Method for detecting brain function communicated area based on signal sparse approximation
A technology of connected areas and detection methods, applied in the directions of diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, sensors, etc., can solve problems such as limited functional connected area detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
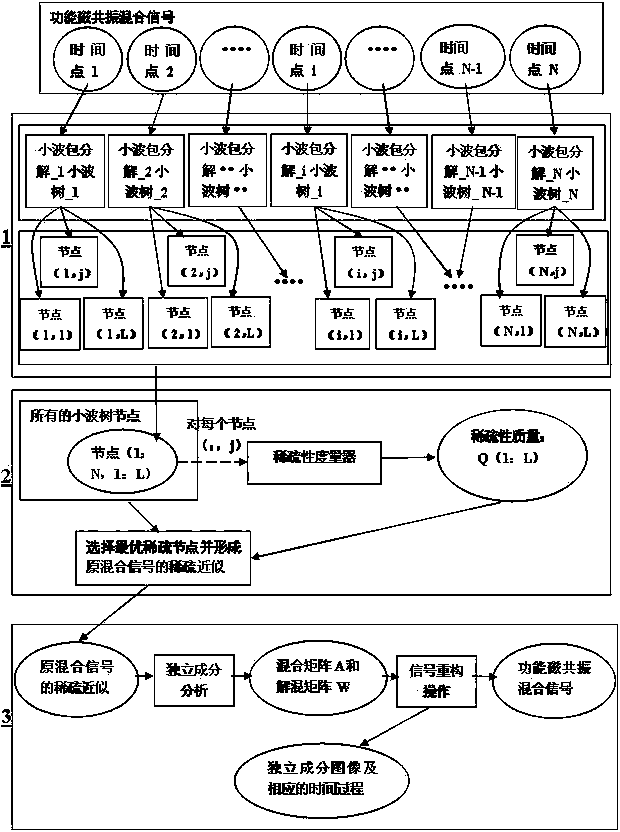
[0014] Such as figure 1 and combine figure 2 As shown, the present invention discloses a method for detecting brain functional connected regions based on signal sparse approximation, the method comprising the following steps:
[0015] Step 1, wavelet packet decomposition: for each time point data of the functional magnetic resonance data, respectively carry out 3 layers of one-dimensional wavelet packet decomposition, wherein the selection of the wavelet base, in the present invention, the wavelet system has anti-symmetry and positive The db2 wavelet base in the Daubechies (abbreviated as: db) family with intersecting and biorthogonal properties; after decomposing the wavelet packet, the corresponding wavelet tree (such as figure 2 shown), each node in the wavelet tree has different sparse attributes. , and an efficient sparse approximation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com