Logical channel grouping method in LTE system
A technology of logical channel groups and logical channels, applied in transmission systems, digital transmission systems, wireless communications, etc., can solve the problems of waste of resources, waste of system air interface resources, and large differences in bit rate requirements, and achieves reduction of resource allocation errors and savings. Air interface resources, the effect of reducing the frequency of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The following three uplink logical channels are defined in the LTE system:
[0033] Common Control Channel (CCCH): Used to transmit control information. When the UE does not establish an RRC connection with the network, this channel is used. Since the CCCH channel is used before the RRC connection is established, there is no need for BSR reporting or logical channels. group;
[0034] Dedicated Control Channel (DCCH): A point-to-point bidirectional channel used to transmit dedicated control information. This channel is used when the UE has an RRC connection;
[0035] Dedicated Traffic Channel (DTCH): DTCH is a point-to-point channel, dedicated to one UE, used to transmit user information, and can be bidirectional. The data service used for DTCH transmission has 9 levels according to different QoS class identifier (QCI) characteristics, as shown in Table 2:
[0036]
[0037] Table 2
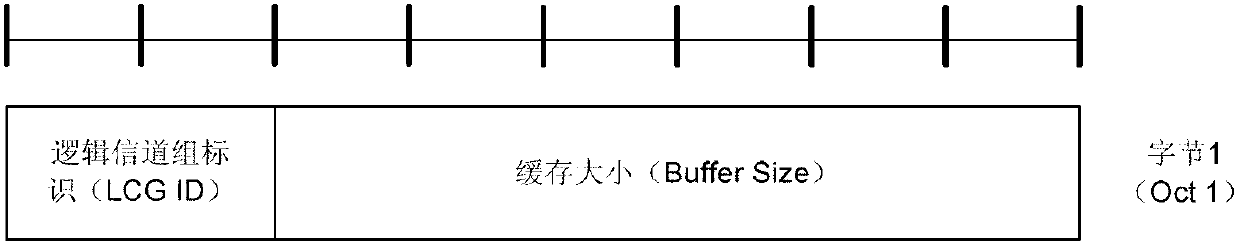
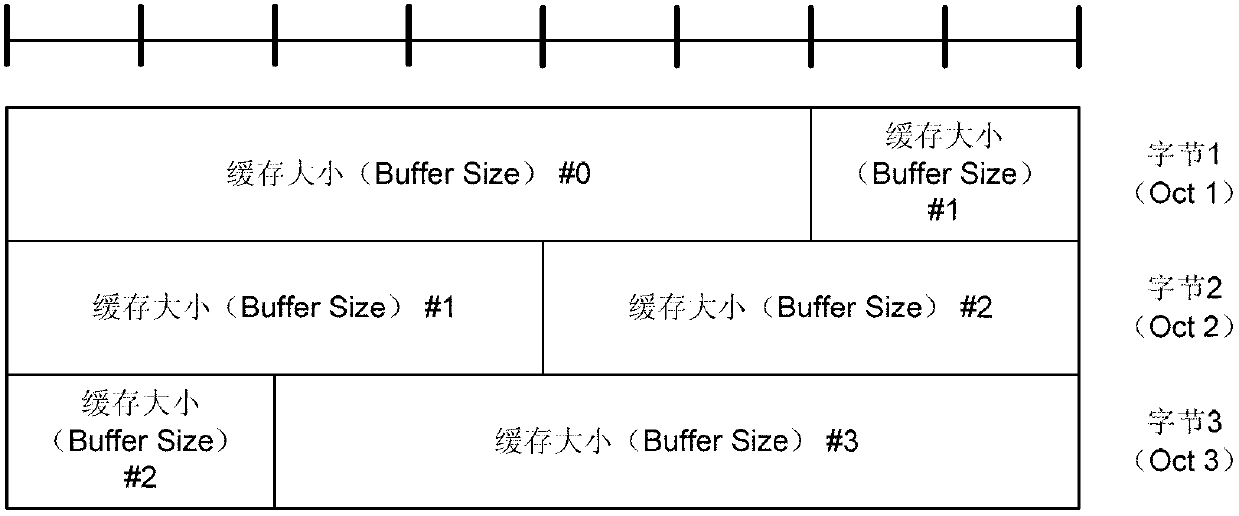
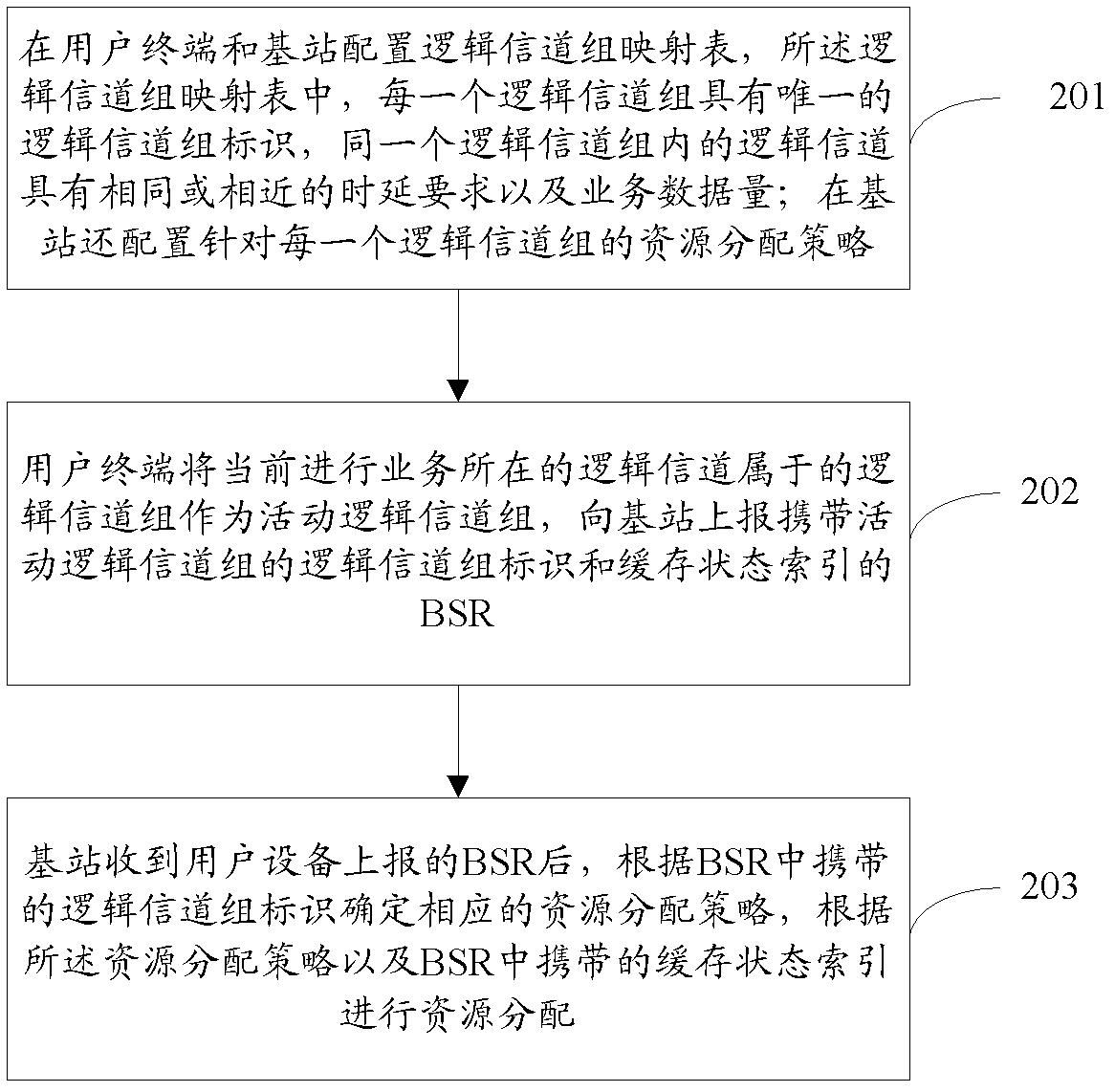
[0038] The logical channel grouping method in the LTE system proposed by the prese...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com