Cutting method for free-space photoisolator chip body
An optical isolator and free space technology, which is applied to fine working devices, stone processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of optical isolator chip body loss and reduce the utilization rate of raw materials, so as to reduce cutting time and save materials , the effect of improving the efficiency of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with test examples and specific embodiments. However, it should not be understood that the scope of the above subject matter of the present invention is limited to the following embodiments, and all technologies realized based on the content of the present invention belong to the scope of the present invention.
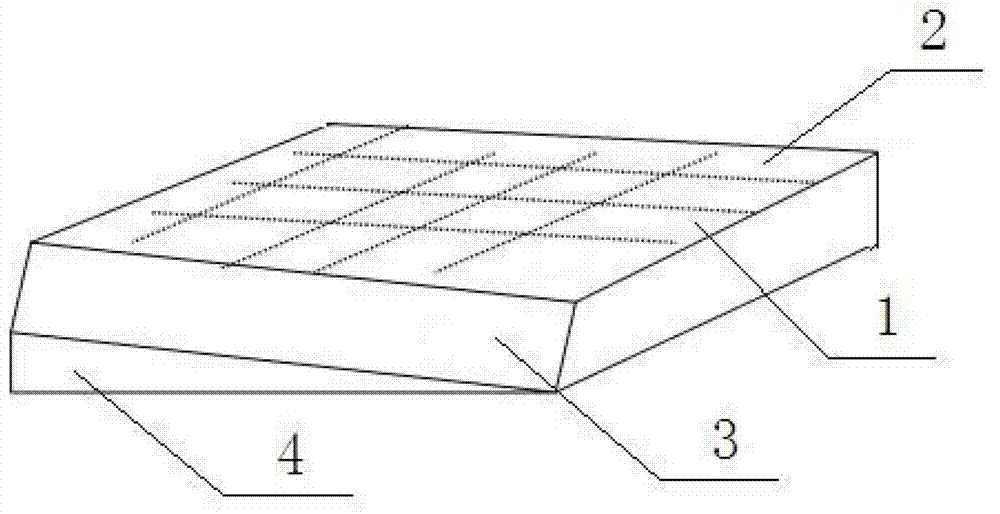
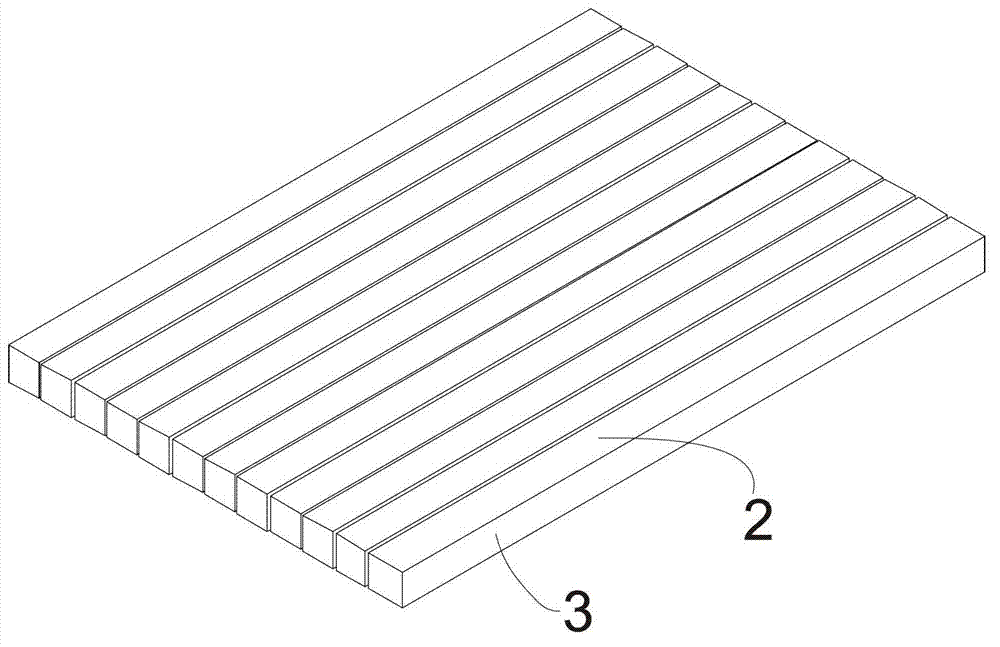
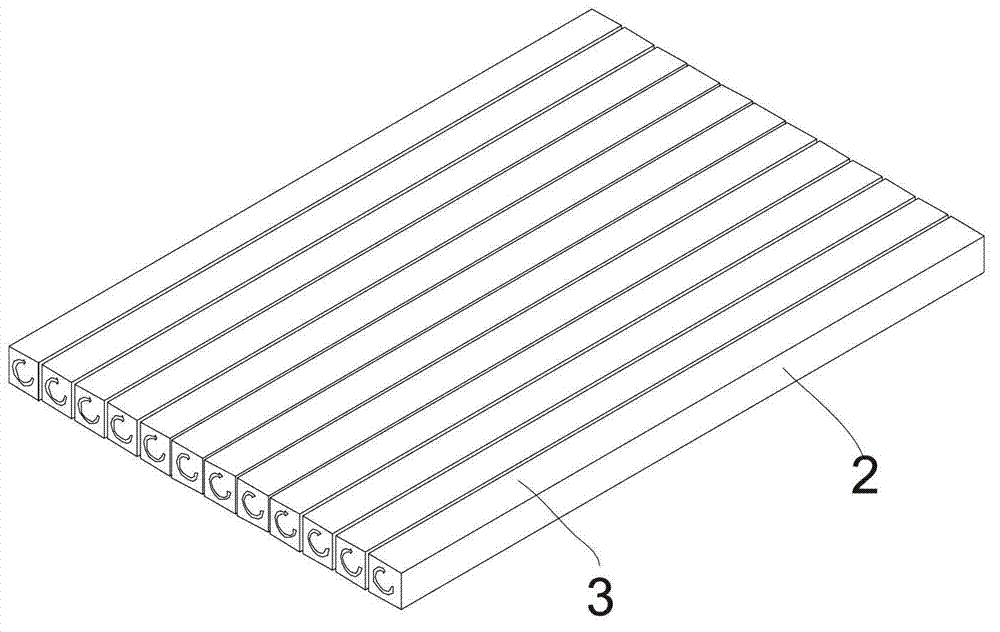
[0025] Such as Figures 2 to 5 Shown, a kind of cutting method of free space optical isolator chip body, the cutting method of described free space optical isolator chip is used for cutting free space optical isolator chip body, free space optical isolator chip body 1 includes as light incident The first plane 2 of the face and the second plane 3 perpendicular to the first plane comprise the following steps:
[0026] A. Set the first plane 2 horizontally upwards, cut the chip body of the free-space optical isolator along the same first cutting direction with a thin blade, and cu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com