Tunable stiffness actuator
An actuator, adjustable technology, applied in the direction of machines/engines, mechanisms that generate mechanical power, electromagnets with armatures, etc., can solve problems such as poor performance and effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] Referring to the drawings, wherein like reference numerals represent like components throughout the several views, Figure 1-7 Components shown in are not drawn to scale. Accordingly, the specific illustrations, dimensions and applications provided in the drawings shown here are not to be considered limiting.
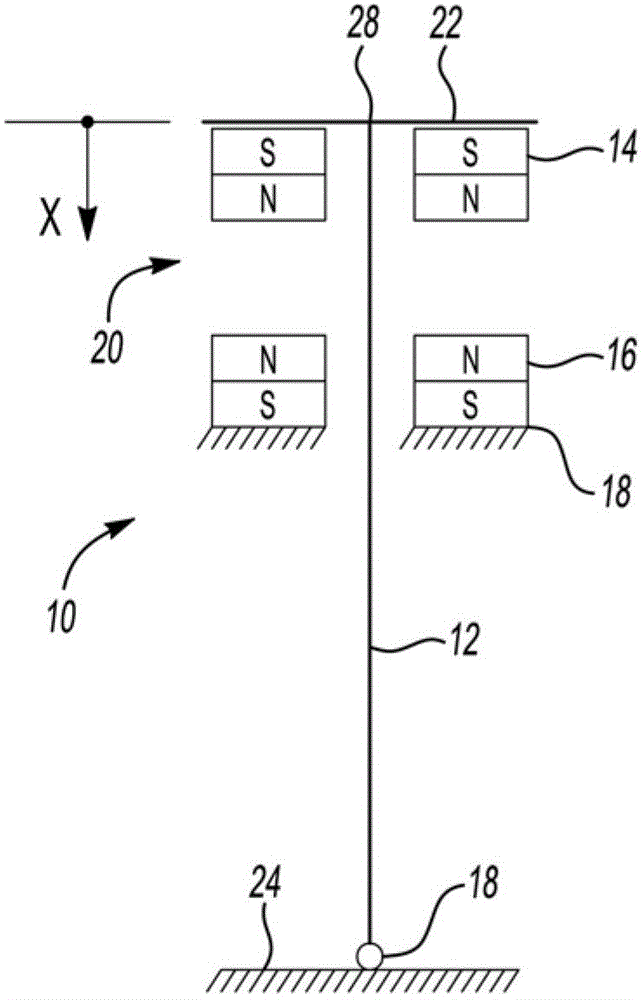
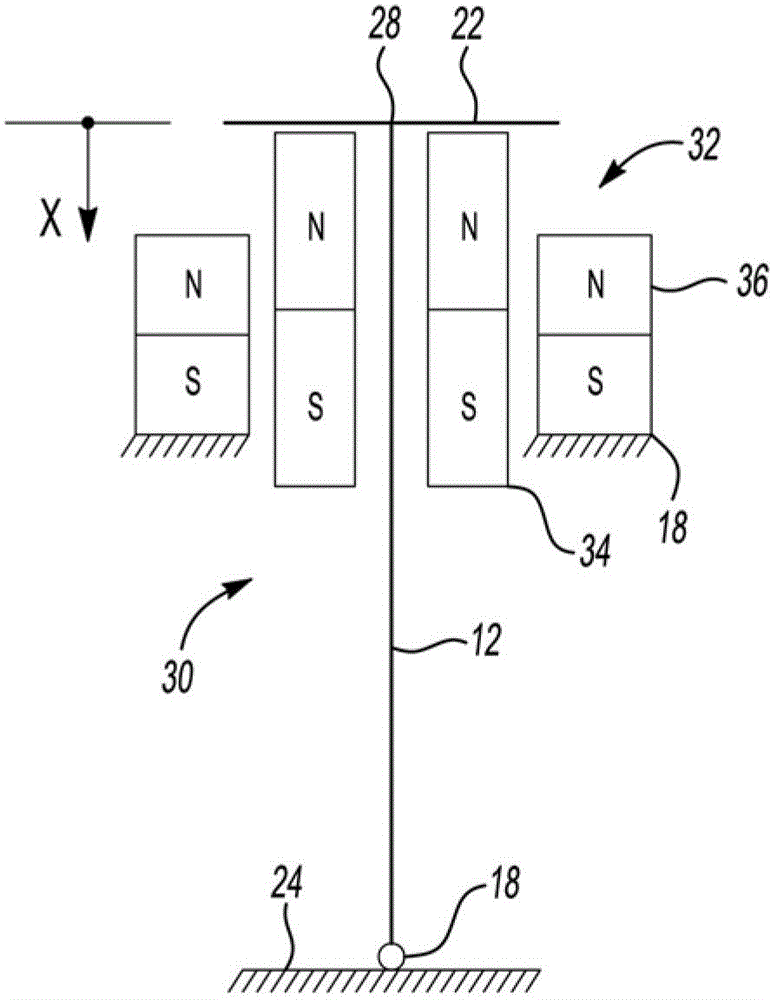
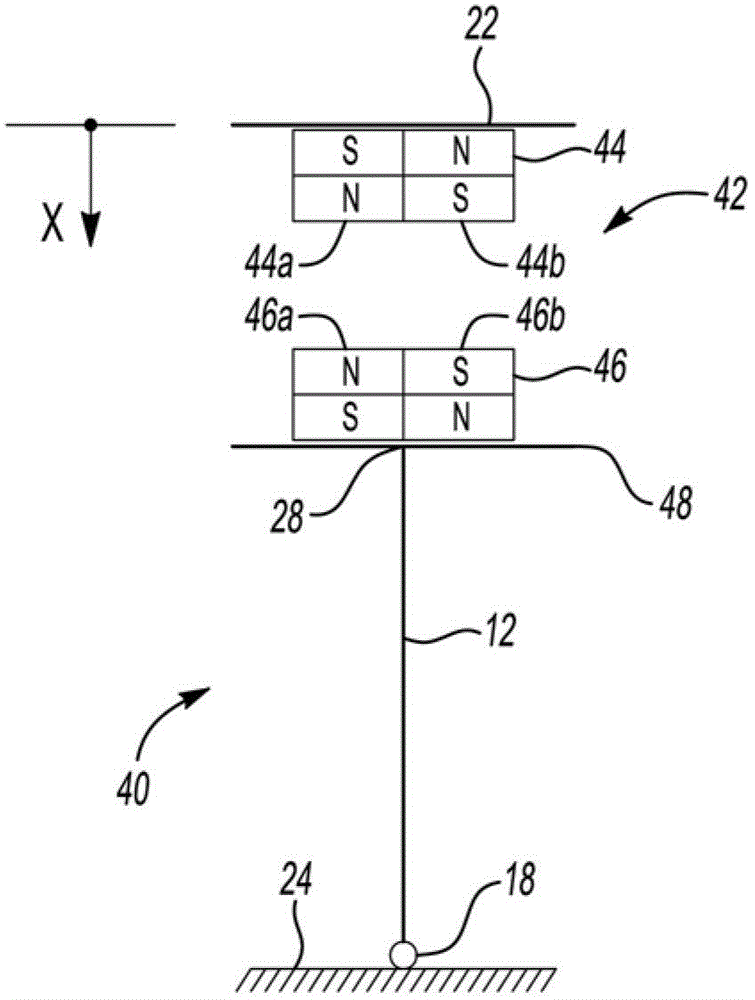
[0018] figure 1 is a schematic diagram of an actuator shown generally at 10 and adapted for adjustable stiffness control. Actuator 10 includes a rigid element 12 and a magnetic bias element shown generally at 20 . Rigid element 12 may comprise a smart material. The biasing element 20 may be configured to be magnetically actuated to provide a biasing force on the rigid element 12 . By way of non-limiting example, biasing elements and rigid elements may be arranged in parallel with each other, as figure 1 with 2 shown. exist figure 1 In , a rigid element 12 is shown in parallel with a biasing element 20 comprising an actuator 10 . exist figure 2 In , a r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com