Probability-based task scheduling method for minimizing energy consumption in embedded system
An embedded system and task scheduling technology, applied in the embedded field, can solve problems such as inapplicability, and achieve the effects of energy saving, better quality, effective processor and voltage distribution scheme
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawings and examples.
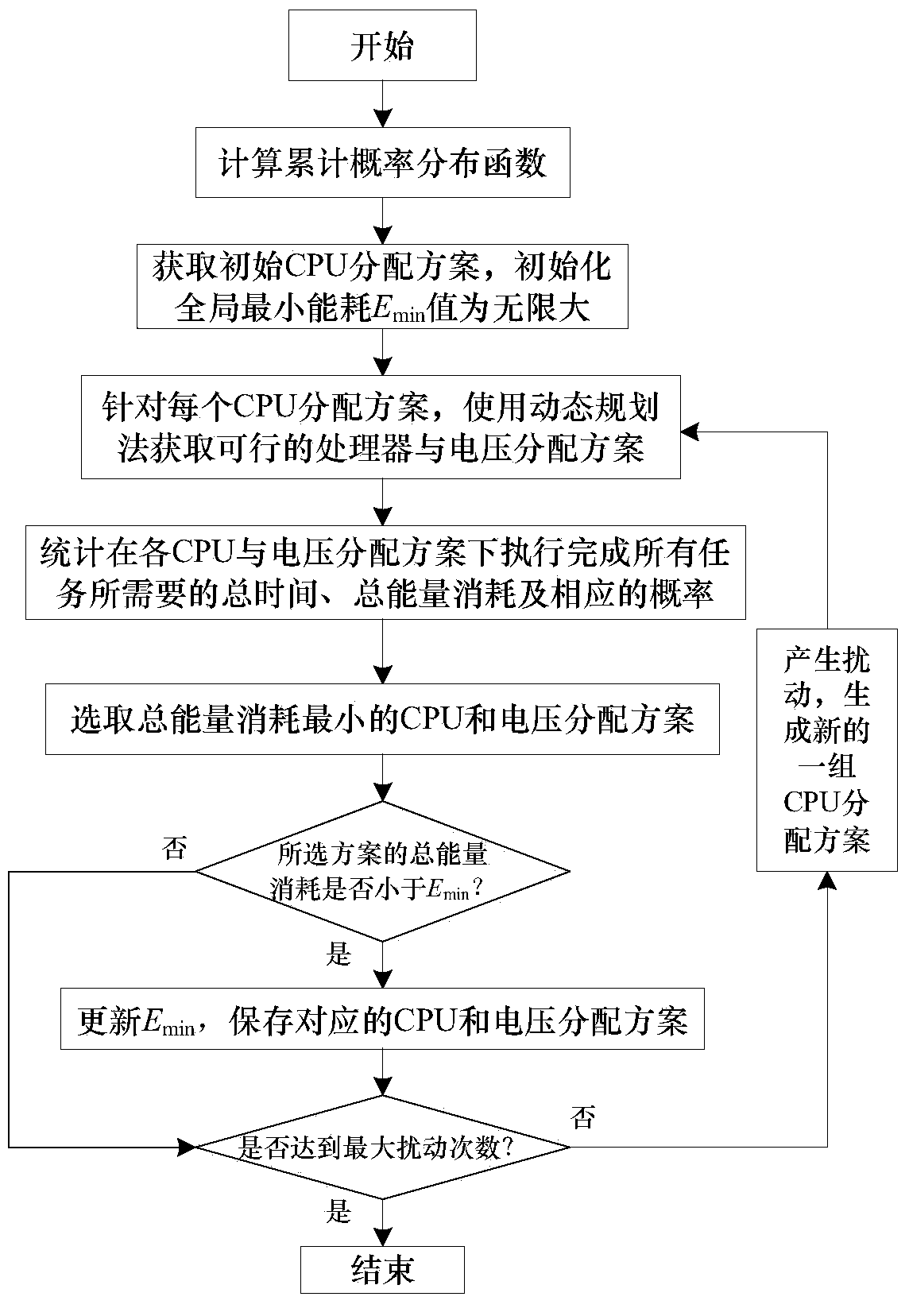
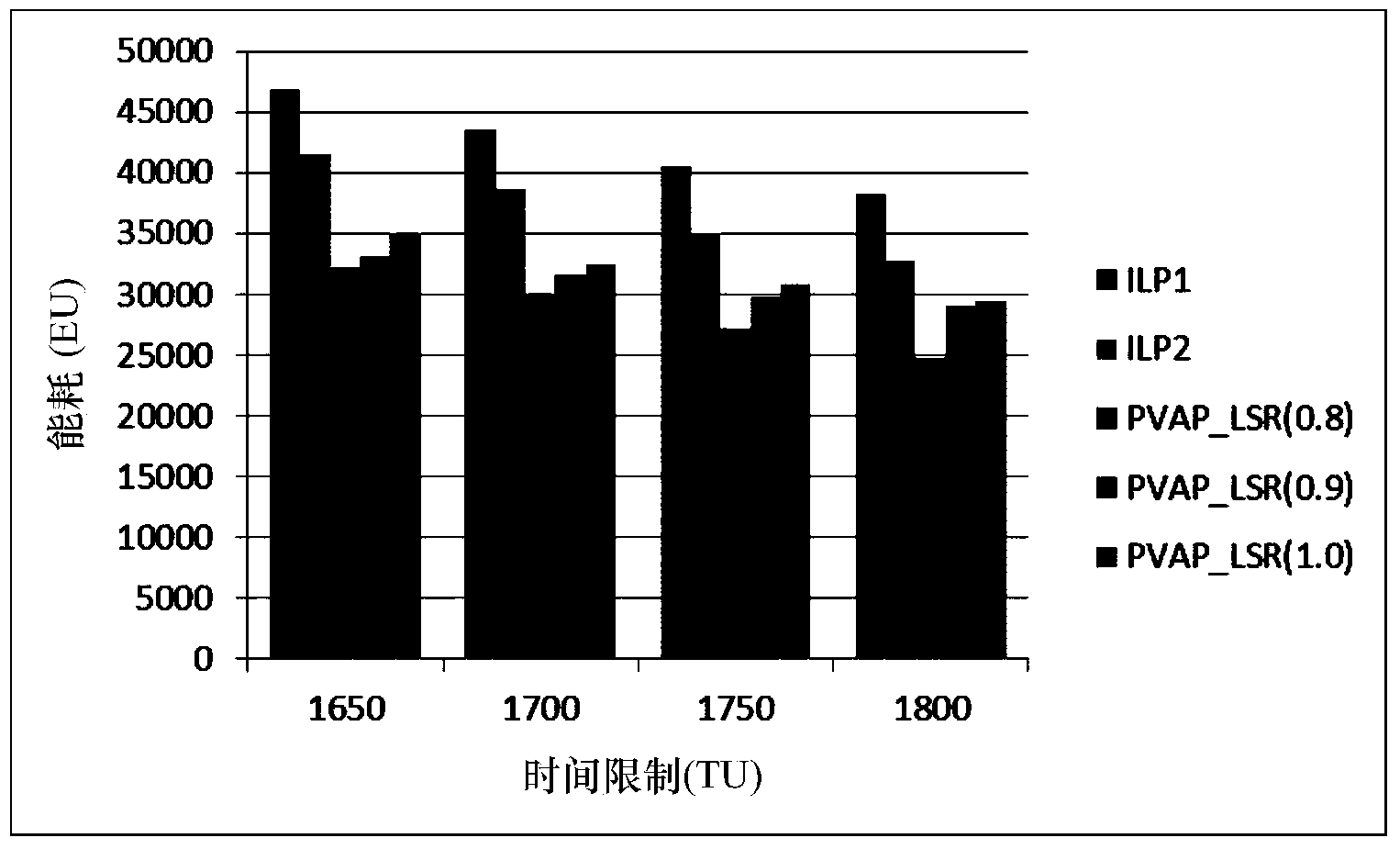
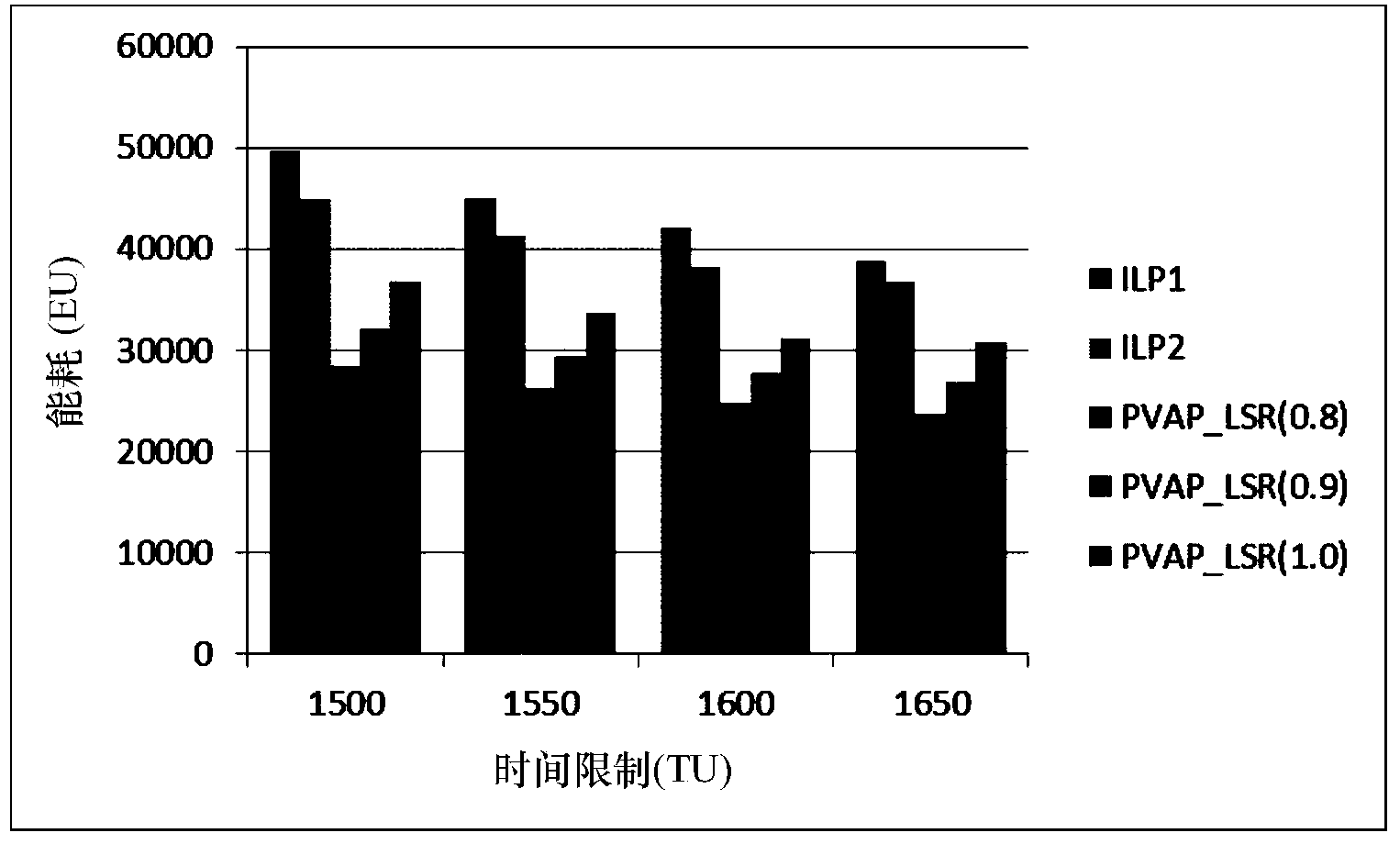
[0036] The task scheduling method based on the probability of minimizing energy consumption in the embedded system proposed by the present invention is mainly suitable for solving the task scheduling problem in the embedded heterogeneous multiprocessor system, and the purpose is to provide a feasible task scheduling scheme, so that the system While all the tasks in the system meet the limit of the total execution time of real-time system tasks with a certain probability, the total energy consumption of the system is as small as possible. The scheduling method of the present invention is not only suitable for soft real-time systems, but also suitable for hard real-time systems.
[0037] The scheduling method proposed by the present invention generally includes the following three steps: (1) use the ASAP algorithm or the ALAP algorithm to initialize an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com