Reducing intake manifold pressure during cranking
A technology of intake manifold pressure and engine, applied in the direction of brakes, electrical control, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reducing fuel economy emissions, difficult engine cold start, ineffective evaporation, etc., to reduce cold start exhaust emissions, provide fuel economy benefits, and demand-reducing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
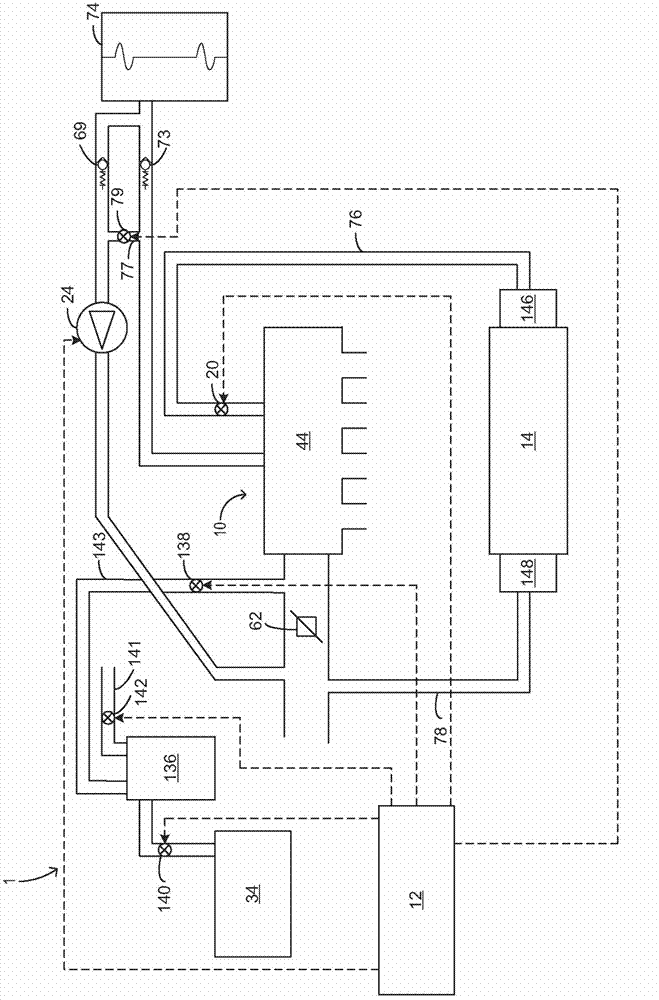
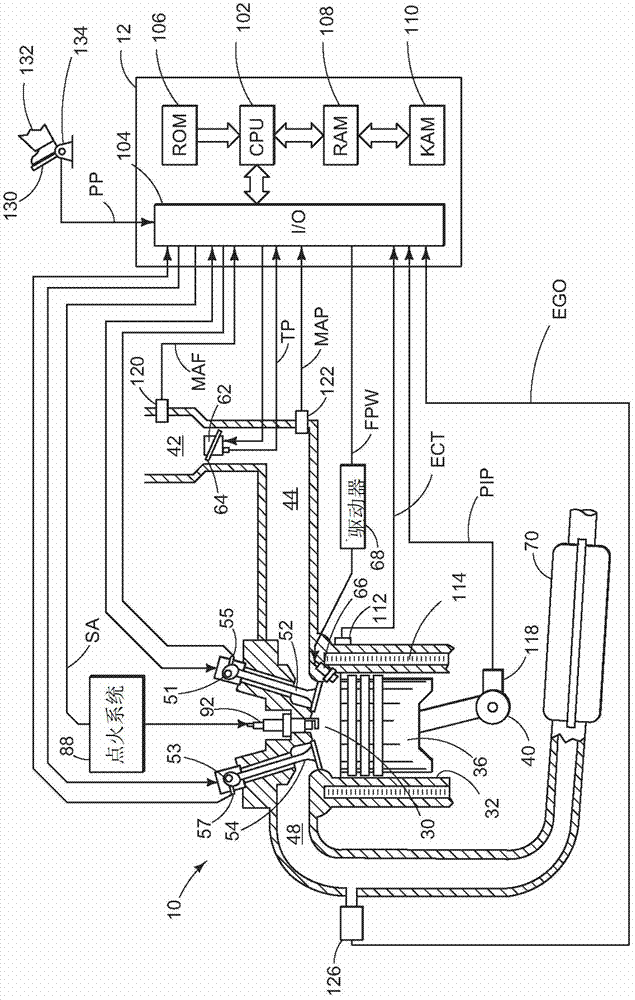
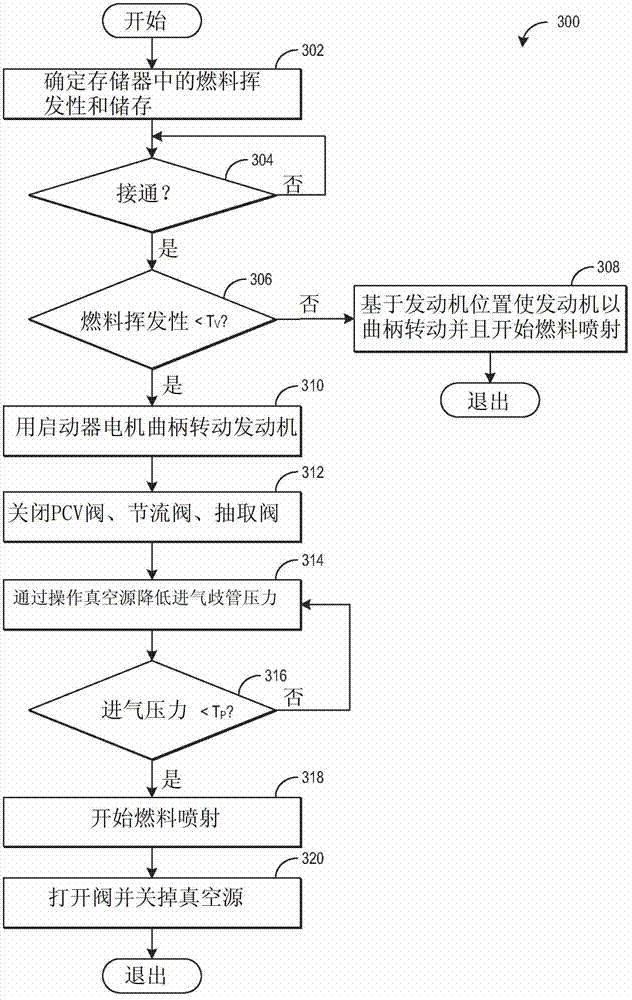
[0027] Low volatility fuels such as ethanol and ethanol-gasoline blends may not evaporate as efficiently as gasoline under typical engine start conditions. As a result, fuel economy and emissions may be reduced, and engine cold starts may be unreliable. To increase evaporation of low volatility fuels, intake manifold vacuum may be increased during cranking via a vacuum source, such as a vacuum pump, connected to the intake manifold. Further, one or more controllable valves connected to the intake manifold, such as a throttle valve and a PCV valve, may be commanded closed to ensure rapid pump down of the intake manifold. Intake manifold vacuum can increase to a critical level, at which point fuel injection can begin. The critical level of vacuum may be proportional to the volatility of the injected fuel. figure 1 and 2 is an example engine diagram that includes the fuel injection system, vacuum pump, electronic PCV valve, and image 3 controller with the method shown in . ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com