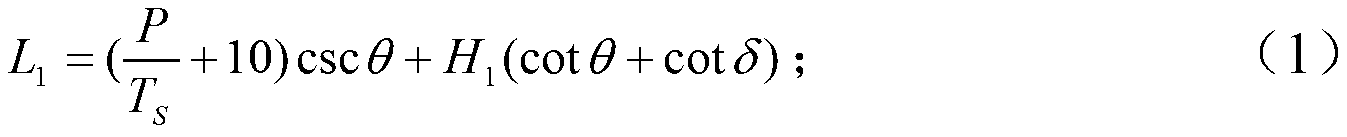Coal pillar setting and extracting method for protecting important water body
A mining method and water body technology, applied in ground mining, earth square drilling, underground mining, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the seepage characteristics of the aquifer, only considering the compressive strength of coal and rock mass, and the existence of water inrush and sand erosion, etc. , to achieve the effect of safe recovery of coal resources, reduction of mine water inflow, and protection of water resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
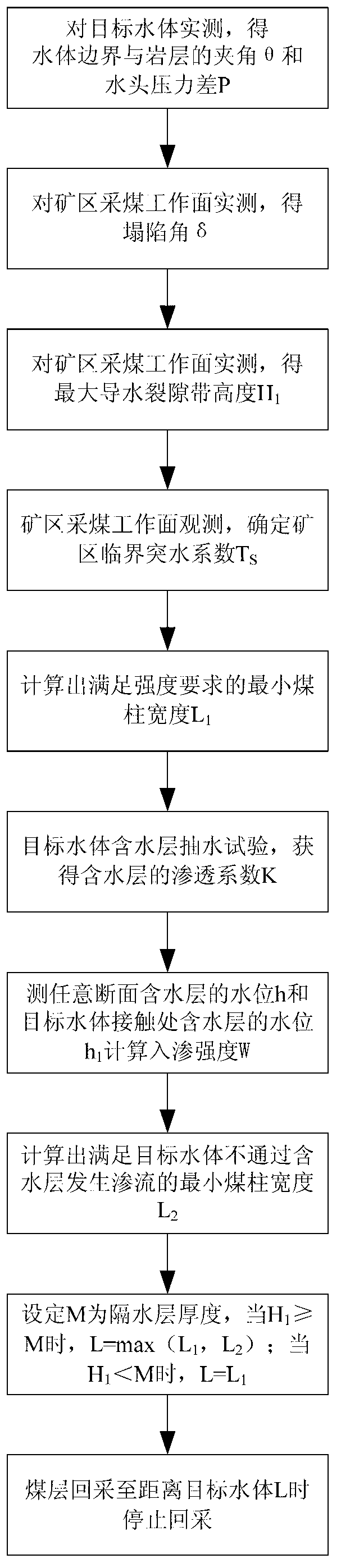
[0026] The step flow chart of a method for mining coal pillars to protect important water bodies according to the present invention is shown in figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
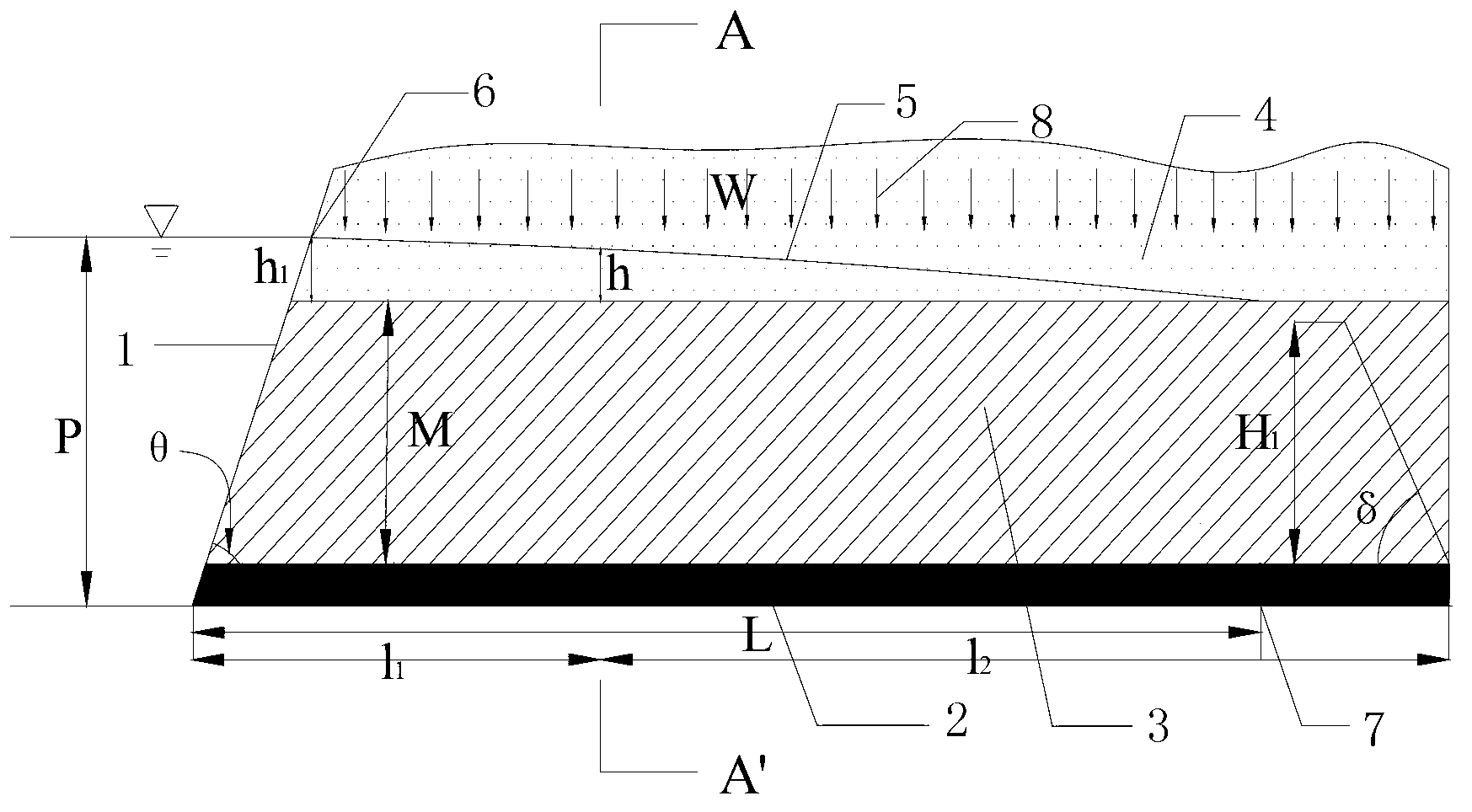
[0027] Step 1: Carry out actual measurement of the target water body protected in the mining area, and obtain the angle θ between the boundary of the water body and the rock formation and the head pressure difference P between the target water body and the coal seam floor;
[0028] Step 2: Measure the collapse angle of the coal mining face in the mining area to obtain the collapse angle δ;
[0029] Step 3: Measure the development height of the maximum water-conducting fracture zone produced by full mining of the coal mining face in the mining area, and obtain the maximum water-conducting fracture zone height H 1 ;
[0030] Step 4: Determi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com