Self-power supply vibration sensor based on ZnO nanowires and manufacturing method thereof
A vibration sensor, self-powered technology, applied in instruments, using electrical devices, using electromagnetic means, etc., can solve the problems of large size and weight, and achieve the effects of small size, light weight, and prolonged vibration time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
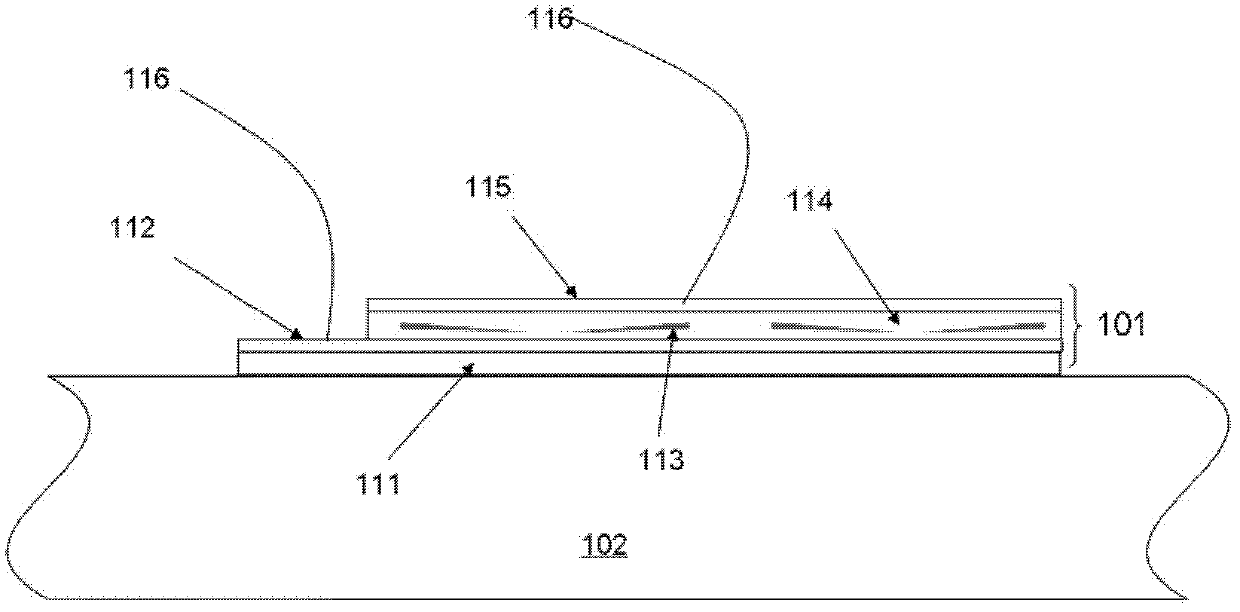
[0054] This embodiment provides a image 3 The self-powered vibration sensor shown consists of:
[0055] PI (polyimide) substrate 111 with a thickness of about 200 μm;
[0056] Cr / Au lower electrode 112 on substrate 111;
[0057] PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) dielectric layer 114 on the lower electrode 112;
[0058] Cr / Au upper electrode 115 on PMMA dielectric layer 114;
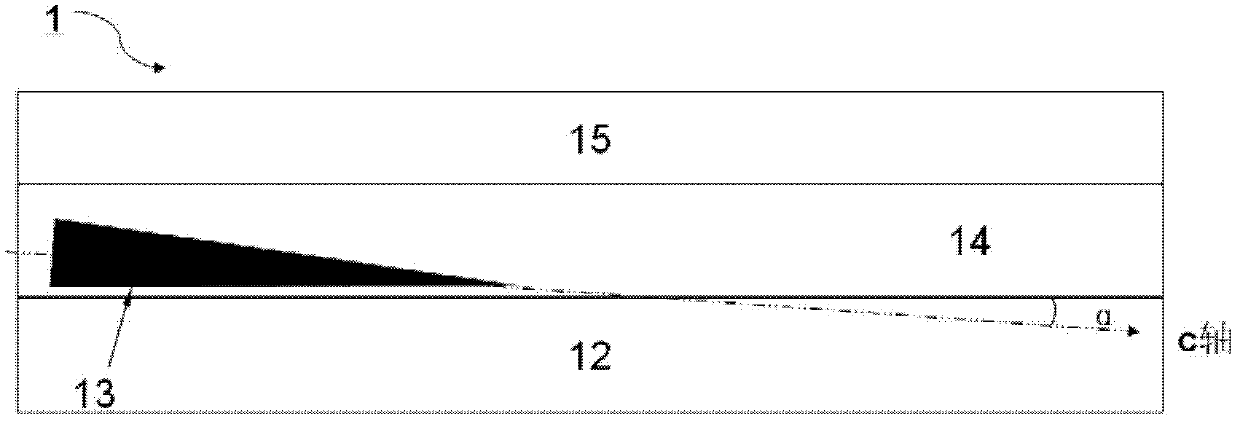
[0059] A plurality of conical ZnO nanowires 113 grown in the c-axis direction are randomly distributed in the dielectric layer, roughly parallel to the upper and lower electrodes, and insulated from the upper and lower electrodes;
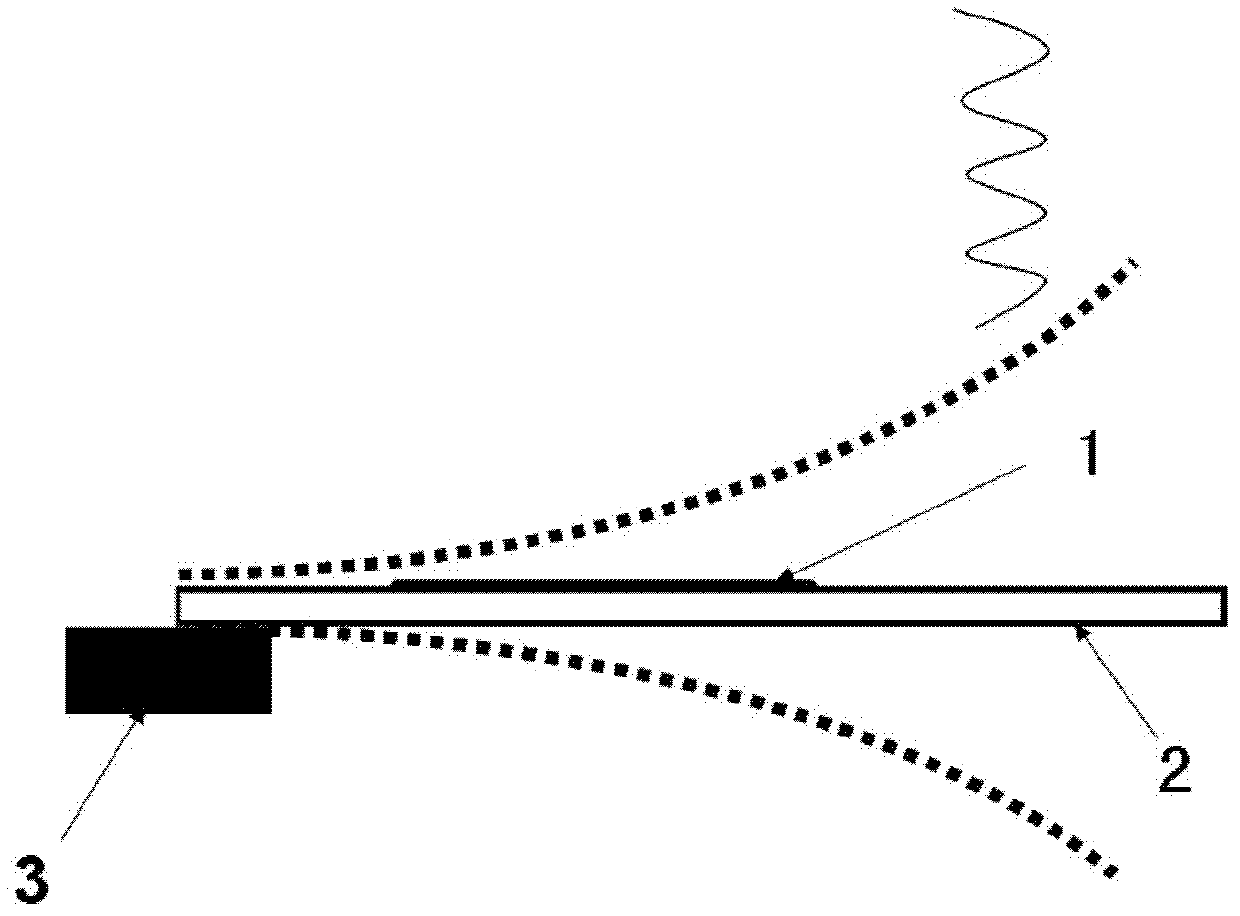
[0060] Cantilever beam 102 supports the dielectric layer and ZnO nanowires between the upper and lower electrodes and the two, and one end of cantilever beam 102 is fixed on the fixed plate (the structure of the fixed plate is the same as that of the fixed plate) figure 1 Same as in , for clarity in image 3 not shown in);
[0061] Two lead wires 116 are electrically conne...
Embodiment 2
[0074] This embodiment provides a Figure 6 The self-powered vibration sensor shown consists of:
[0075] PI (polyimide) substrate 211 with a thickness of about 200 μm;
[0076] Cr / Au lower electrode 212 on substrate 211;
[0077] The first sub-dielectric layer 214a and the second sub-dielectric layer 214b on the lower electrode 212, each sub-dielectric layer 214a, 214b has a plurality of tapered ZnO nanowires 213 grown in the c-axis direction, ZnO nanometer The line 213 is roughly parallel to the upper and lower electrodes and insulated from the upper and lower electrodes, and the first and second sub-dielectric layers are made of PMMA;
[0078] Cr / Au upper electrode 215 on the second sub-dielectric layer 214b;
[0079] Cantilever beam 202 supports the dielectric layer and ZnO nanowires between the upper and lower electrodes and the two, and one end of the cantilever beam 202 is fixed on the fixed plate (the structure of the fixed plate is the same as that of the fixed pla...
Embodiment 3
[0092] This embodiment provides a Figure 7 The self-powered vibration sensor shown consists of:
[0093] Fixed on the fixed piece (the structure of the fixed piece is the same as figure 1 Same as in , for clarity in Figure 7 Not shown in the cantilever beam 302 on), made of conductive material;
[0094] Dielectric layer 314 on cantilever beam 302;
[0095] an upper electrode 315 on the dielectric layer 314;
[0096] A plurality of tapered ZnO nanowires 313 grown in the c-axis direction are located in the dielectric layer, approximately parallel to the upper electrode and the cantilever beam 302 , and insulated from the upper electrode and the cantilever beam 302 .
[0097] The dielectric layer, the upper electrode, and a plurality of tapered ZnO nanowires together constitute the sensor element 301 .
[0098] The self-powered vibration sensor provided by this embodiment can be made by the following methods:
[0099] 1) Spin coating a dielectric material layer with a thi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com