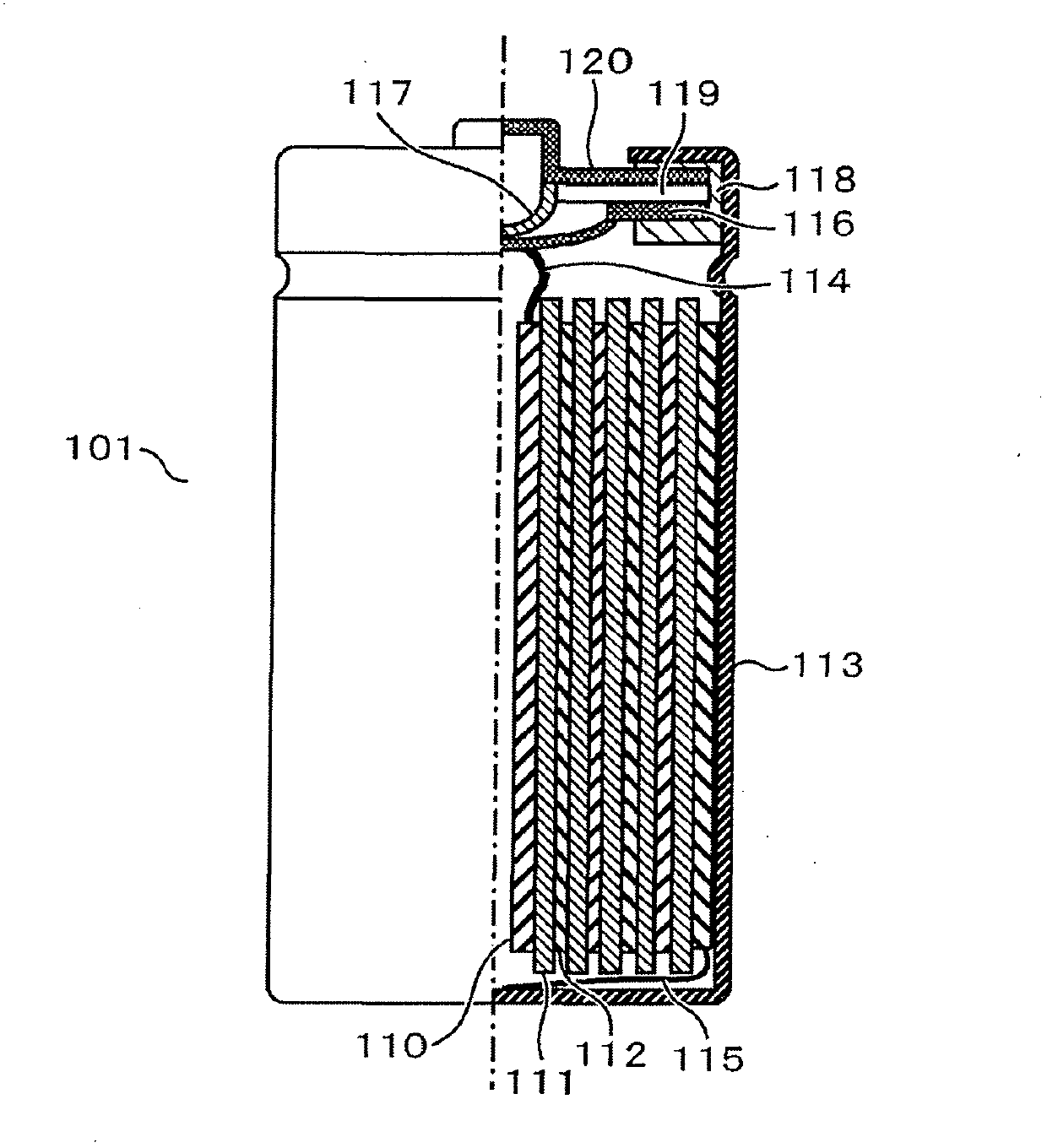
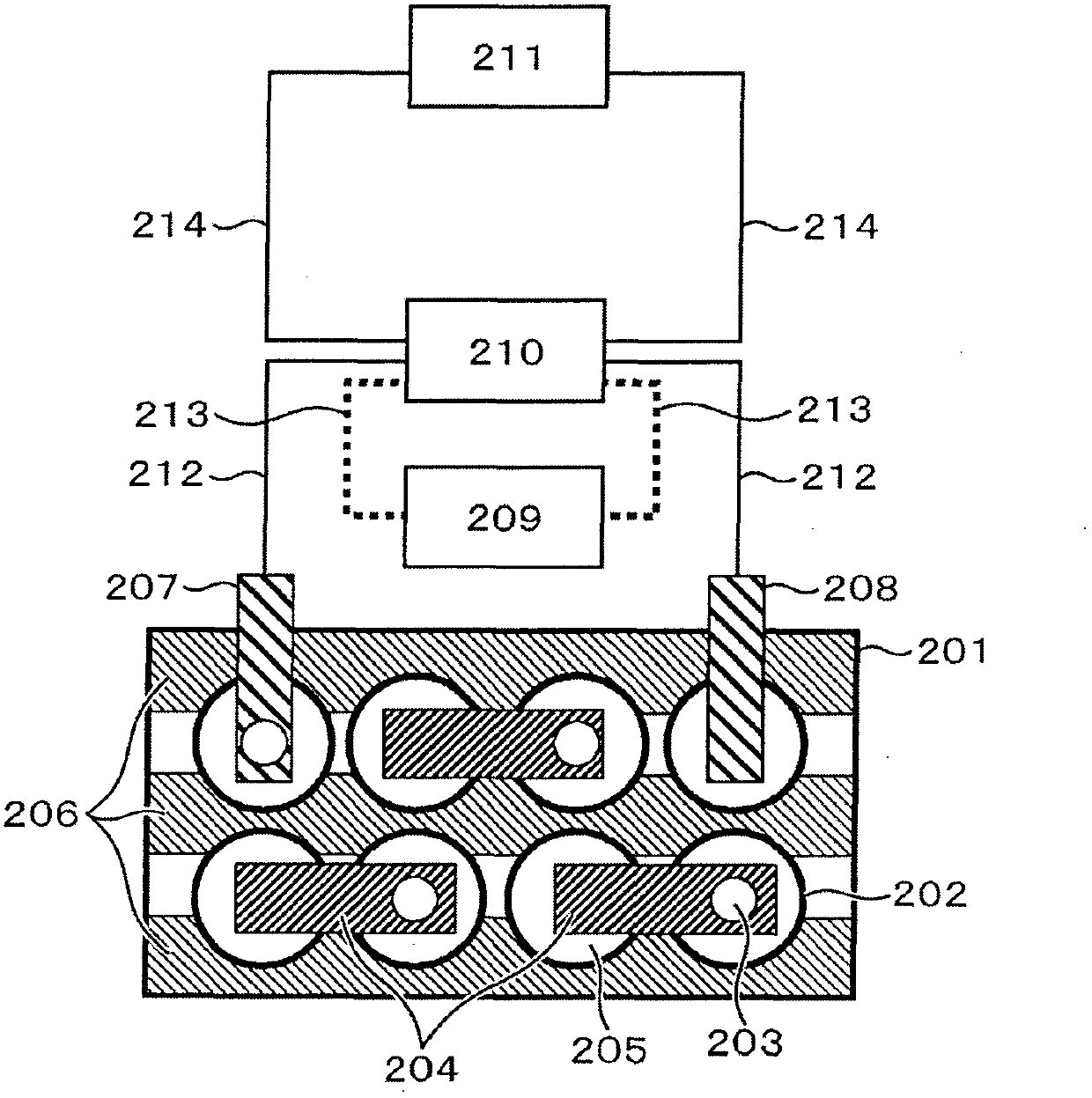
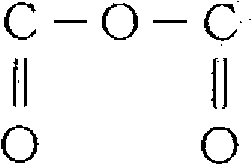Polymer-coated active material and lithium secondary battery using the same
An active material and secondary battery technology, applied in secondary batteries, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as battery life degradation, uneven heating of batteries, and deviation of lithium ion storage and release, so as to improve load characteristics, long life effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0157] 〈Making of positive electrode〉
[0158] Utilize the positive electrode active material LiNi with an average particle size of 10 μm 1 / 3 mn 1 / 3 co 1 / 3 o 2, The following test was carried out on a positive electrode made of carbon black as a conductive agent and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) as a binder. The weight composition of the positive electrode active material, the conductive agent, and the binder is set to 88:7:5. The area of the electrode coated with the positive electrode slurry was set at 400 cm×5 cm, and the thickness of the mixture was set at 50 μm. In addition, the polymer compound of the present invention was not used for the positive electrode.
[0159] 〈Making of Negative Electrode〉
[0160] As the negative electrode active material, natural graphite with an average particle size of 15 μm is used, and as the polymer compound, [CH 3 -(OCH 2 CH 2 )nCO] 2 O (in structure I, X is CH 3 -, Y is a single bond, R is H, and n is 200 to 300) of carbox...
Embodiment 2
[0169] 〈Making of Negative Electrode〉
[0170] In Example 1, the n of the polymer compound was increased to 600 to 700, and the negative electrode was manufactured with the other conditions being the same as in Example 1.
[0171]
[0172] The initial capacity after initial aging was 1.8±0.1 Ah. The reason why the initial capacity is lower than in Example 1 is that the initial DC resistance is also increased by 20 to 30%. The capacity retention after 500 cycles at 50°C was 93±2%. The capacity retention rate was almost the same as the result of Example 1, but the initial capacity was low, so the capacity after 500 cycles also decreased.
Embodiment 3
[0174] 〈Making of Negative Electrode〉
[0175] In Example 1, the binder (styrene-butadiene rubber) used in the negative electrode was omitted, and a negative electrode with an increased amount of negative active material was produced instead. That is, the weight composition of natural graphite, polymer compound, binder, and tackifier was set to 96.5:2:0:1.5.
[0176] Other conditions were the same as in Example 1, and were produced and evaluated.
[0177]
[0178] The capacity retention rate (the ratio of the discharge capacity to the initial capacity of 2 ± 0.1 Ah) after 500 cycles was 91 ± 2%. The DC resistance increased by 160±10% from the initial value.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com