Method for processing deep minipore with large gradient on difficult-to-process material
A large-slope, difficult-to-machine technology, applied in the field of mechanical processing, can solve the problems of difficult dissipation of cutting heat, affect surface integrity, and lengthen the tool, and achieve the effects of excellent cutting performance, good positioning and reasonable thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] Describe the present invention below in conjunction with specific embodiment:
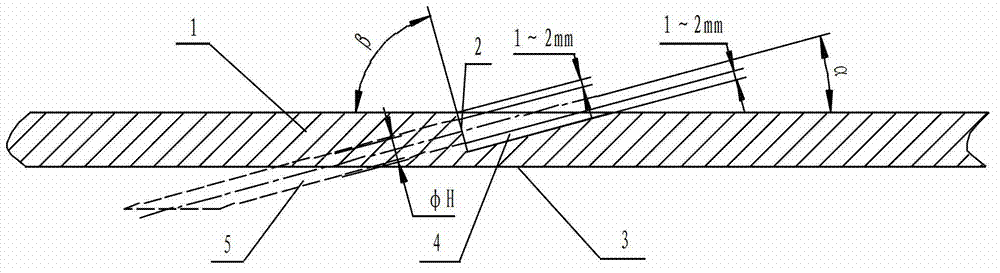
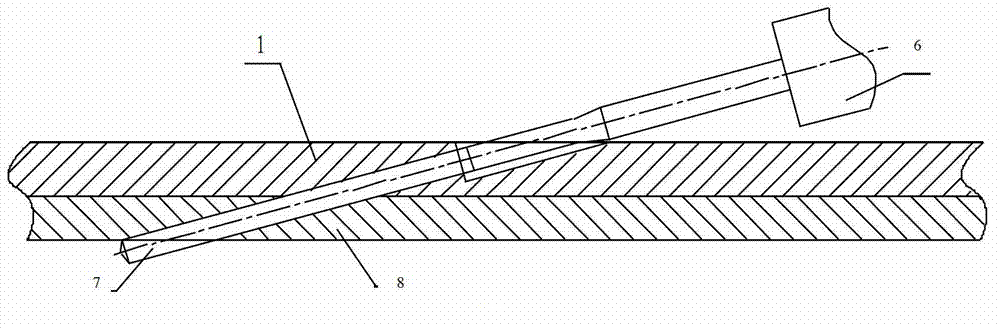
[0027] In this embodiment, the processing material is GH4169 in solid solution and aging state, and the diameter of the oblique hole is Take an oblique hole with an inclination angle of 15° to the processing plane, a vertical thickness of the workpiece of 8mm, and a hole depth of 39mm as an example.
[0028] Step 1: Use bolts to attach and fix the guide plate to the processing surface of the workpiece to be processed.
[0029] Theoretically, using a guide plate with the same material and state as the workpiece to be processed is more beneficial to processing, but if the part material is expensive, using a guide plate with the same material and the same state will increase the test cost and deteriorate the economy. Furthermore, for difficult-to-machine materials, when the guide plate of the same material and thickness is used, the tool wear will increase during the machining process, the fr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com