes a connection with the accepting node.
[0061] Step 303: the joining node sends a joining request to the accepting node, requesting to join the P2P network, and hopes to take over the data under part of the resource identifier of the accepting node;
[0062] Here, the joining node can know which part of the data under the resource ident...
Embodiment 2
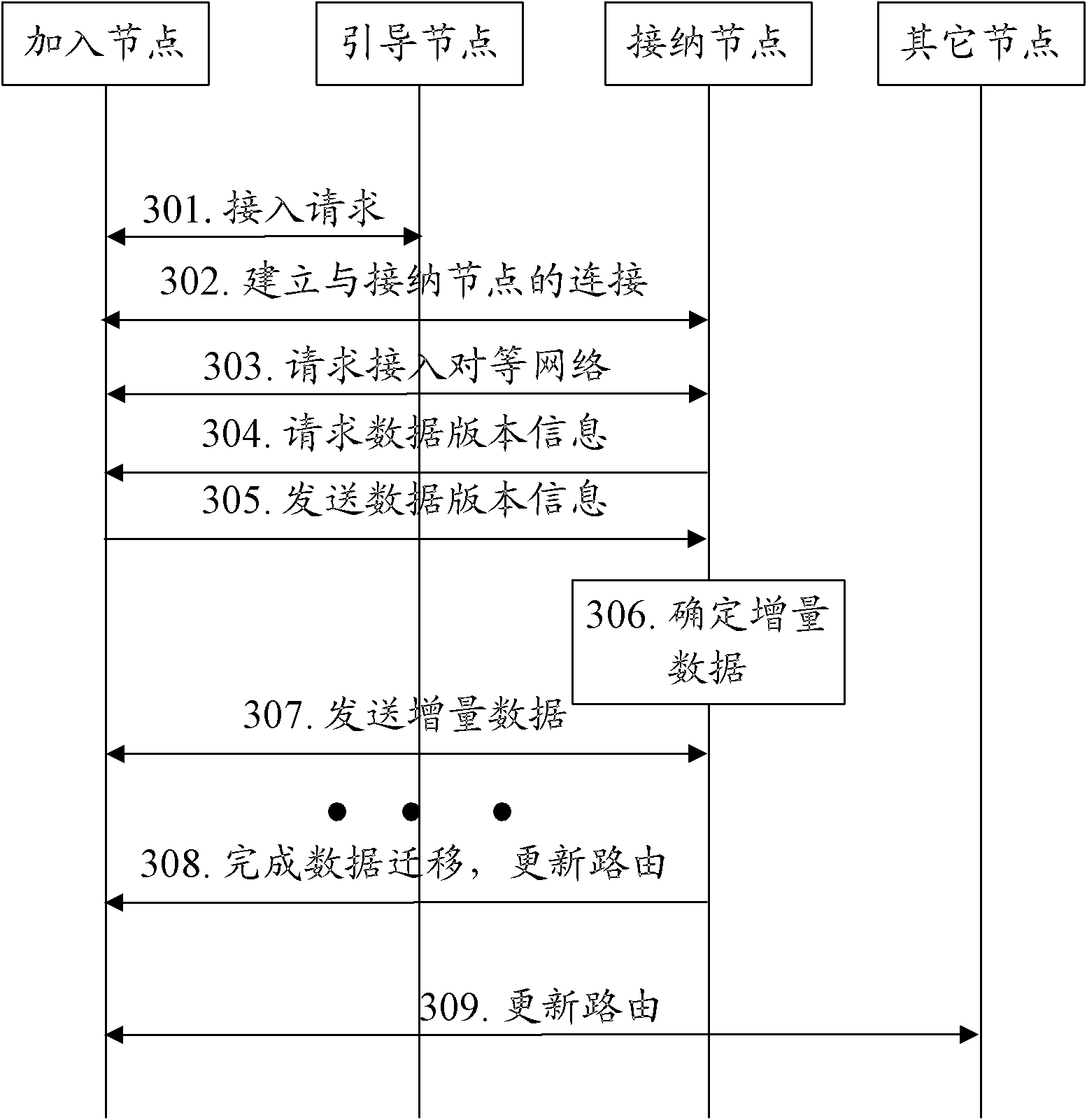
[0077] The application scenario of this embodiment is: the node join process, and the requested data includes quasi-static data and dynamic data; wherein, the quasi-static data refers to data that does not change much over time under the resource identifier, and the dynamic data Refers to: data that changes frequently under the resource identifier. In actual application, whether the data is quasi-static data or dynamic data can be determined by specific services. For example, in a P2P Internet Protocol (IP, Internet Protocol) telephone service, all data of each user can be stored under the same resource identifier, but there are few changes in the user number information and user service subscription information, so , can be used as quasi-static data. The user's online information and location information change rapidly, so they can be used as dynamic data. In the following description, a node requesting to join is called a joining node, and a node currently responsible for ...
Embodiment 3
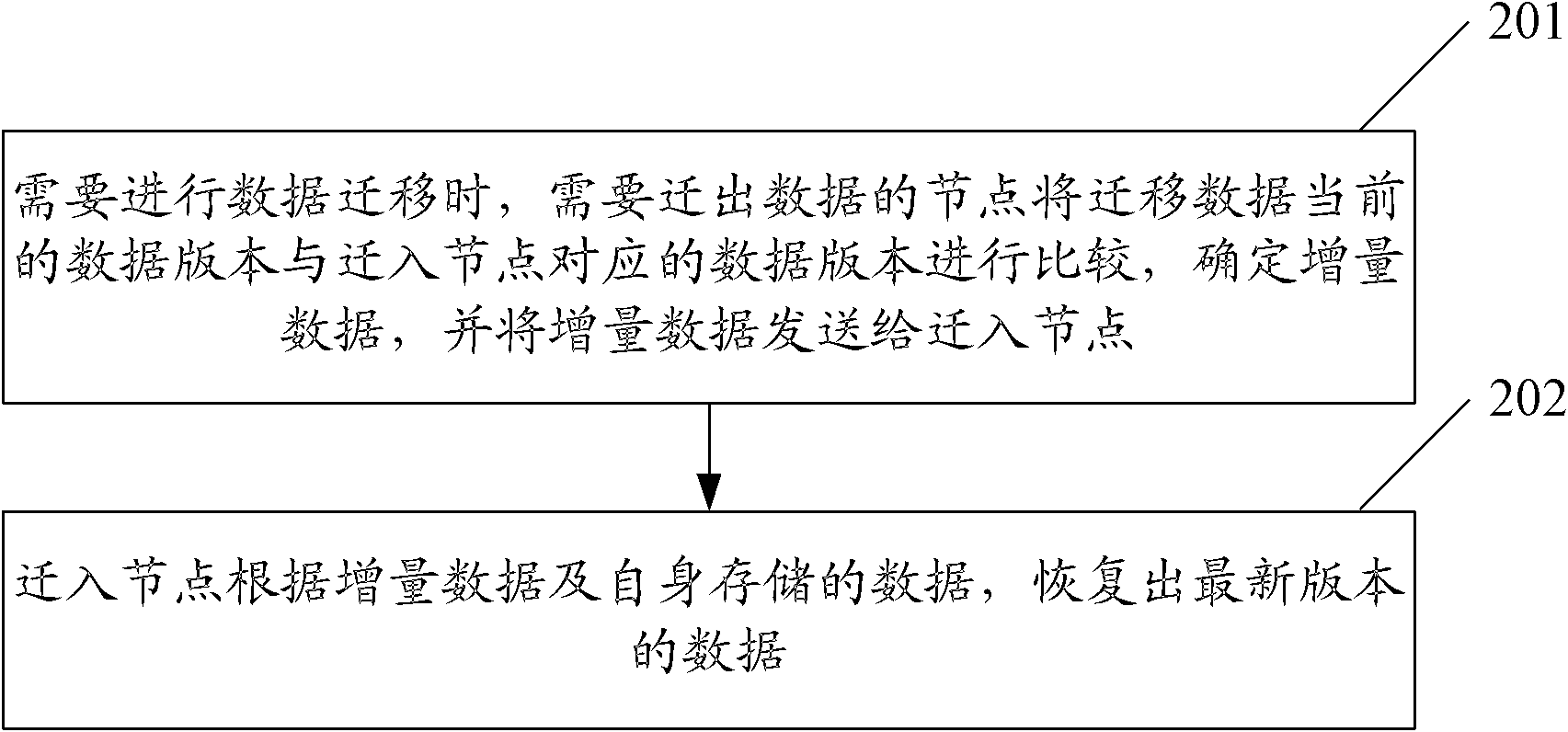
[0098] The application scenario of this embodiment is: the data version information is the data version number. In the following description, the node that migrates data is called the source node, and the node that migrates data is called the target node. This embodiment implements data migration method, such as Figure 5 shown, including the following steps:
[0099] Step 501: When data migration is required, the target node sends the locally stored data version number to the source node;
[0100] Here, the format of the data version number can be an integer that increases sequentially, the format of the main version number plus this version number, or a timestamp. For example, if the format of the data version number is an integer that increases sequentially , the data version number can be 1, 2, 3, etc. If the format of the data version number is the main version number plus this version number, the data version number can be 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, etc.
[0101] Step 502: After t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com