Physical downlink shared channel (PDSCH) scheduling method and device
A technology of physical downlink sharing and scheduling method, which is applied in the direction of adjusting transmission mode, adjusting channel coding, wireless communication, etc. It can solve problems such as high channel coding rate, affecting user performance, cell capacity, and failure to receive data, so as to improve transmission performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
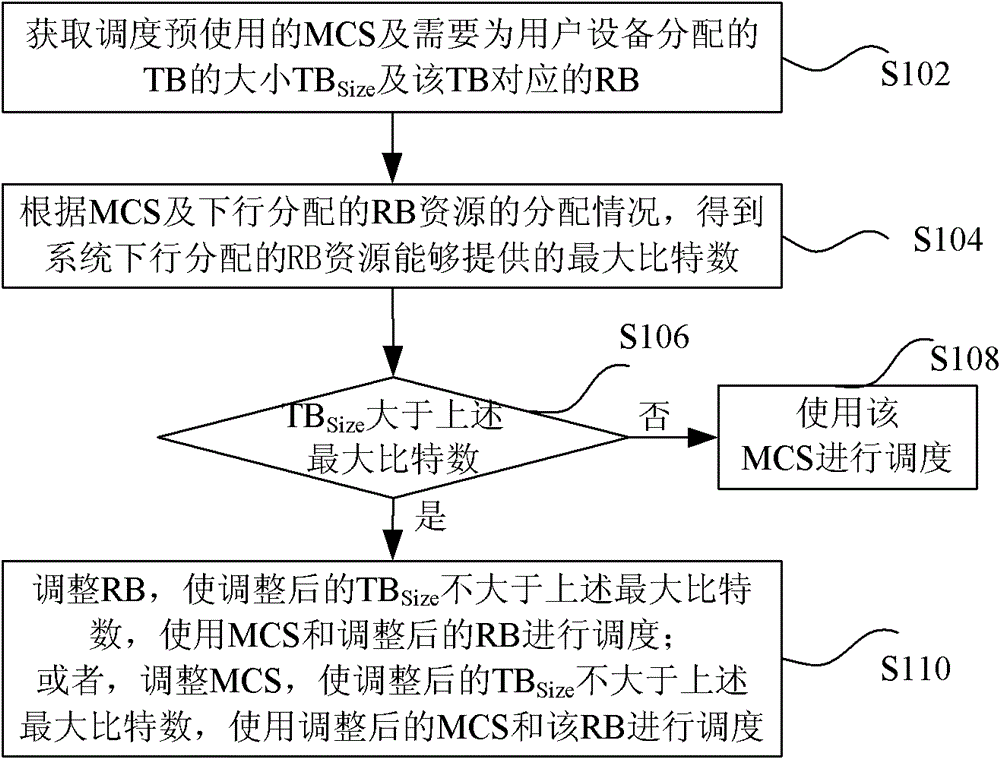
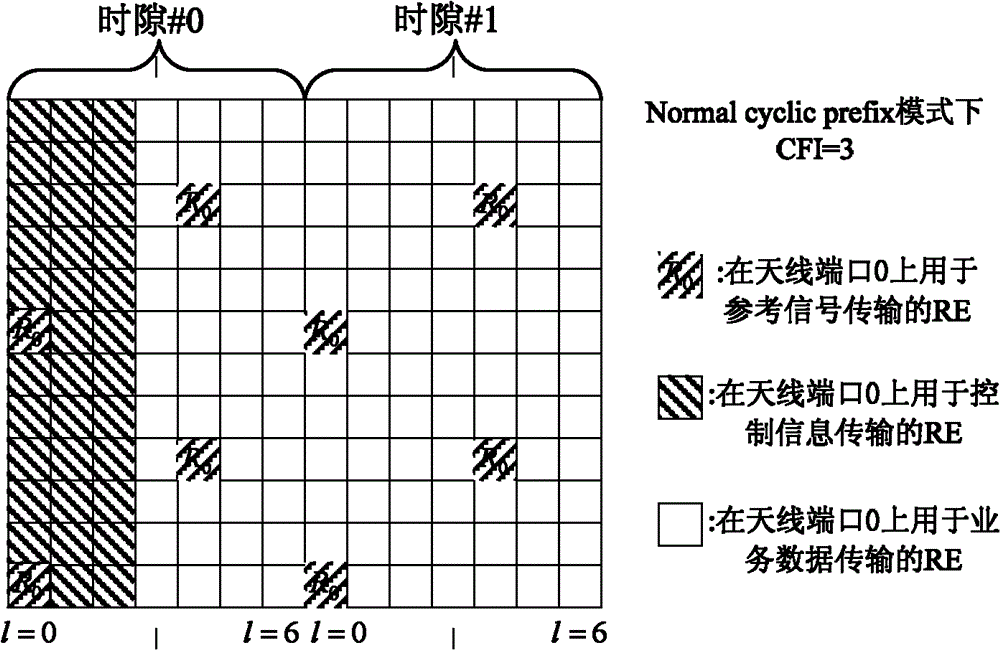
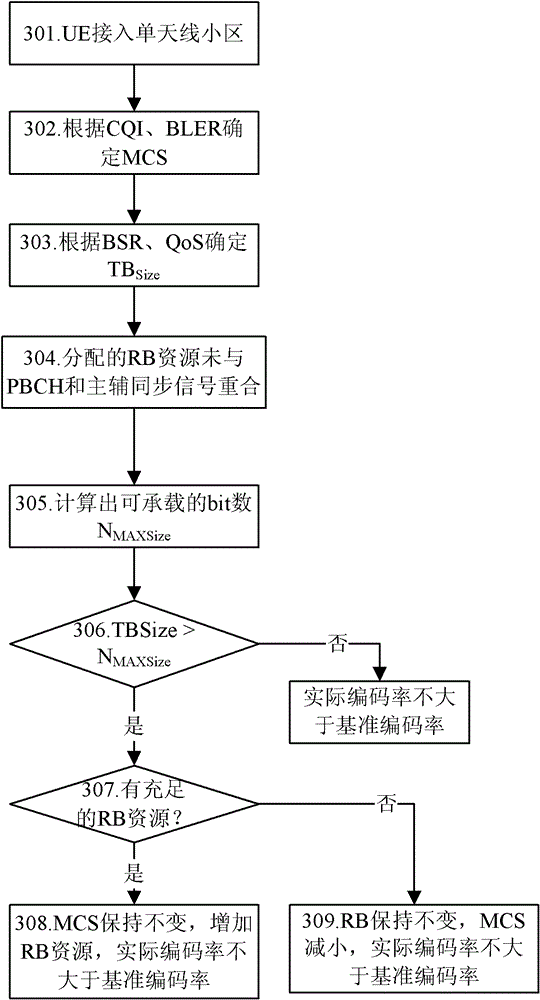
[0046] This embodiment takes figure 2 The time-frequency resource of the single antenna port shown is taken as an example for illustration, image 3 It is a flowchart of scheduling in this embodiment when the UE accesses a single-antenna cell (that is, the downlink transmission mode is TM1), as shown in image 3 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0047] Step S301, the UE accesses a single-antenna cell, and the downlink transmission mode is TM1;
[0048] Step S302, the eNB obtains the radio link quality information of the user equipment, and obtains the pre-scheduled MCS according to the BLER of the PDSCH channel;
[0049] Step S303, according to factors such as BSR and QoS, determine the TB block size TB that needs to be scheduled Size ;
[0050] Step S304, the RB resources allocated for the downlink do not coincide with the PBCH and the primary and secondary synchronization signals;
[0051] Step S305, according to figure 2 , calculate the number of R...
Embodiment 2
[0057] This embodiment takes Figure 4 The time-frequency resources of the two antenna ports shown are taken as an example for illustration, Figure 5 It is a flowchart of scheduling when the UE accesses a two-antenna cell (that is, the downlink transmission mode is TM3) in this embodiment, as shown in Figure 5 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0058] Step S501, the UE accesses a cell with one or two antennas, and the downlink transmission mode is TM3;
[0059]Step S502, the eNodeB obtains the radio link quality information of the user equipment, and obtains the MCS for dual-stream pre-scheduling according to the BLER of the PDSCH channel;
[0060] Step S503, according to factors such as BSR and QoS, determine the TB block size TB that needs to be scheduled Size ;
[0061] Step S504, the RB resource part of the downlink allocation overlaps with the PBCH;
[0062] Step S505, according to Figure 4 , calculate the number of REs that can actually be used ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] This embodiment takes Image 6 The time-frequency resources of the shown four antenna ports are taken as an example for illustration, Figure 7 It is a flow chart of scheduling when the UE accesses a four-antenna cell (that is, the downlink transmission mode is TM4) in this embodiment, as shown in Figure 7 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0069] Step S701, the UE accesses a four-antenna cell, and the downlink transmission mode is TM4;
[0070] Step S702, the eNB obtains the radio link quality information of the user equipment, and obtains the pre-scheduled MCS of each stream according to the BLER of the dual streams of the PDSCH channel;
[0071] Step S703, according to factors such as BSR, QoS, determine the TB block size TB that needs to be scheduled Size ;
[0072] Step S704, all the RB resources allocated for the downlink overlap with the PBCH;
[0073] Step S705, according to Image 6 , calculate the number of REs that can actually be used...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com