Trust-based on-demand multipath vector routing algorithm of Ad Hoc network
A multi-path and routing technology, applied in the direction of wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems such as the stability of the transfer rate and the quality of service that have not been significantly improved, the balance of the transfer rate and overhead, and the fixed network environment. Achieve the effect of realizing the credibility of the monitoring path, the evaluation process is simple and efficient, and the scalability is strong
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
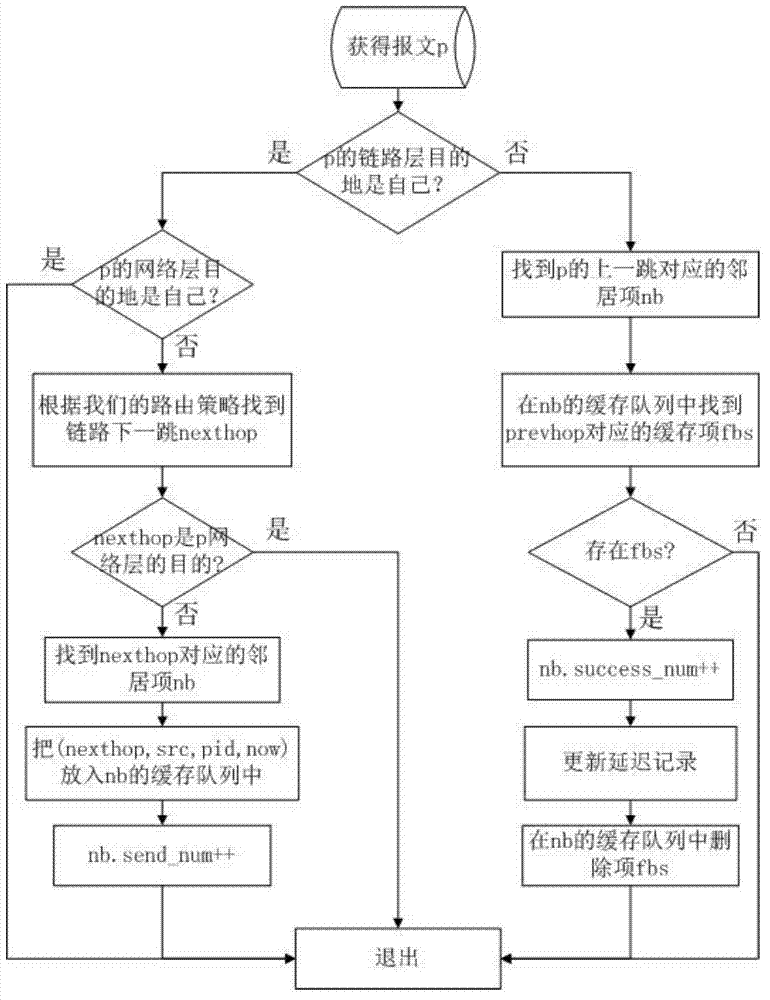
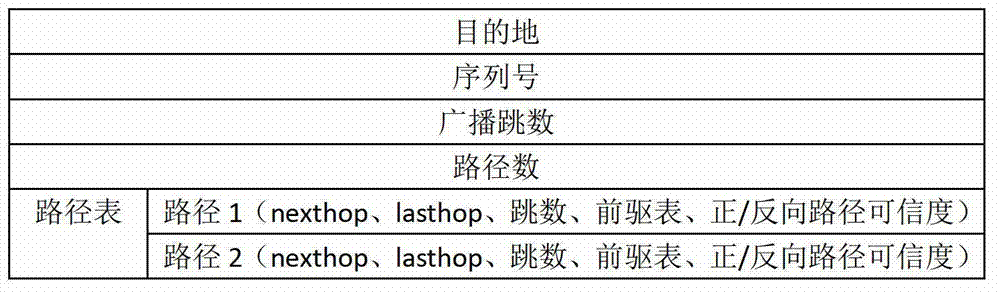
[0072] Example 1 explains the routing maintenance mechanism, such as Figure 7 . Assume that source node 0 has established two link-disjoint paths 01235 and 04265 to destination node D. In the initial state, the latter path is more credible, so it is selected as the forwarding path by the source node. At a certain moment, node 6 defected and randomly discarded the packets transmitted from node 2. After a short period of time, node 2's evaluation of 6 has become lower than the threshold value of 0.26. When the next data packet arrives at node 2, node 2 finds that the next hop is 6 according to the previous hop query path precursor table, and node 6 is a malicious node, thus triggering a path error. Node 2 puts the problem path and other path information whose next hop is node 6 into the path error message, and sends the data packet to the upstream node 4 in unicast. After node 4 receives it, it deletes the relevant problem path, and sends a path error message to the path pre...
example 2
[0073] Example 2 describes another common situation, such as Figure 8. The above example is multiple paths of the same source / destination node pair, while the second example is different paths of different node pairs. Nodes 1 and 2 in the figure are source nodes, and node 6 is a common destination node. The routing table in the normal state is as shown in the figure, and the current nodes 1 and 2 both use the path 3456 to transmit data. And when node 5 defected, after a short period of time, neighbor 4 detected that node 5 defected, and after encountering the data packet sent upstream, node 4 started the path error mechanism to unicast and send it to node 3. Node 3 unicasts to source nodes 1 and 2, but these paths have no predecessors at this time, so they are no longer forwarded. If node 1 wants to send data again, it needs to reroute the request, and node 2 automatically switches to the path passing through node 7.
[0074] Therefore, using the route maintenance mechani...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com