Path selecting method and device
A technology for selecting paths and devices, applied in the communication field, it can solve the problems of high management complexity, inability to communicate with access devices at Layer 2, and hierarchical networking cannot meet the requirements of large Layer 2, so as to achieve the effect of traffic balance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
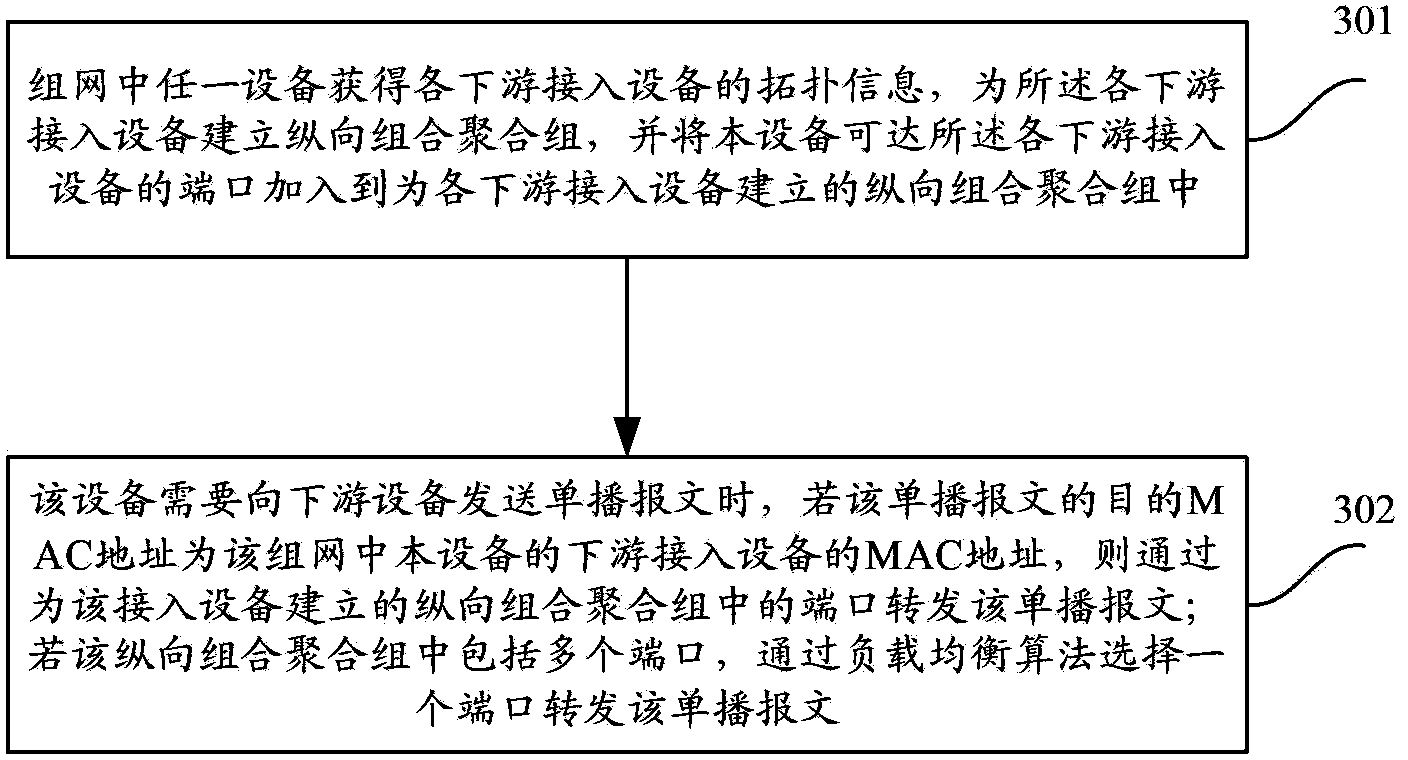
[0048] see image 3 , image 3 It is a schematic flowchart of the path selection method in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The specific steps are:
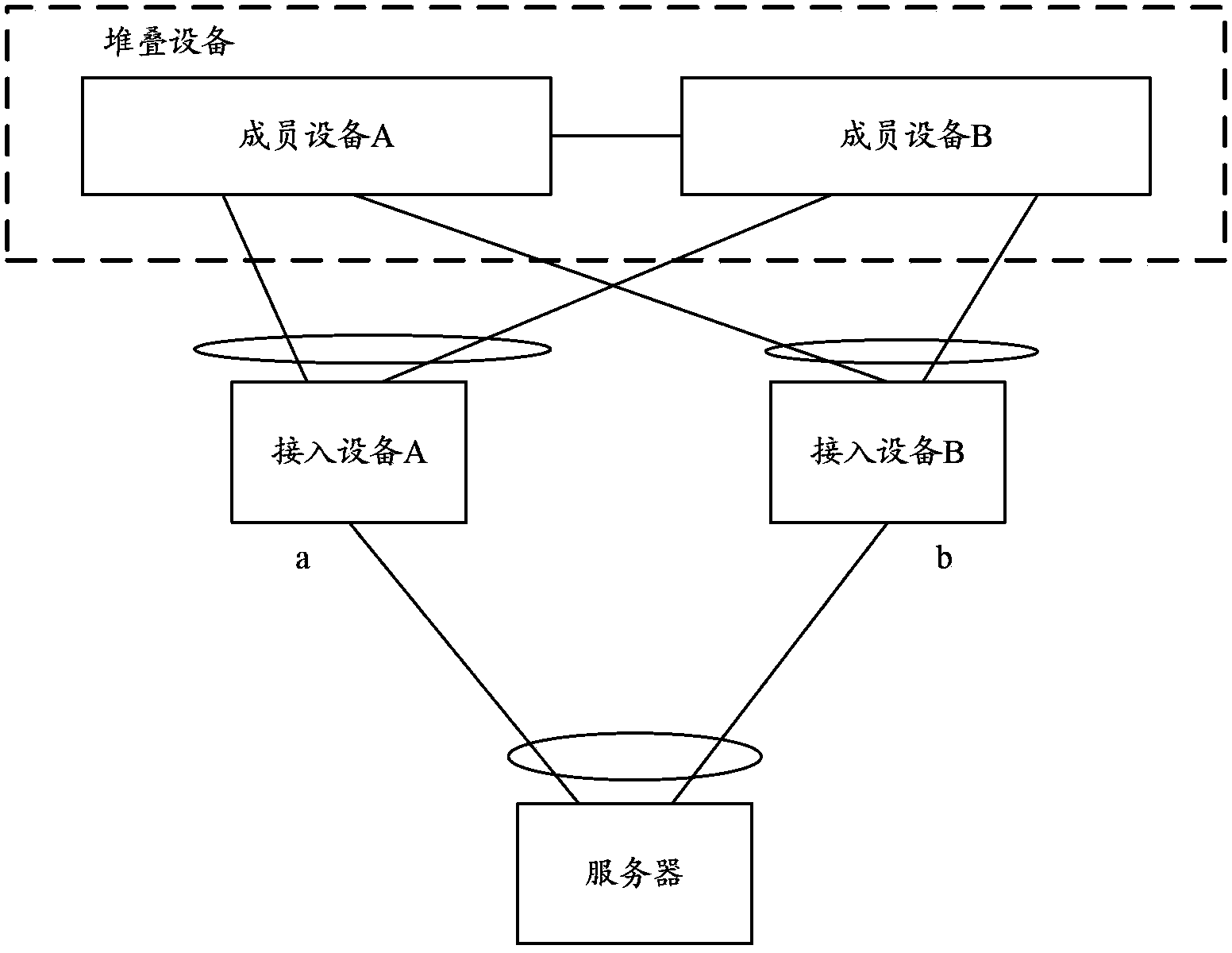
[0049] Step 301, any device in the networking obtains the topology information of each downstream access device, establishes a vertical combination aggregation group for each downstream access device, and adds the ports that the device can reach to each downstream access device to the In the vertical combination aggregation group established for each downstream access device.
[0050] In this step, a vertical combination aggregation group is established for each of the downstream access devices, including a vertical combination physical aggregation group and a vertical combination logical aggregation group. The ports contained in the vertical combination physical aggregation group are connected to the same access device directly connected to the device The ports in the vertical combination logical aggregation group are t...
Embodiment 2
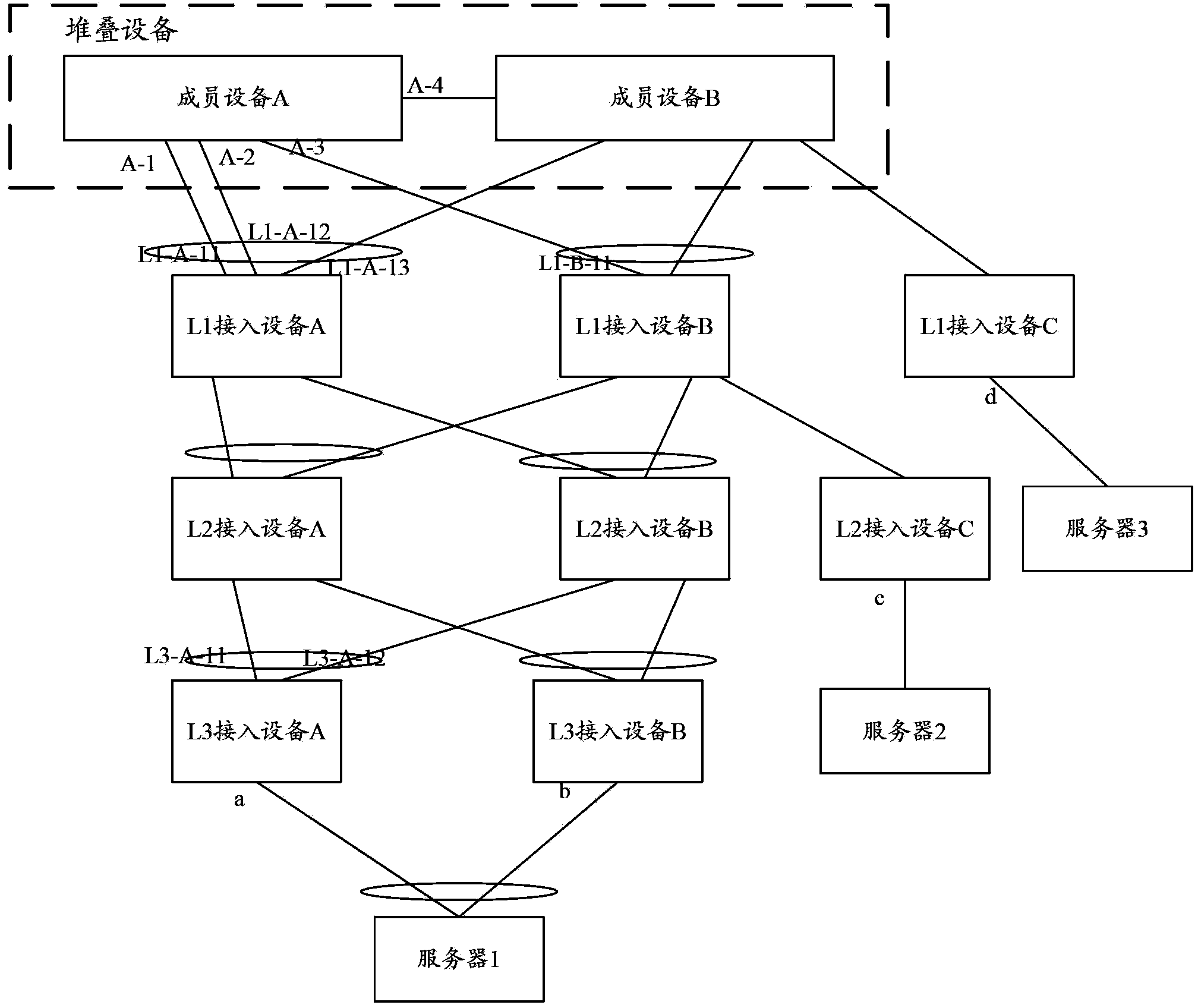
[0062] In the specific embodiment of the present invention, the UNI includes ports other than the port connected between the aggregation device and the access device, and the port connected between the access device and the access device, such as the port connected to the server in the user network , the port connected to the switch or router in the user network, etc., here we collectively call it user equipment. In the specific embodiments of the present invention, for the convenience of description, the data message sent by the server is received through the UNI as an example, that is, the MAC address of the server is learned as an example, and the processing methods for other cases are the same.
[0063] Any device in the networking creates a UNI aggregation group for downstream access devices with aggregated UNIs. Any UNI aggregation group contains UNIs connected to the same server. There are multiple UNIs in the UNI aggregation group that do not belong to the same access ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] During the specific implementation of the present invention, when forwarding a unicast message, according to the forwarding of the destination MAC address of the unicast message, the MAC address may be learned from each port in the vertically combined logical aggregation group, or may be learned into the vertically combined physical aggregation group on each port. However, when forwarding broadcast packets, the locally established longitudinally combined logical aggregation group is not considered, and only the established vertically combined physical aggregation group is used.
[0091] see Image 6, Image 6 It is a schematic diagram of three message forwarding processes in the embodiment of the present invention. The specific steps are:
[0092] Step 601, when any device in the networking needs to send a unicast message to a downstream device, it matches the destination MAC address of the unicast message with the locally learned MAC address, and if it matches, the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com