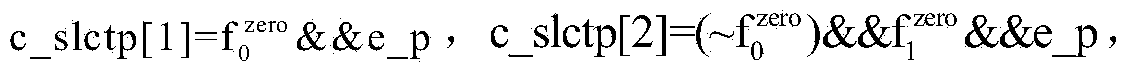Rounding prediction method for floating point adder
A prediction method and adder technology, applied in the direction of instruments, electrical digital data processing, digital data processing components, etc., can solve problems such as power consumption, increased delay, and complicated calculation process, and achieve the effect of reducing time consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0054] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
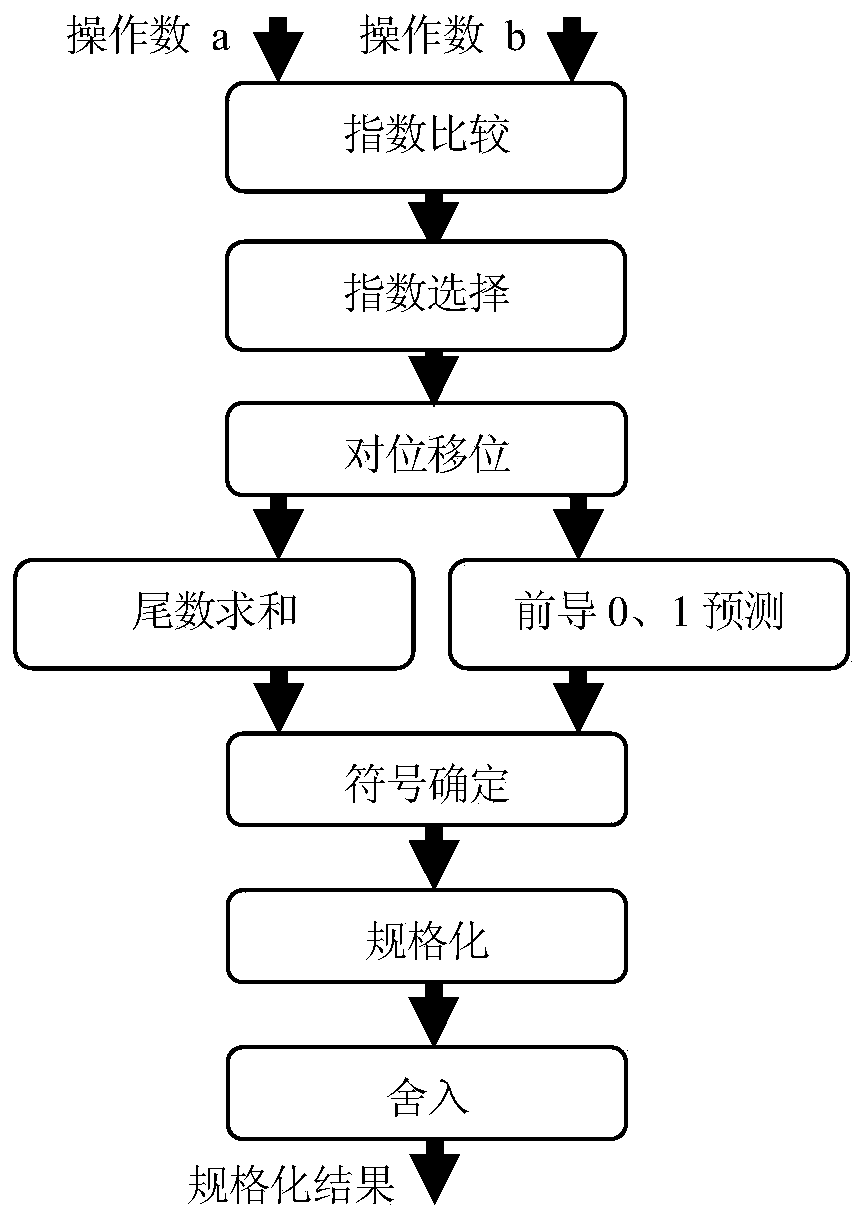
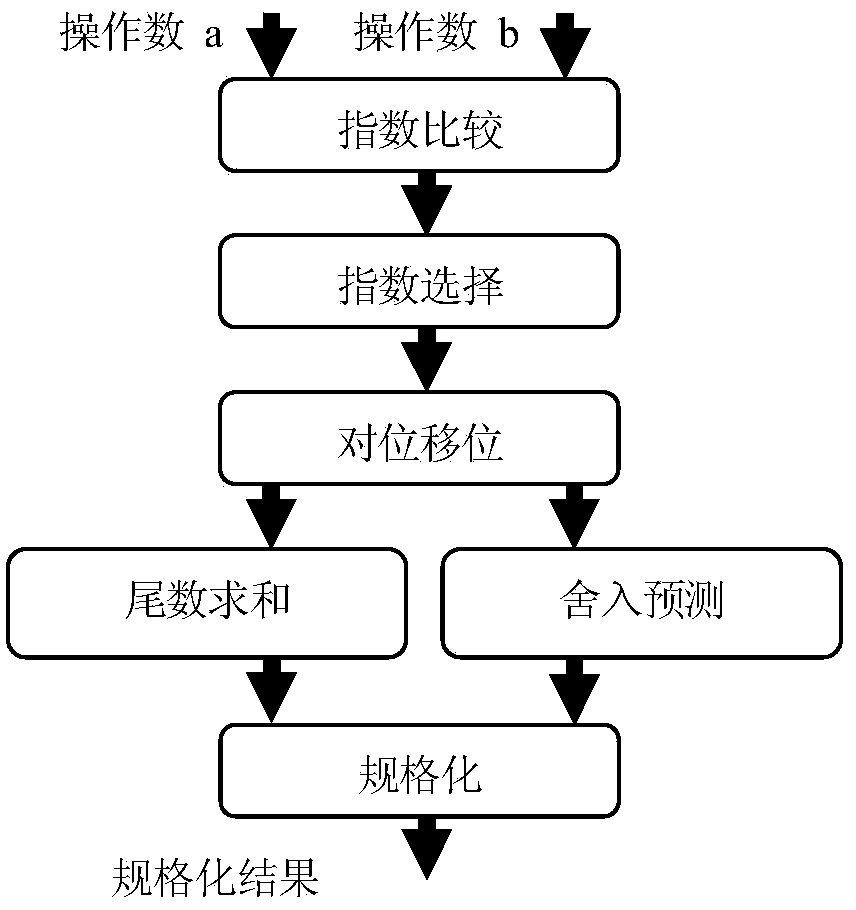
[0055] see Figure 1-2 As shown, it is assumed that two N-bit binary floating-point numbers a and b conforming to the IEEE754 standard are the two input operands of the floating-point adder, which contain an E-bit exponent and an M-bit mantissa. Then the sign bits of a and b are a[N-1] and b[N-1] respectively, and the exponent part is a[N-2:N-1-E] and b[N-2:N-1-E] ], the mantissa part is {1,a[M-1:0]} and {1,b[M-1:0]}. For the addition of two floating-point numbers, the IEEE754 standard specifies four rounding methods. A 2-bit binary array rmc[1:0] is used to represent the rounding method of the floating-point adder specified in the IEEE754 standard, and the floating-point adder The relationship between dynamic rounding bit values, rounding values and rounding methods is shown in Table 1, where "towards -∞", "towards +∞" and "towards 0" are directly rounde...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com