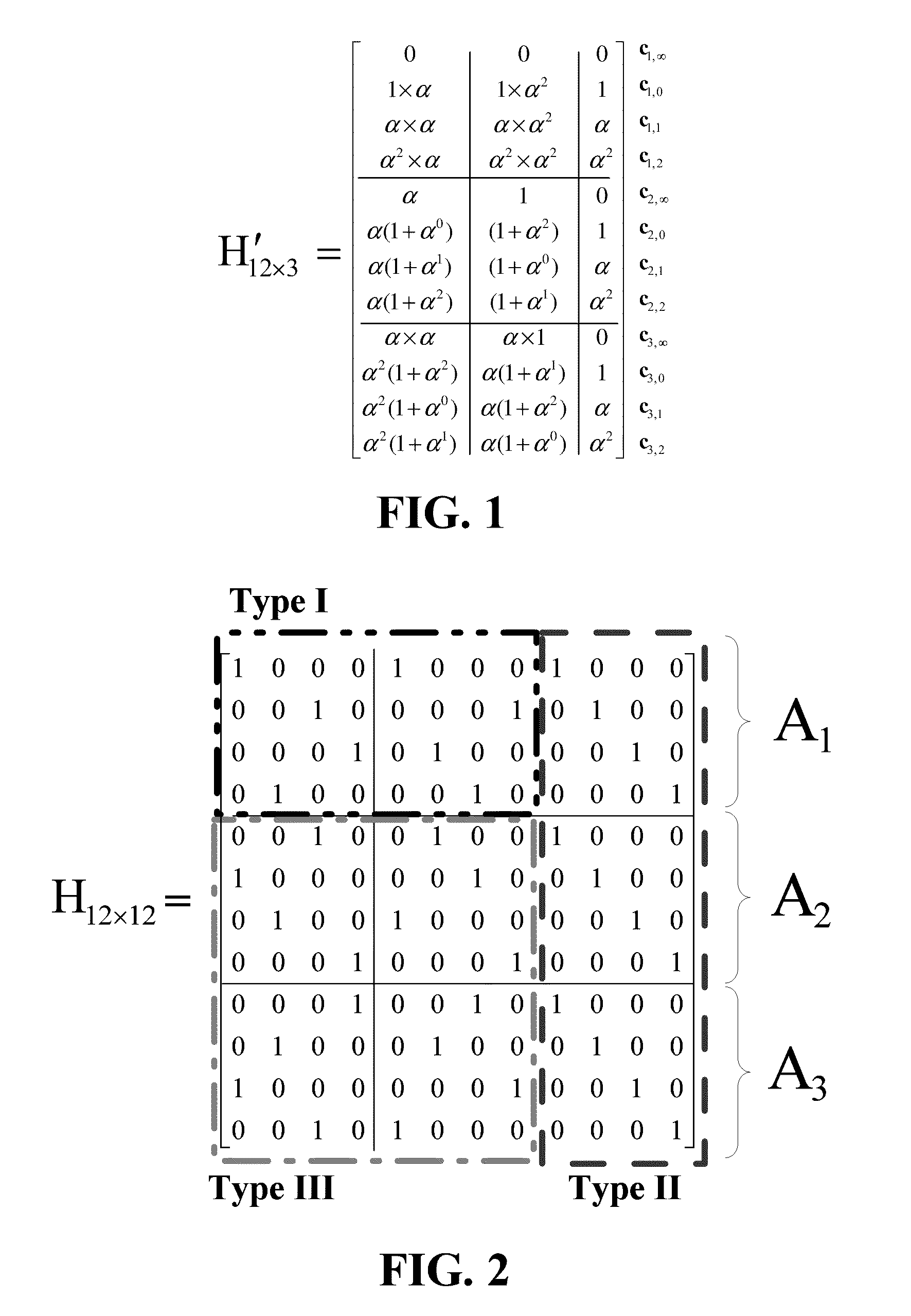
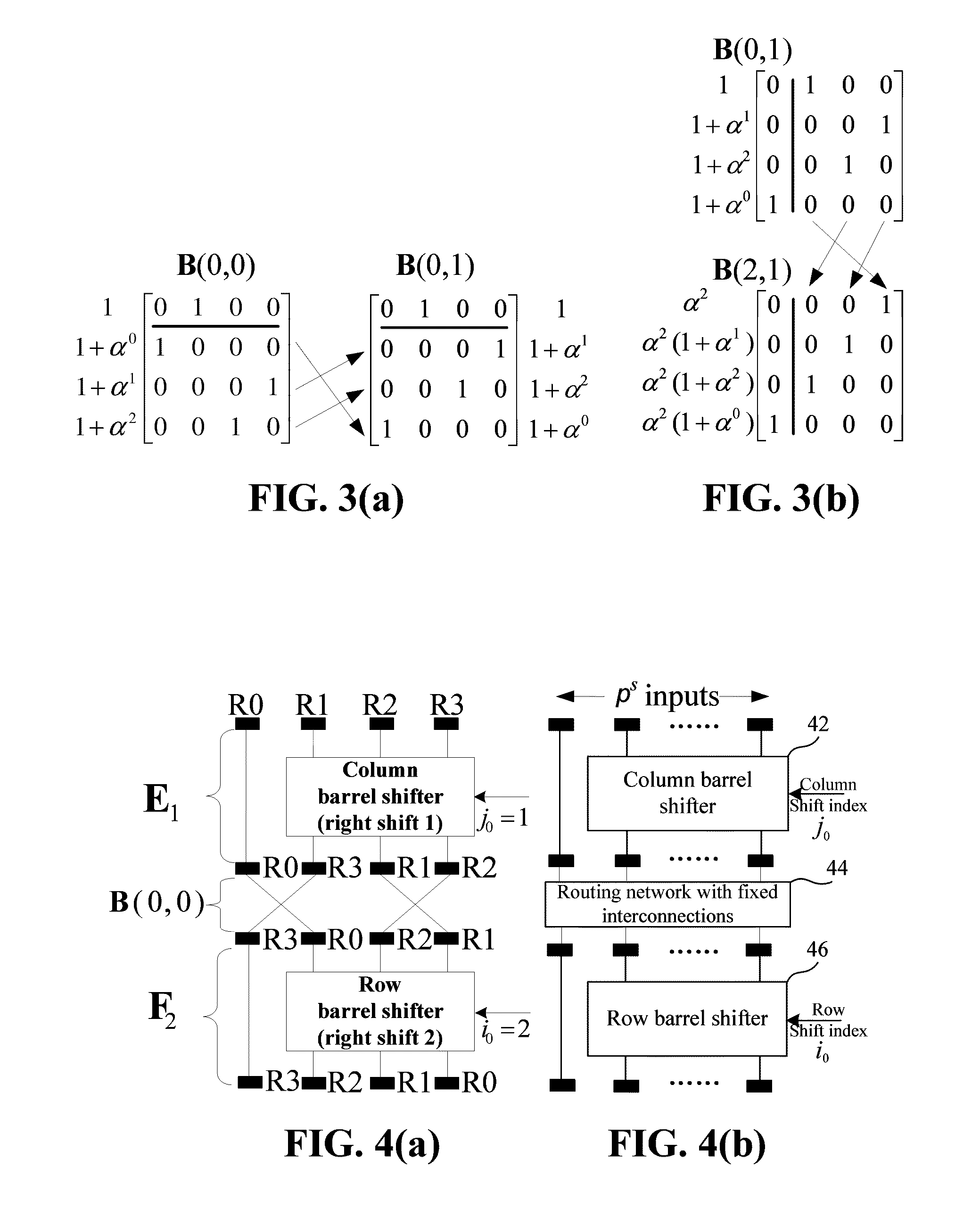
Patents
Literature
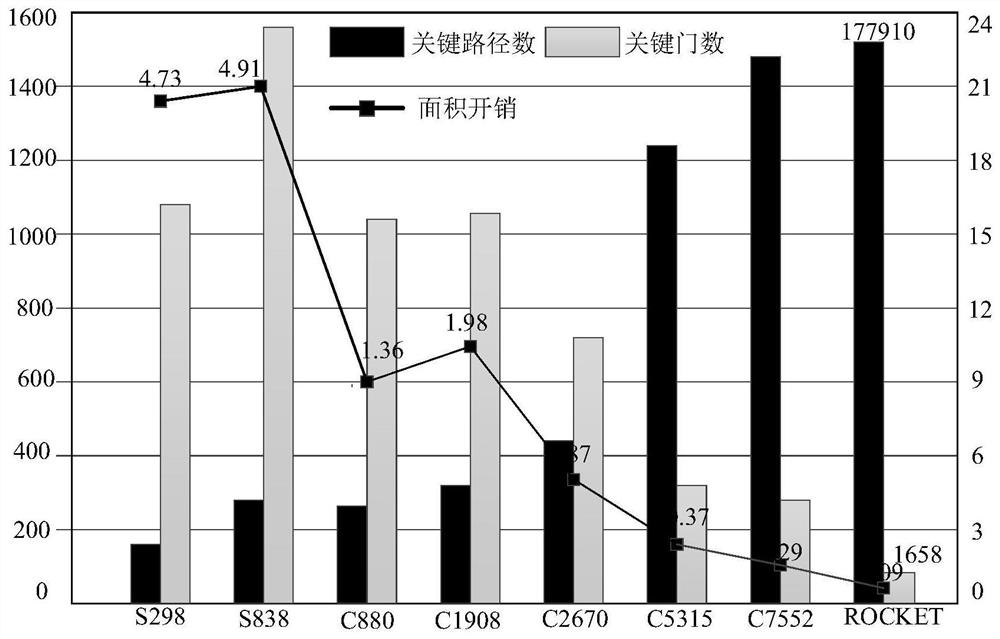
51 results about "Critical path delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
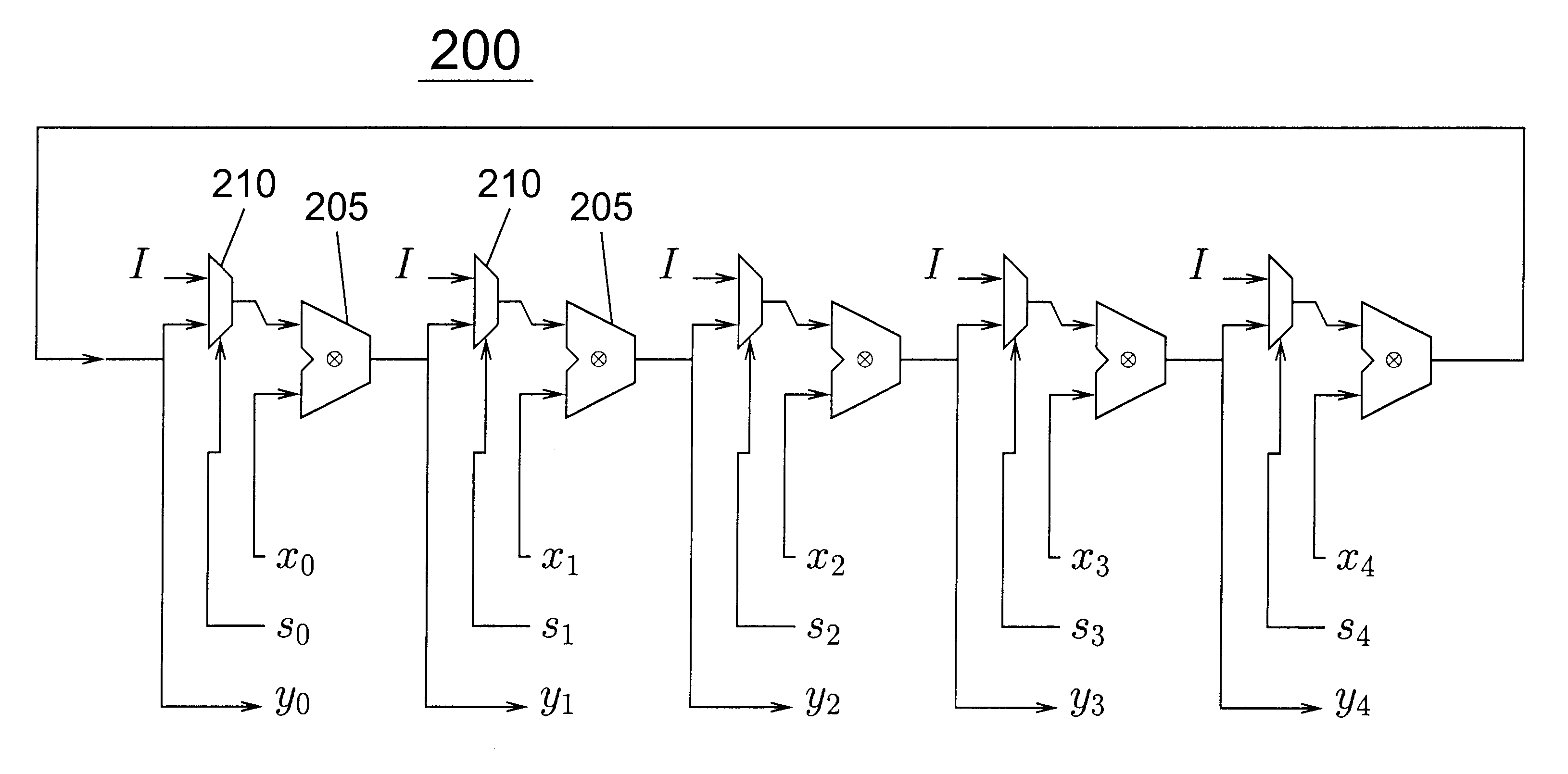
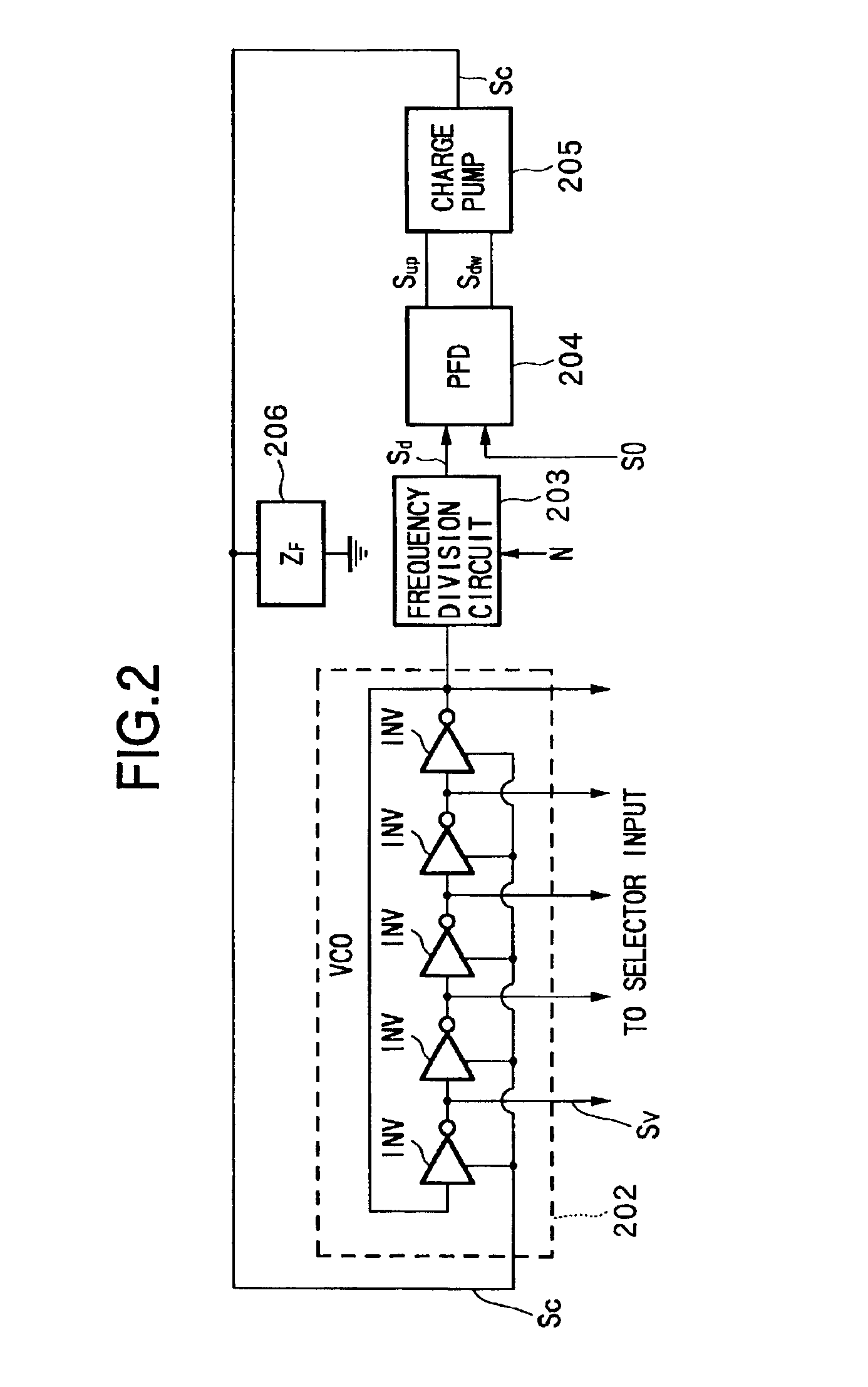
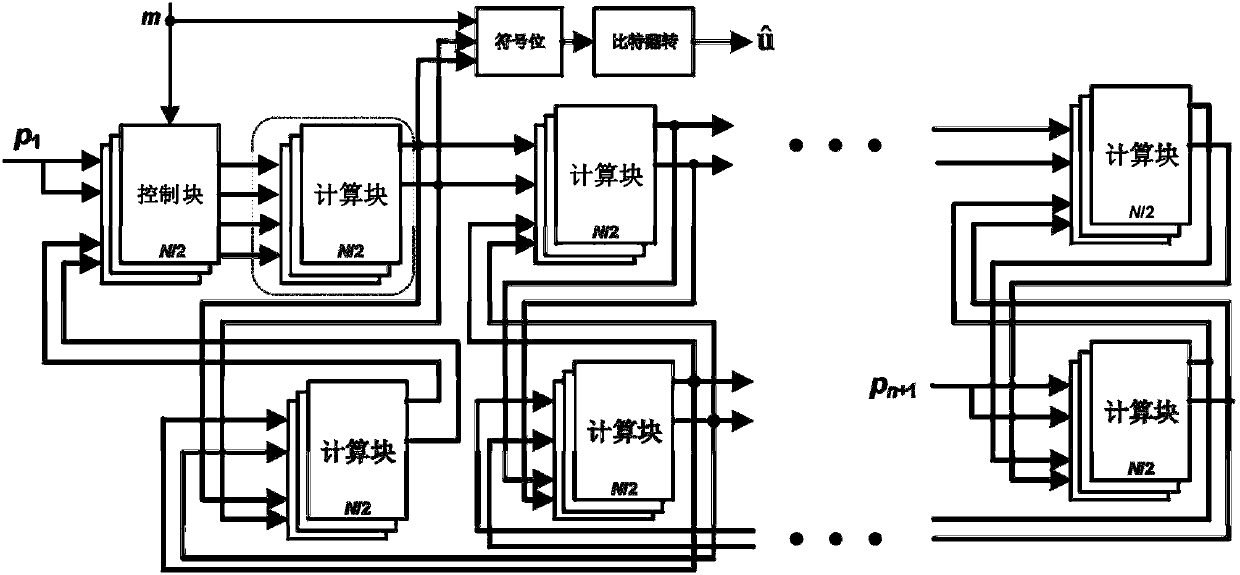
Cycle segmented prefix circuits
InactiveUS6609189B1Improve performanceAvoid performanceComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral purpose stored program computerExtensibilityScalar processor
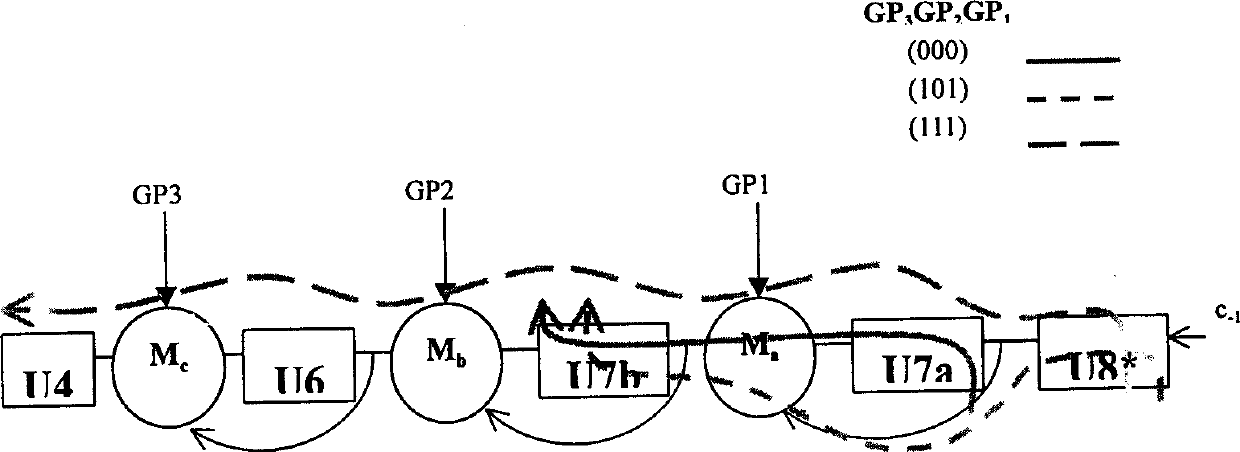
The poor scalability of existing superscalar processors has been of great concern to the computer engineering community. In particular, the critical-path delays of many components in existing implementations grow quadratically with the issue width and the window size. This patent presents a novel way to reimplement these components and reduce their critical-path delay growth. It then describes an entire processor microarchitecture, called the Ultrascalar processor, that has better critical-path delay growth than existing superscalars. Most of our scalable designs are based on a single circuit, a cyclic segmented parallel prefix (cspp). We observe that processor components typically operate on a wrap-around sequence of instructions, computing some associative property of that sequence. For example, to assign an ALU to the oldest requesting instruction, each instruction in the instruction sequence must be told whether any preceding instructions are requesting an ALU. Similarly, to read an argument register, an instruction must somehow communicate with the most recent preceding instruction that wrote that register. A cspp circuit can implement such functions by computing for each instruction within a wrap-around instruction sequence the accumulative result of applying some associative operator to all the preceding instructions. A cspp circuit has a critical path gate delay logarithmic in the length of the instruction sequence. Depending on its associative operation and its layout, a cspp circuit can have a critical path wire delay sublinear in the length of the instruction sequence.
Owner:YALE UNIV
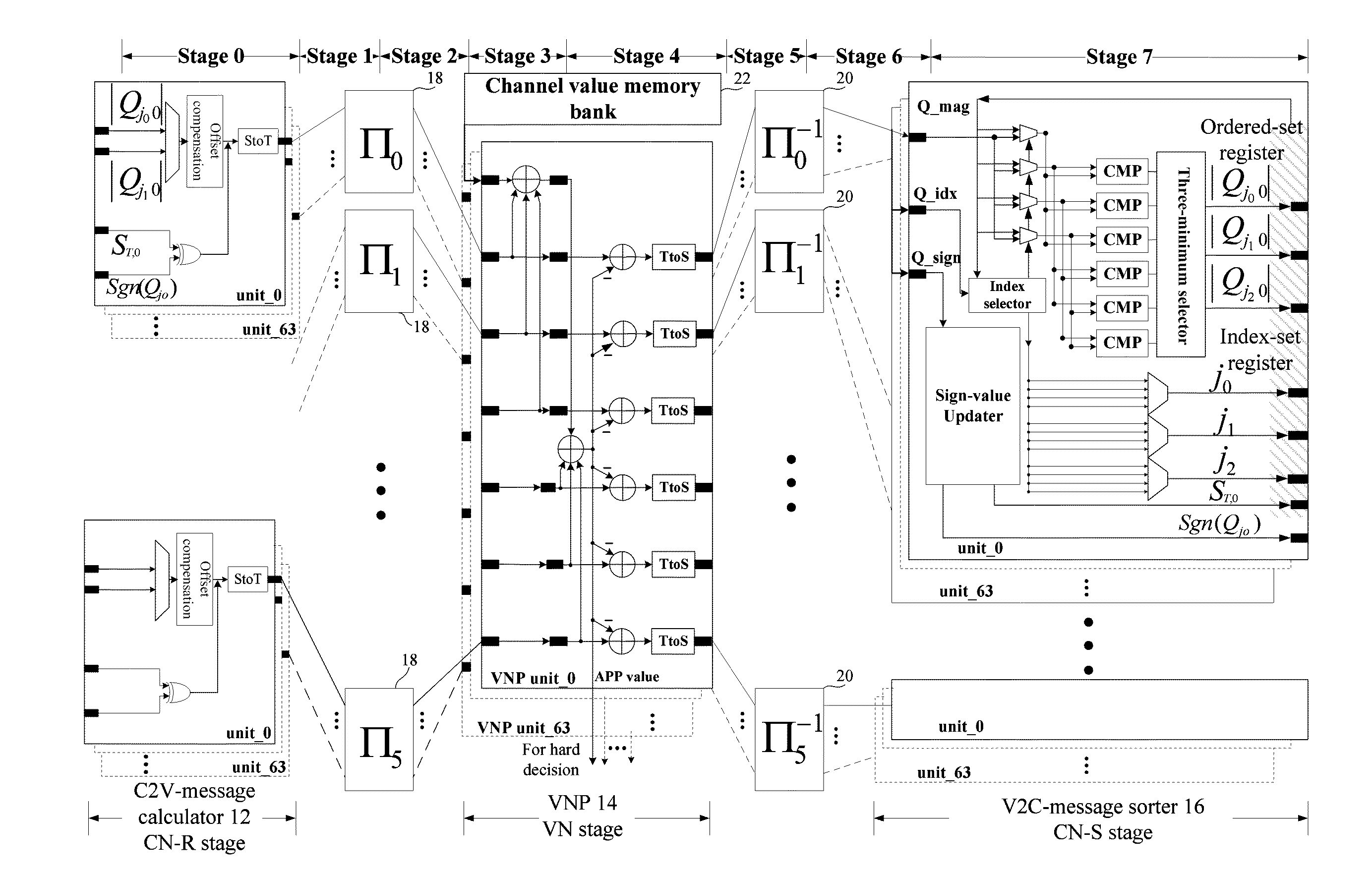
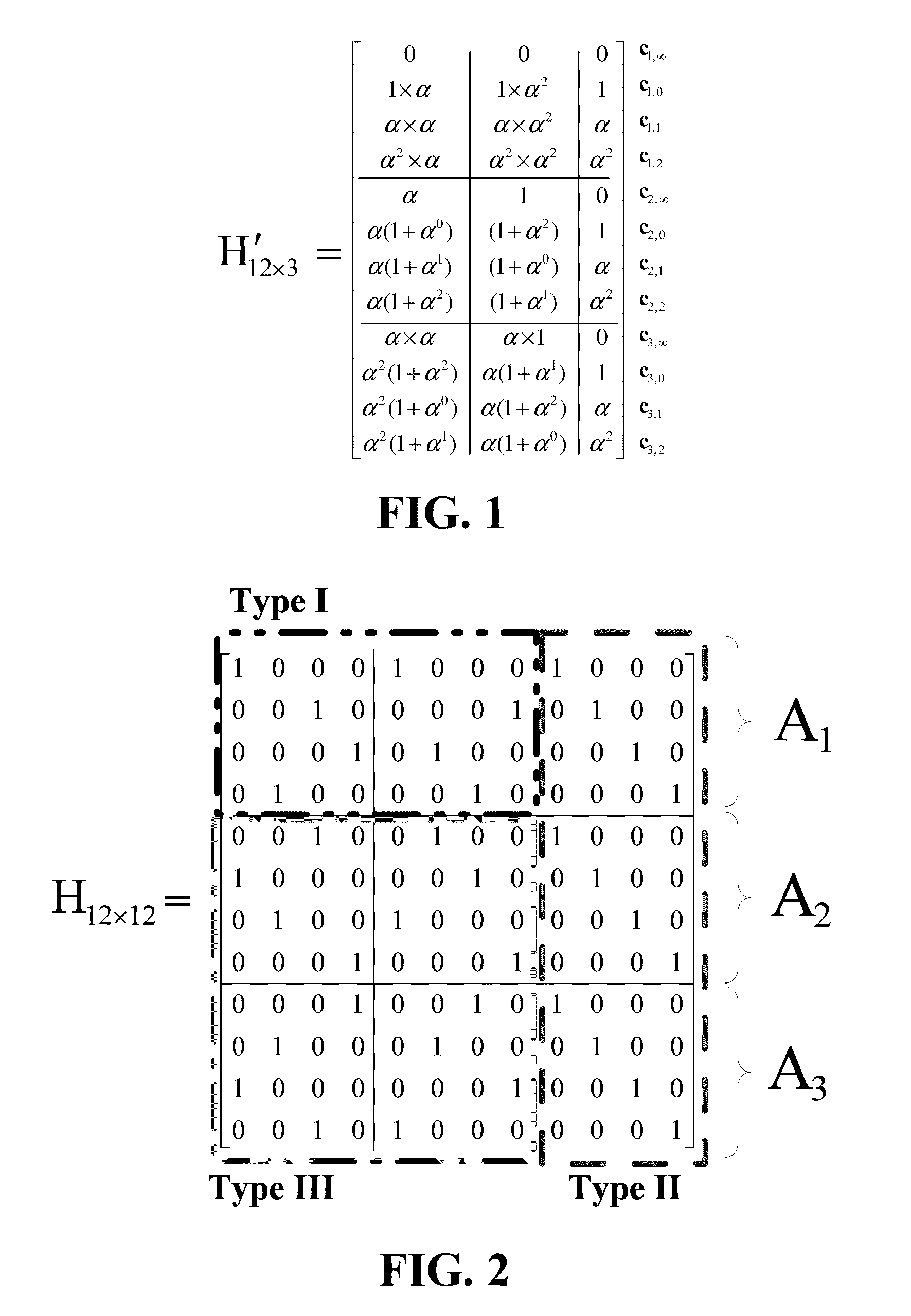
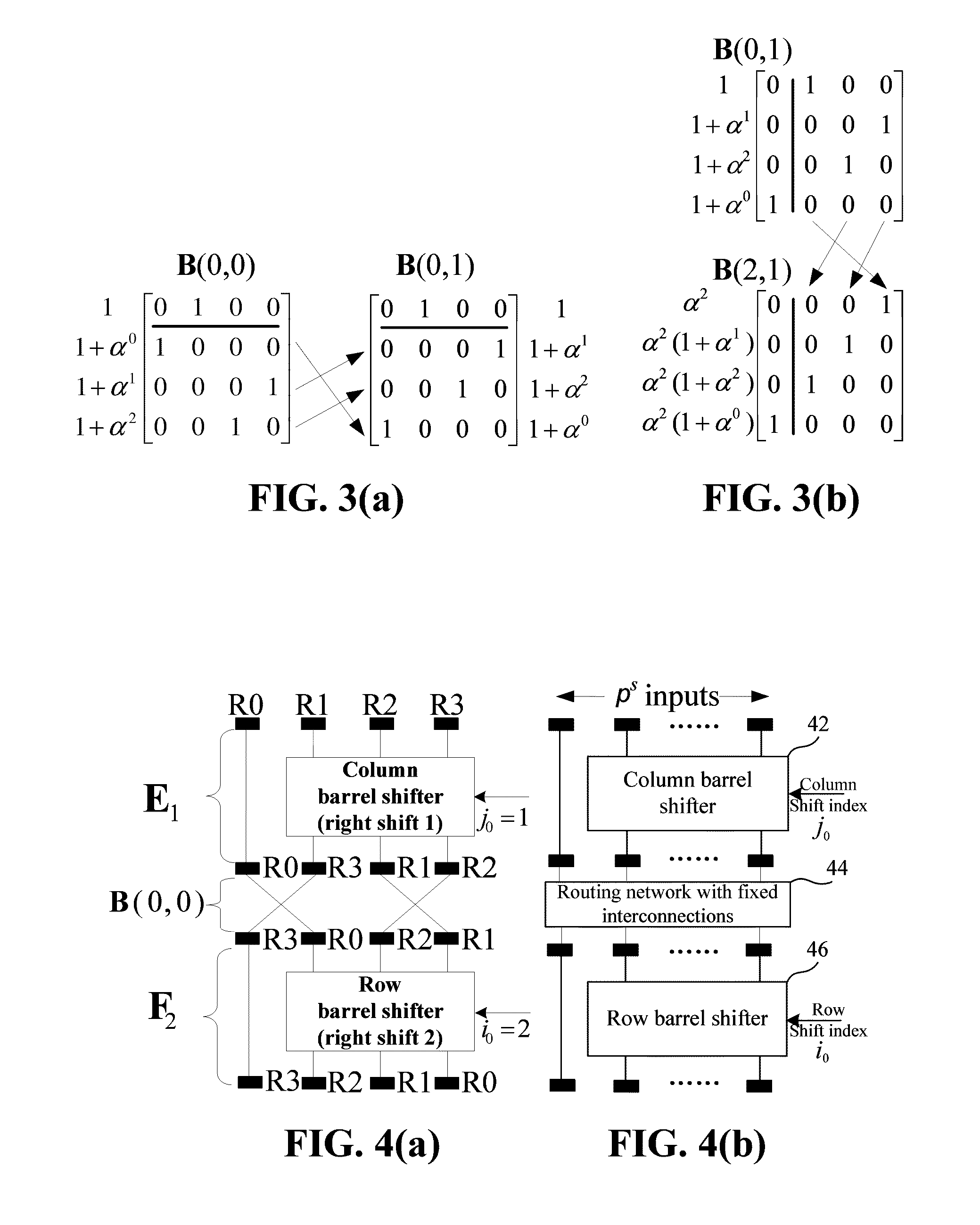
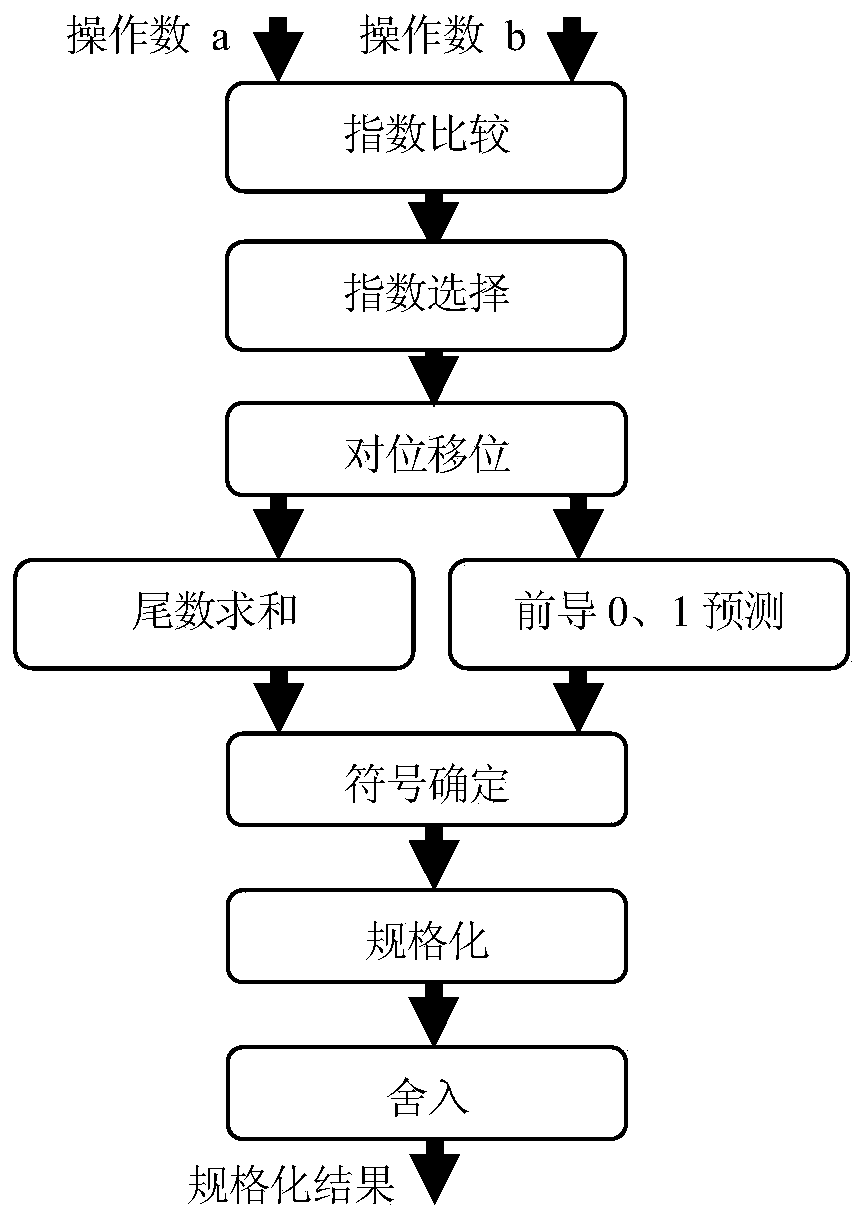
Decoder and decoding method for low-density parity check codes constructed based on reed-solomon codes
ActiveUS20110126078A1Easy to useMitigate increase in implementation complexityCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer architectureLow density
Configurable permutators in an LDPC decoder are provided. A partially-parallel architecture combined with the proposed permutators is used to mitigate the increase in implementation complexity for the multi-mode function. To overcome the difficulty in efficient implementation of a high-throughput decoder, the variable nodes are partitioned into several groups, and each group is processed sequentially in order to shorten the critical-path delay and, hence, increase the maximum operating frequency. In addition, shuffled message-passing decoding can be adopted in decoders according to the invention to increase the convergence speed, which reduces the number of iterations required to achieve a given bit-error-rate performance.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
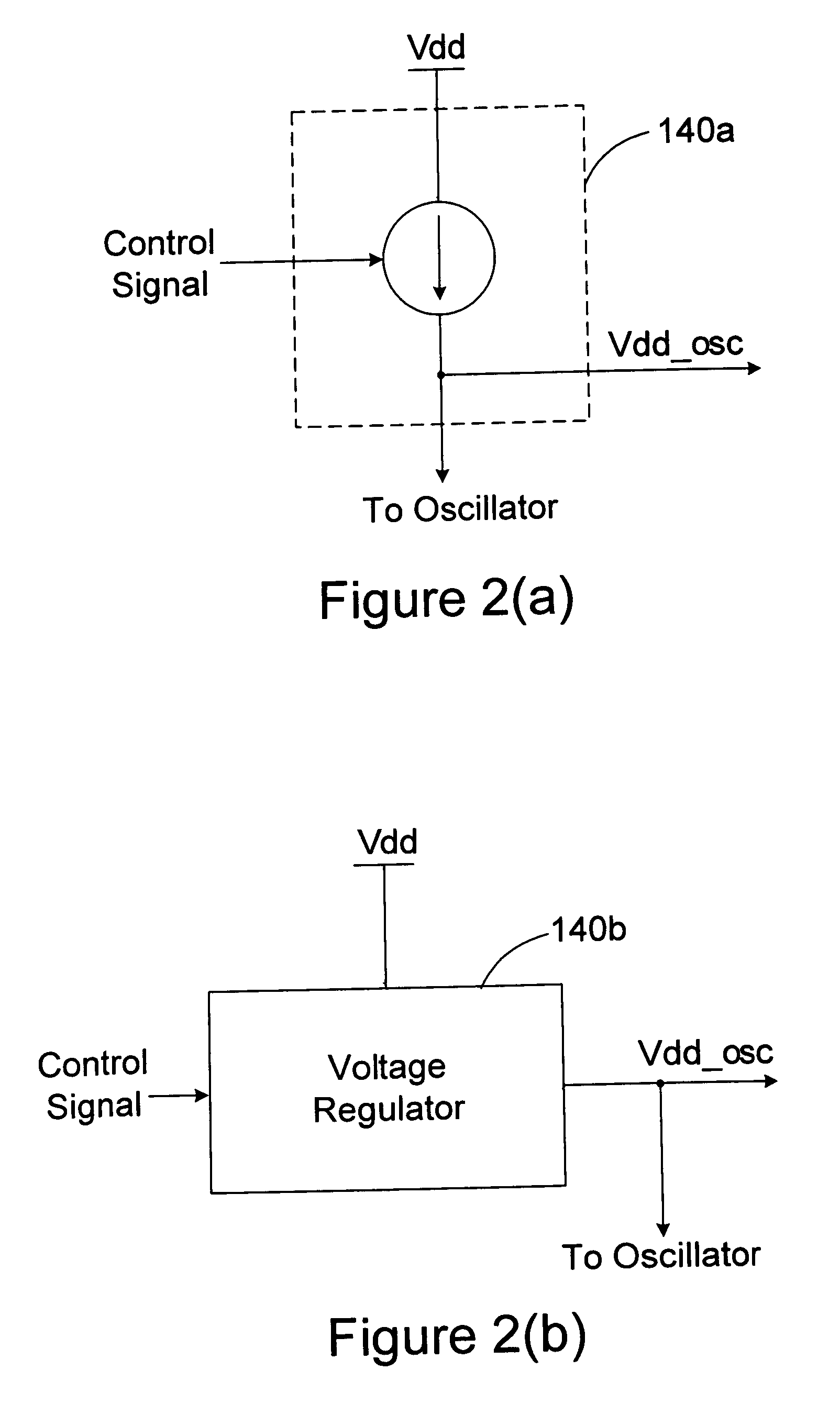
Power supply control device, semiconductor device and method of driving semiconductor device
InactiveUS6924679B2Increase in sizeSolve low usageEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlPhase differenceControl signal
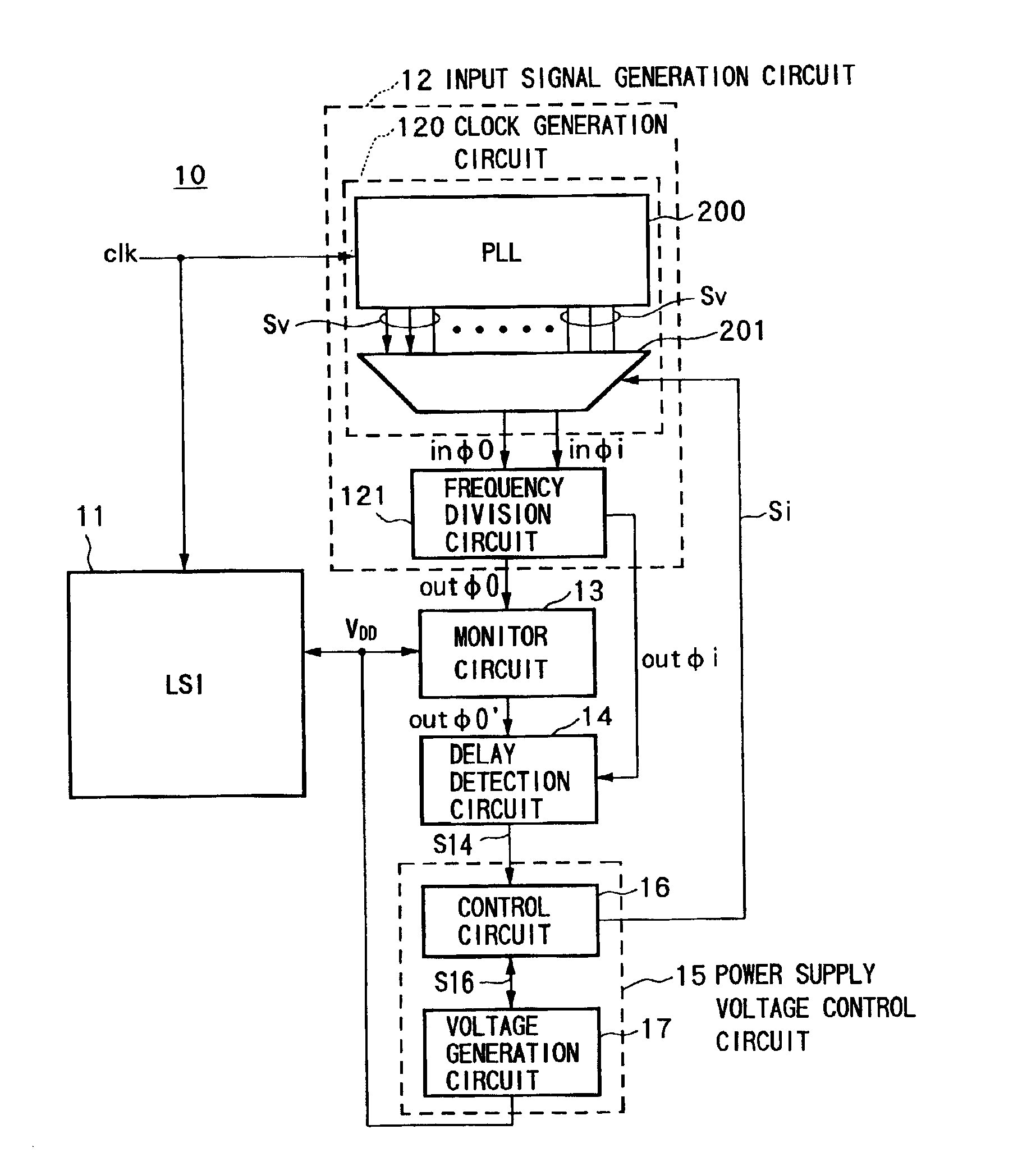
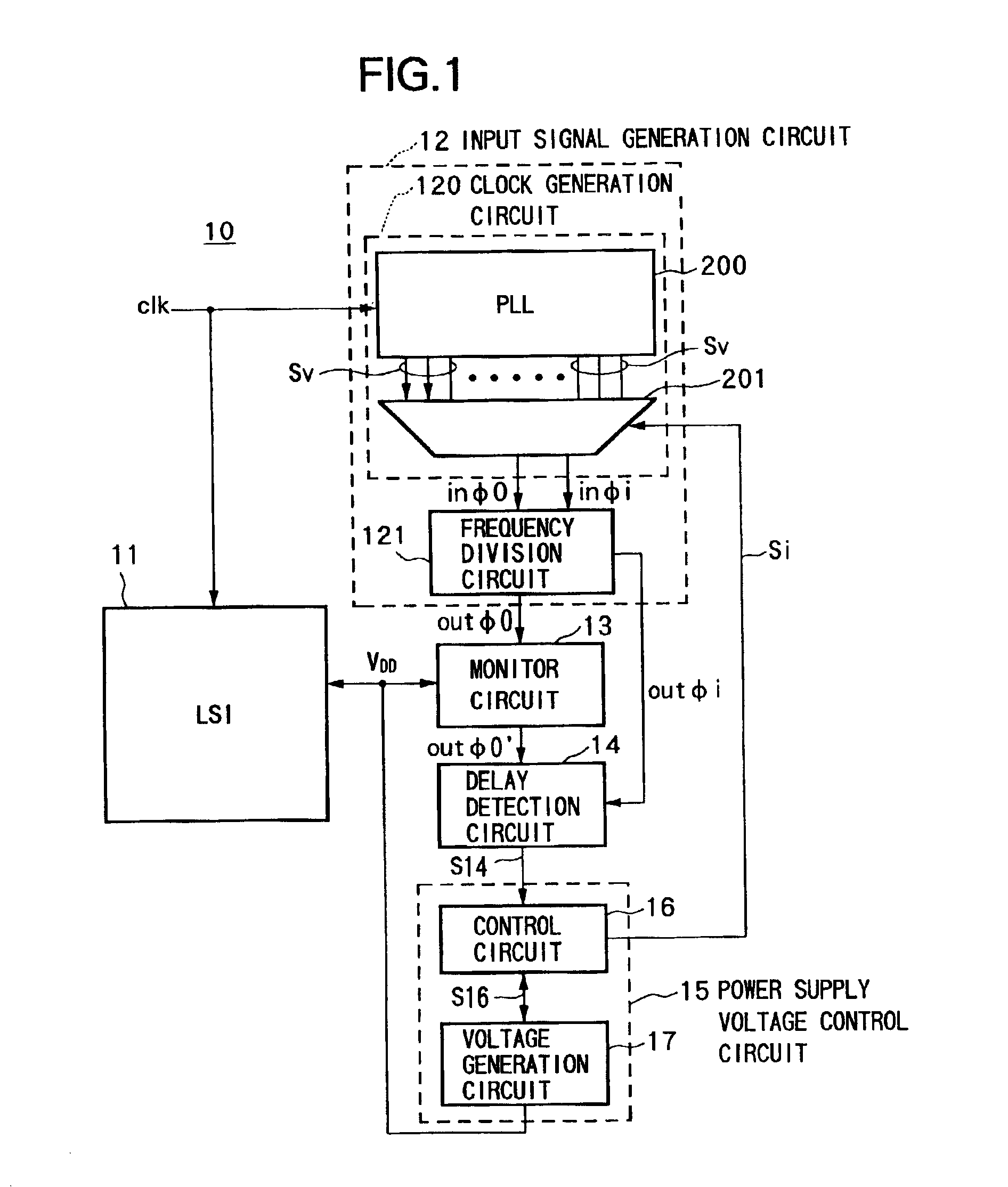
A power supply voltage control apparatus including an input signal generation circuit of wide uses or a small-sized monitor circuit of a novel configuration, and a semiconductor circuit and a method for driving the same, having a semiconductor circuit 11, an input signal generation circuit 12 able to change the phase difference i of a reference signal outφi and an input signal outφ0 in accordance with a control signal Si when generating the two signals from a clock, a monitor circuit 13 having a characteristic between a power supply voltage and delay the same as that of a critical path of the semiconductor circuit 11, propagating the input signal outφ0, and outputting a delayed signal outφ0′ to be delayed exactly by a time equivalent to a delay of the critical path (or smaller by a constant ratio), a delay detection circuit 14 for detecting a delay of the delayed signal outφ0′ relative to the reference signal outφi, and a power supply voltage control circuit 15 for controlling a power supply voltage VDD supplied to the semiconductor device 11 and the monitor circuit 13 based on the detection result.
Owner:SONY CORP
Distributed processing LDPC (low density parity check) decoder
ActiveUS20090013237A1Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionCommunication deviceThroughput
Distributed processing LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) decoder. A means is presented herein that includes an LDPC decoding architecture leveraging a distributed processing technique (e.g., daisy chain) to increase data throughput and reduce memory storage requirements. Routing congestion and critical path latency are also improved thereby. Each daisy chain includes a number of registers, and a number of localized MUXs (e.g., MUXs having merely 2 inputs each). The means presented herein also does not contain any barrel shifters, high fan-in multiplexers, or interconnection networks; therefore, the critical path is relatively short and it can also be pipelined to further increase data throughput. If desired, a communication device can include multiple configurations of such daisy chains to accommodate the decoding of various LDPC coded signals (e.g., such as for an application and / or communication device that must decoded LDPC codes using different low density parity check matrices).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
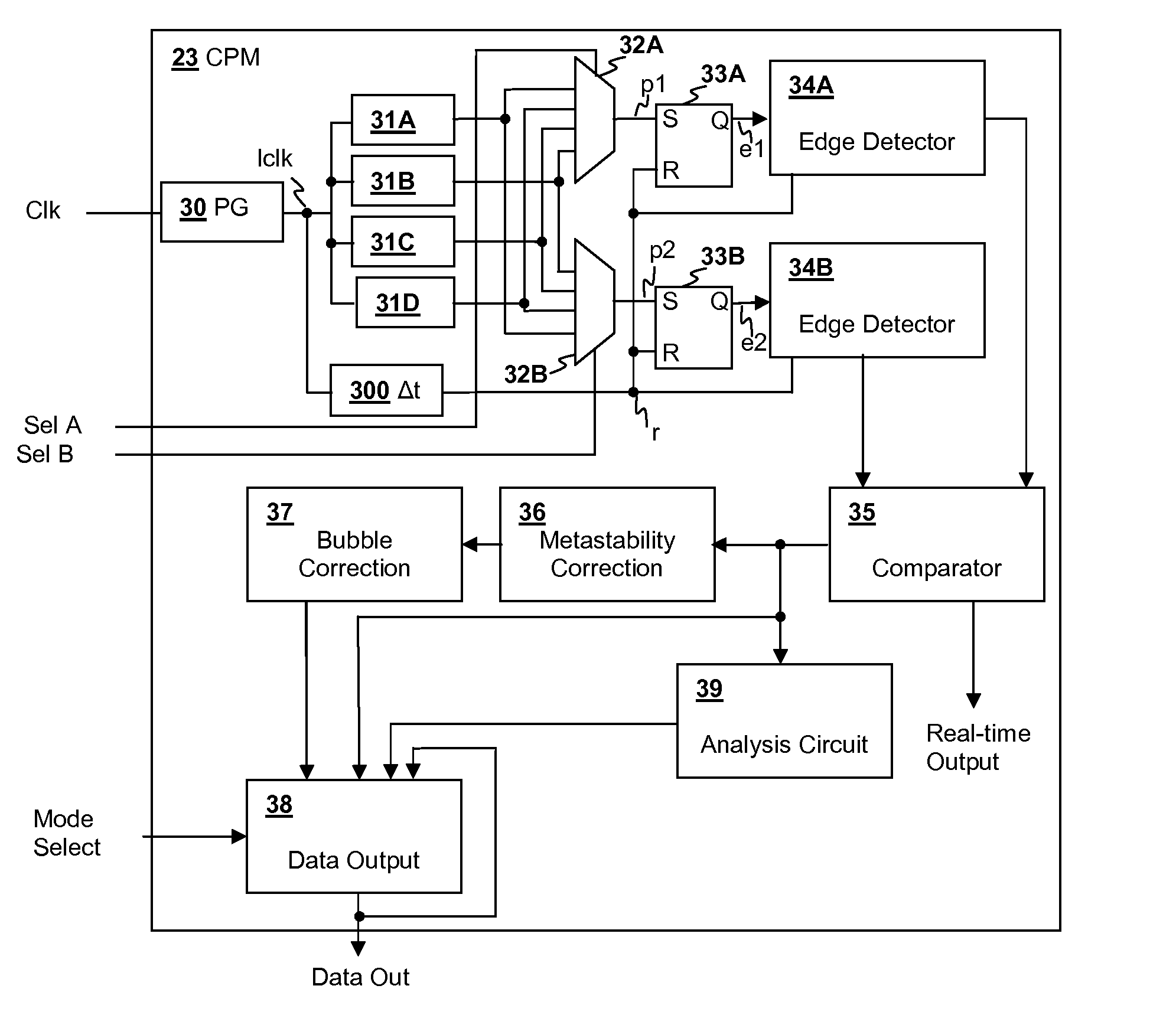
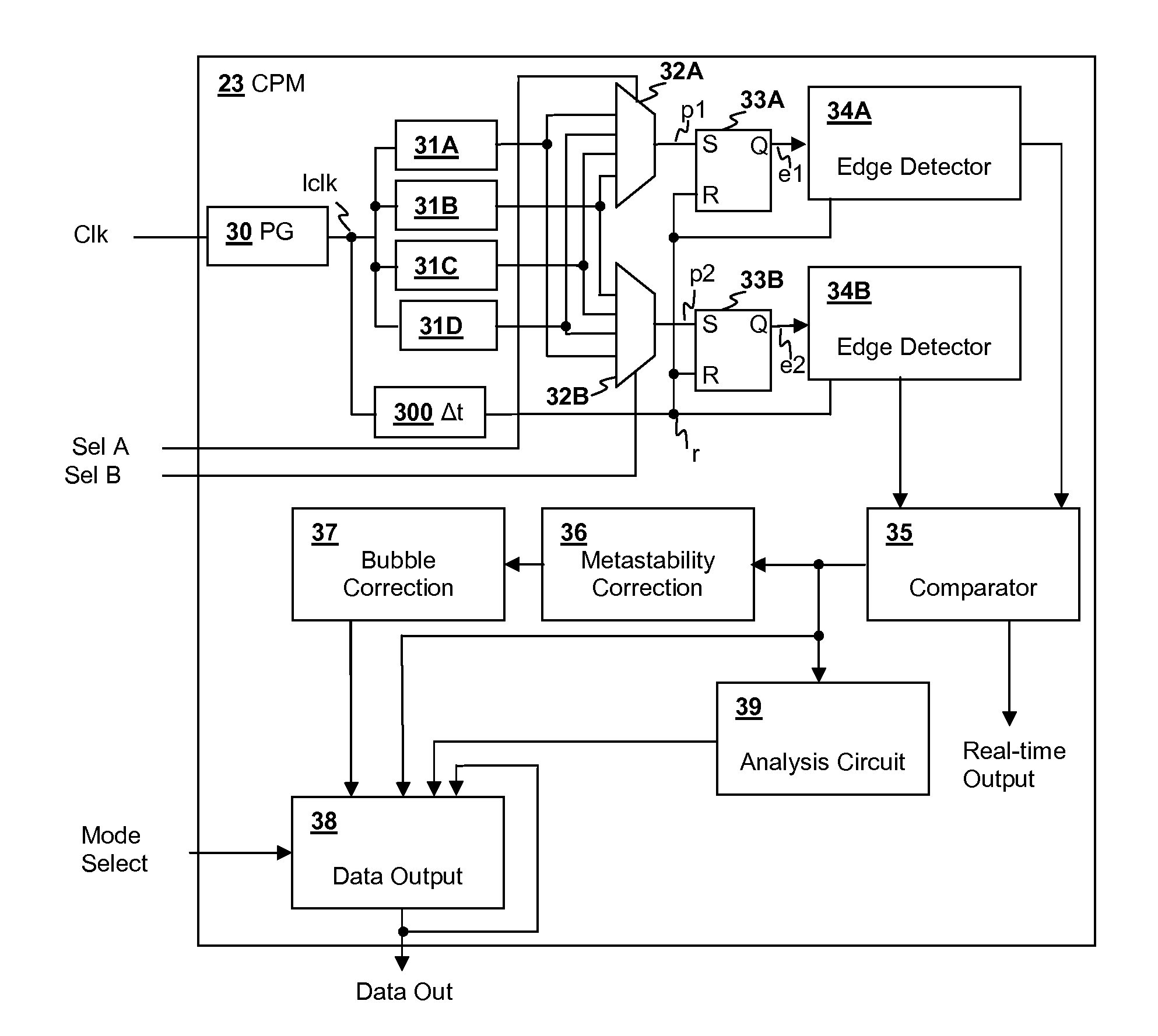
Critical path monitor having selectable operating modes and single edge detection
A critical path monitor having selectable data output modes provides additional information about critical path delay variation. A pulse is propagated through a synthesized path representing a critical path in a functional logic circuit and a synthesized path delay is measured by a monitoring circuit that detects the arrival of an edge of the pulse at the output of the synthesized delay. The measured delay is provided as a real-time output and a processed result of the measured delay is processed according to a data output mode selected from multiple selectable output modes, thereby providing different information describing the real-time data about critical path delay, such as a range of edge positions corresponding to a variation of the critical path delay.
Owner:IBM CORP
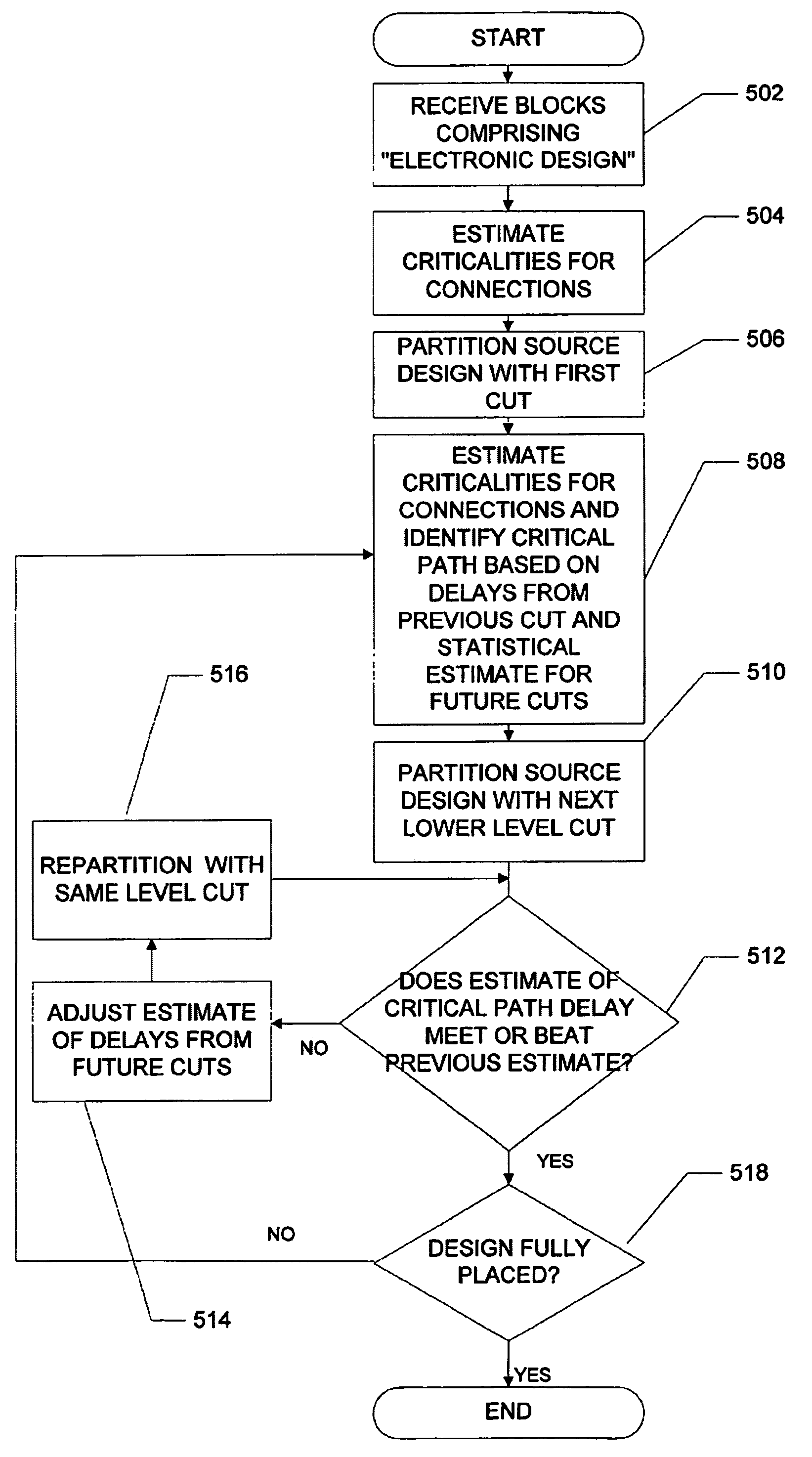
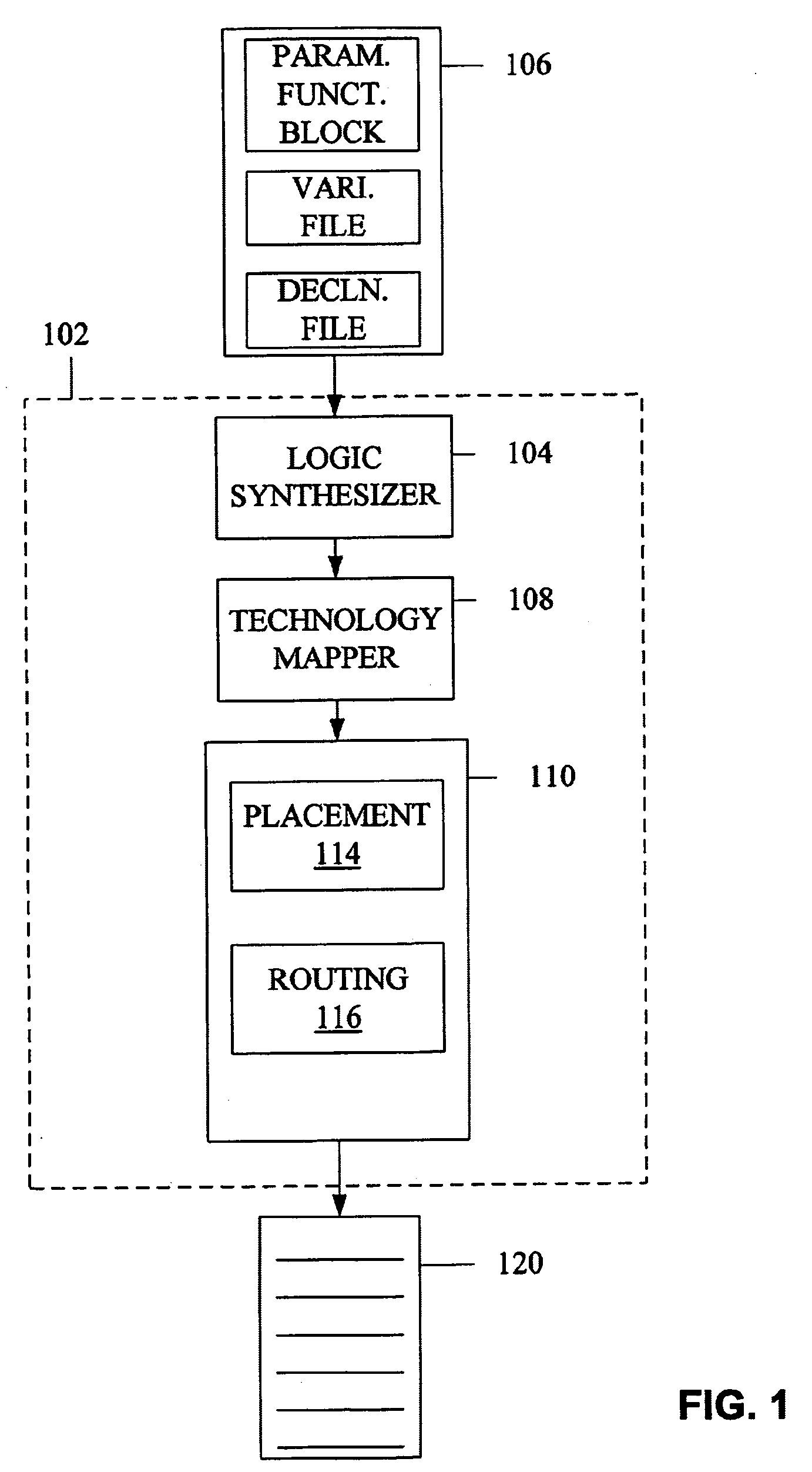
Method for adaptive critical path delay estimation during timing-driven placement for hierarchical programmable logic devices
InactiveUS7133819B1Accurate estimateDelay minimizationComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProgrammable logic deviceTheoretical computer science
Provided is a method for estimating delay data comprising receiving an electronic representation of a source electronic design, estimating the criticality of connections which have not yet been placed across a boundary based on statistical data received from at least one other design and revising the design in a manner that biases the design towards a state in which connections with the highest criticality have their delays minimized. A statistical estimate is generated for uncut connections on a path in a partially placed source design comprising receiving at least one source design, partitioning the design, and generating statistical data corresponding to each type of partitioning cut.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
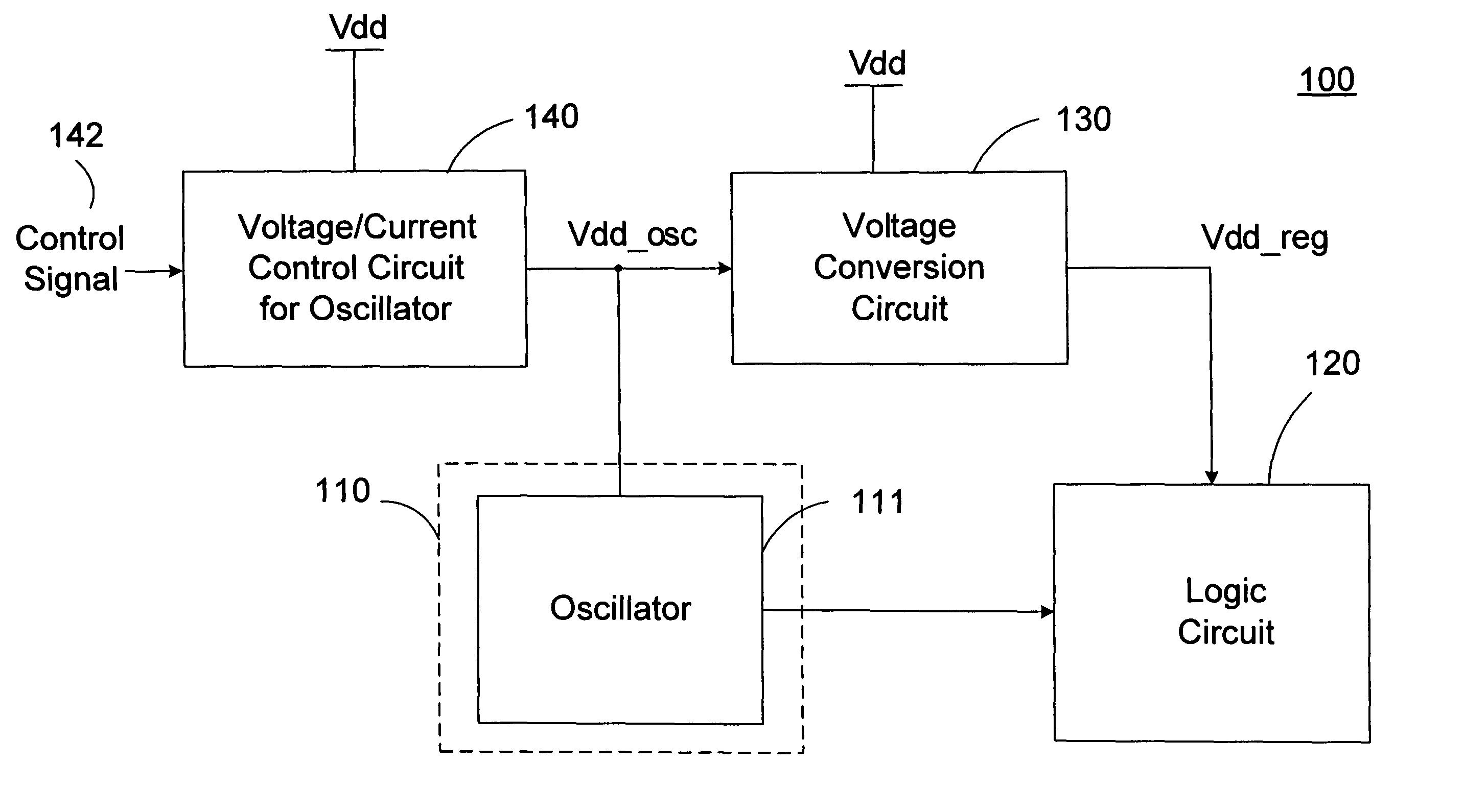
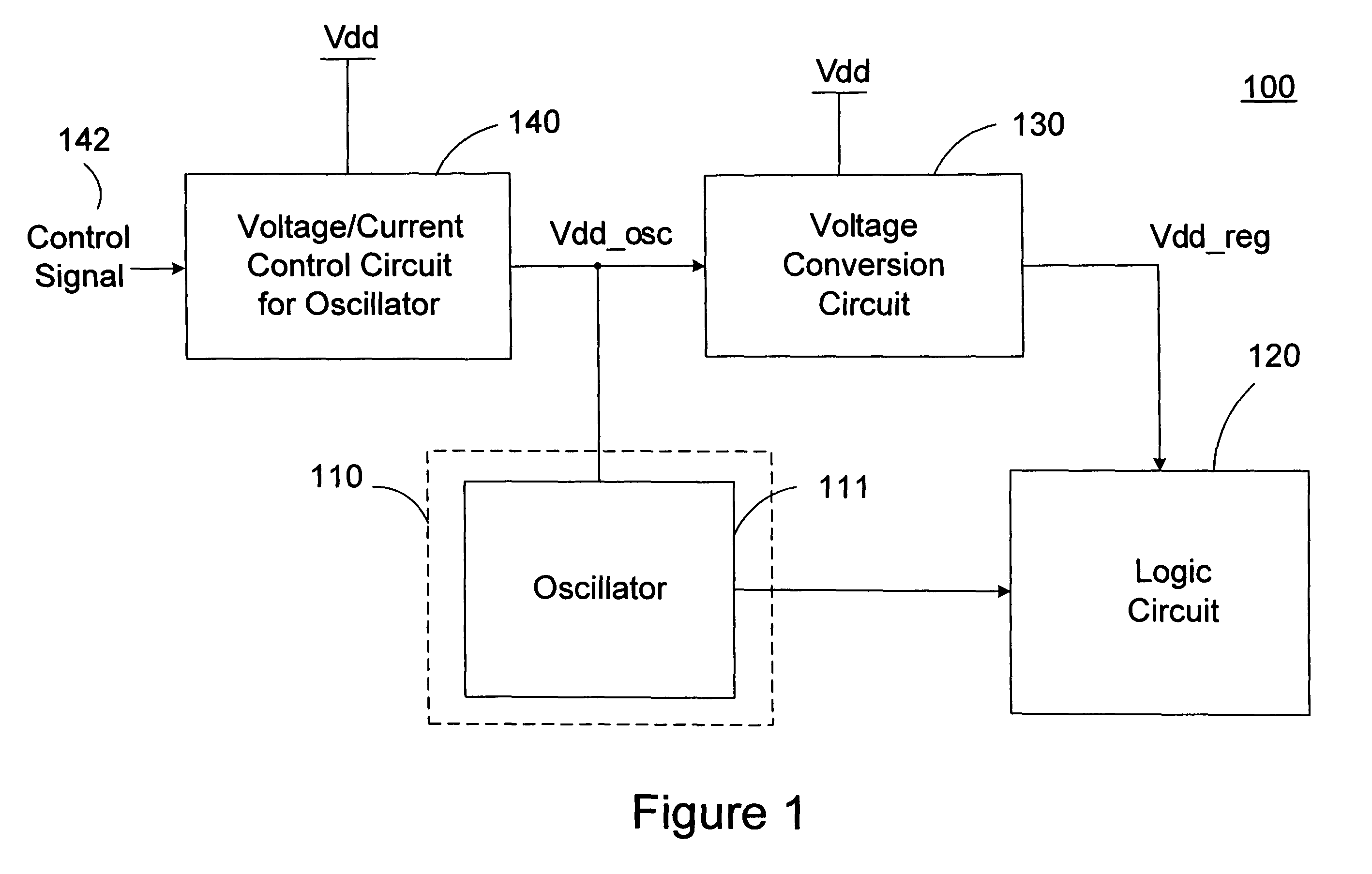
Logic system with adaptive supply voltage control
ActiveUS7095288B2Minimize power consumptionPower reduction by control/clock signalPulse automatic controlEngineeringSelf adaptive
A logic system with adaptive supply voltage control comprising a logic circuit clocked by a clock signal from a clock generating circuit and a voltage conversion circuit for generating a dynamically regulated supply voltage for powering the logic circuit. A critical path delay of the logic circuit is designed to be equal to or shorter than a period of the clock signal. The voltage conversion circuit dynamically regulates the supply voltage of the logic circuit based on a bias voltage of the clock generating circuit. According to the invention, the power consumption is effectively minimized while ensuring the logic circuit to function correctly throughout all conditions.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
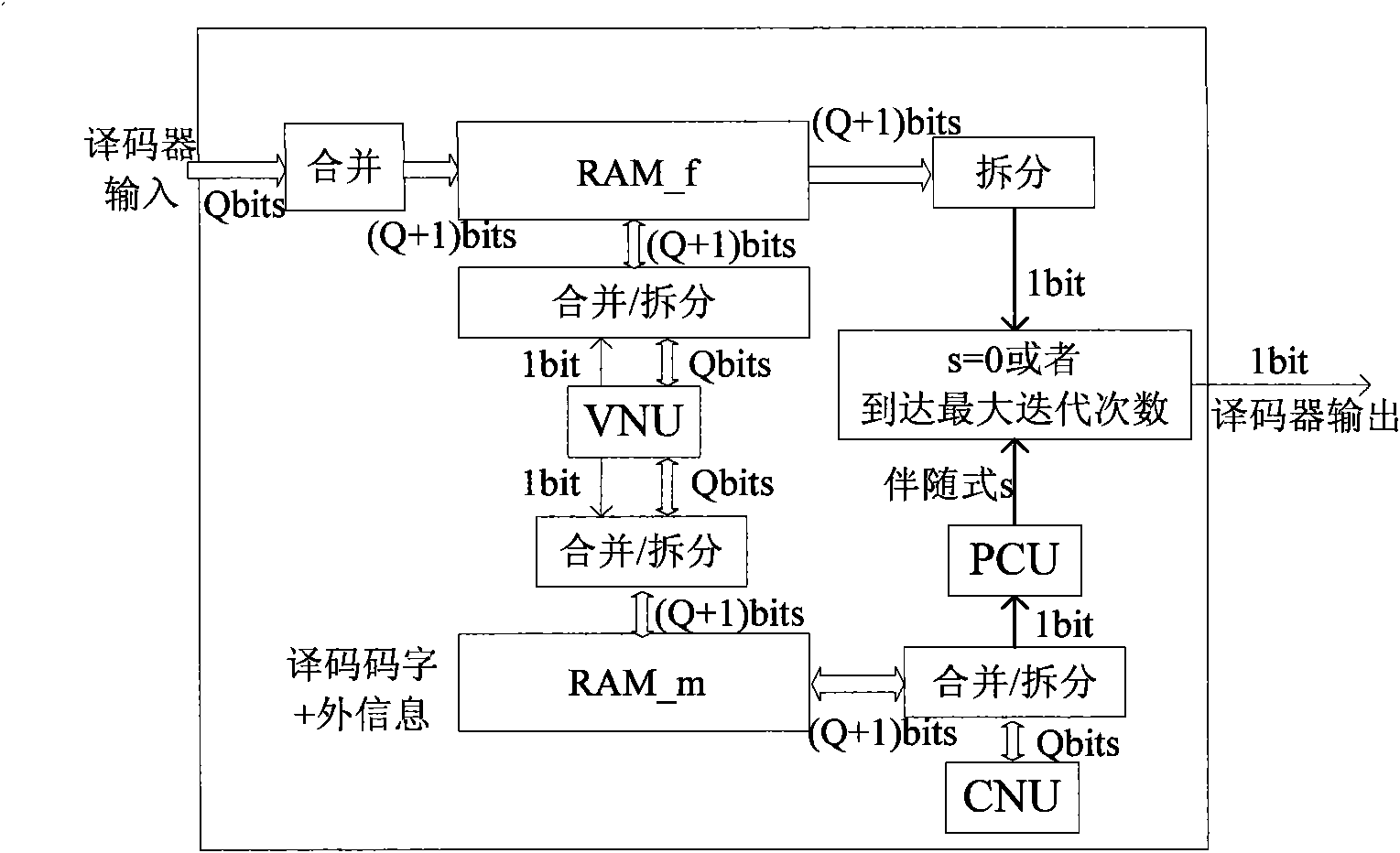
High efficiency storing method for coding digit of LDPC coder based on FPGA
ActiveCN101599302ASave logic resourcesReduce the quantity requiredData representation error detection/correctionRead-only memoriesProduction lineAddress generation unit
The invention discloses a high efficiency storing method for the coding digit of an LDPC coder based on an FPGA. In the method, the coding digit and external information (or channel information) share one storage block, thereby effectively reducing the requirement of the coder to the quantity of the storage resources; and the coding digit and the external information can be withdrawn when reading the storage block. Therefore, a check equation computational unit PCU and a check node update unit CNU can share one group of address information, and the PCU does not need additional address generation units; and finally, the design method of a step thinning production line is adopted to realize process units VNU, CNU and PCU, thereby effectively reducing the key path delay of the coder and providing a necessary safeguard to improve the throughput of the LDPC coder. When realizing the method with the FPGA, the invention not only can save a large number of the resources for respectively storing the digit and the logic resources for generating addresses which are needed by the PCU, but also can improve the throughput of the coders.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Critical path monitor having selectable operating modes and single edge detection
A critical path monitor having selectable data output modes provides additional information about critical path delay variation. A pulse is propagated through a synthesized path representing a critical path in a functional logic circuit and a synthesized path delay is measured by a monitoring circuit that detects the arrival of an edge of the pulse at the output of the synthesized delay. The measured delay is provided as a real-time output and a processed result of the measured delay is processed according to a data output mode selected from multiple selectable output modes, thereby providing different information describing the real-time data about critical path delay, such as a range of edge positions corresponding to a variation of the critical path delay.
Owner:IBM CORP
Decoder and decoding method for low-density parity check codes constructed based on reed-solomon codes
ActiveUS8549375B2Easy to useMitigate increase in implementation complexityError preventionCode conversionComputer architectureRound complexity
Configurable permutators in an LDPC decoder are provided. A partially-parallel architecture combined with the proposed permutators is used to mitigate the increase in implementation complexity for the multi-mode function. To overcome the difficulty in efficient implementation of a high-throughput decoder, the variable nodes are partitioned into several groups, and each group is processed sequentially in order to shorten the critical-path delay and, hence, increase the maximum operating frequency. In addition, shuffled message-passing decoding can be adopted in decoders according to the invention to increase the convergence speed, which reduces the number of iterations required to achieve a given bit-error-rate performance.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
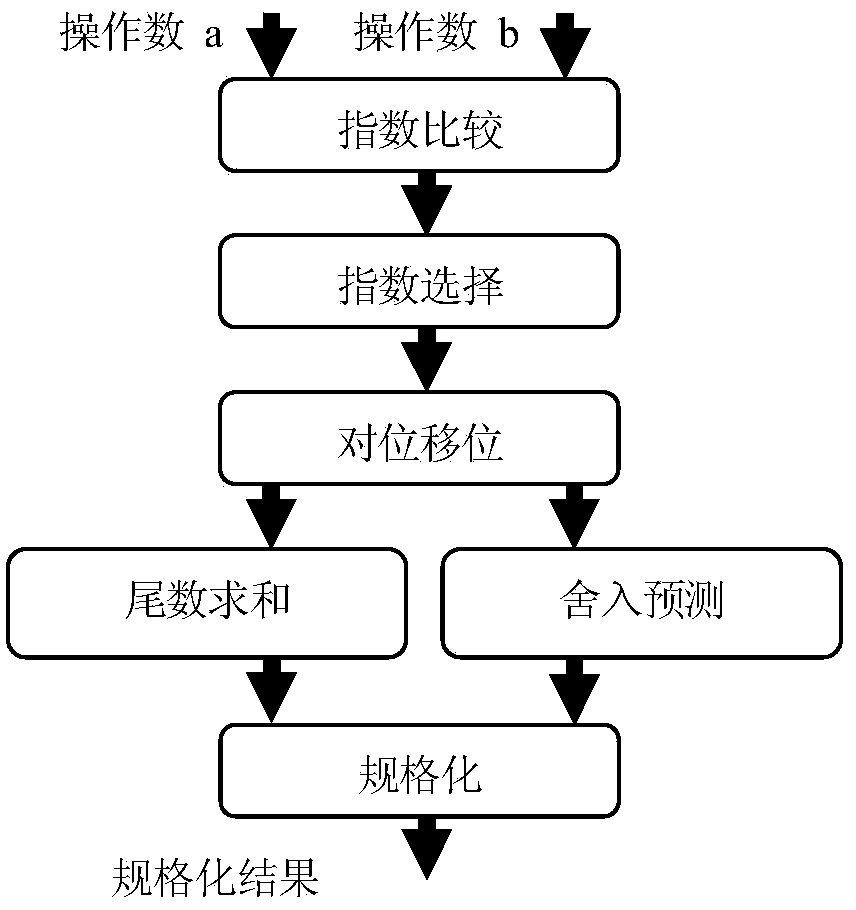
Rounding prediction method for floating point adder
InactiveCN103455305AReduce stepsDigital data processing detailsVery large scale integrated circuitsPredictive methods
The invention discloses a rounding prediction method for a floating point adder. The performance of the adder can be improved. A rounding prediction unit realized by using the method works in parallel with a mantissa adder of the adder to generate a normalized displacement control signal and a mantissa adjustment control signal including rounding information. A mantissa and an index are adjusted by a post-order unit by using the normalized displacement control signal, so that a normalized result including round-up information can be obtained; the displaced mantissa is then adjusted by using the mantissa adjustment control signal, so that a final result of the adder can be obtained. Thus, according to the adder using the prediction unit, symbol confirmation and rounding operations are successfully fallen into the normalization operation, and the operation of two-stage consumption time in the adder is reduced. The area and the critical path delay of the unit are not increased with the increase in precision of the operation processed by the unit, so that the method is particularly suitable for a high-precision adder and is realized through a super-large-scale integrated circuit.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
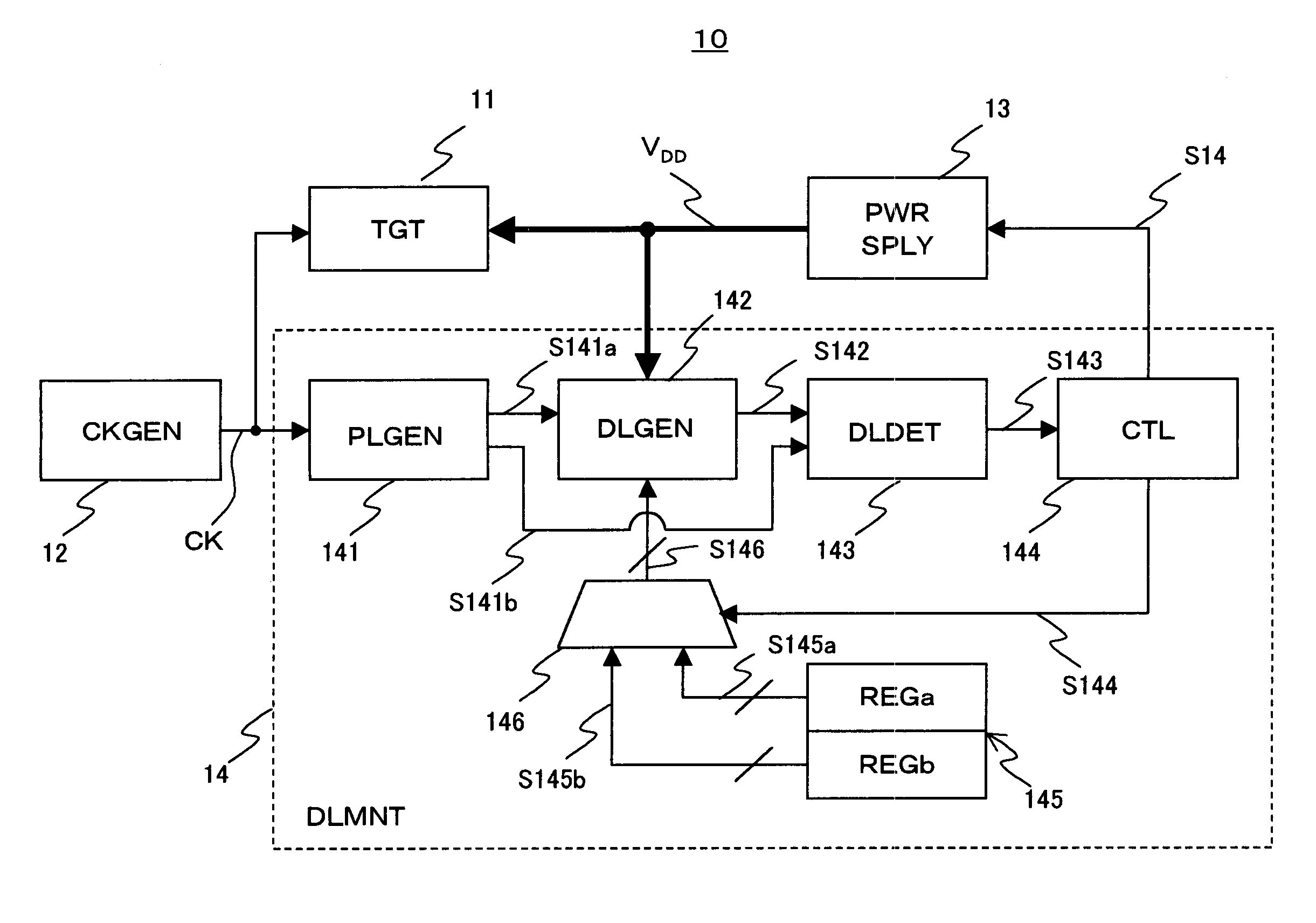
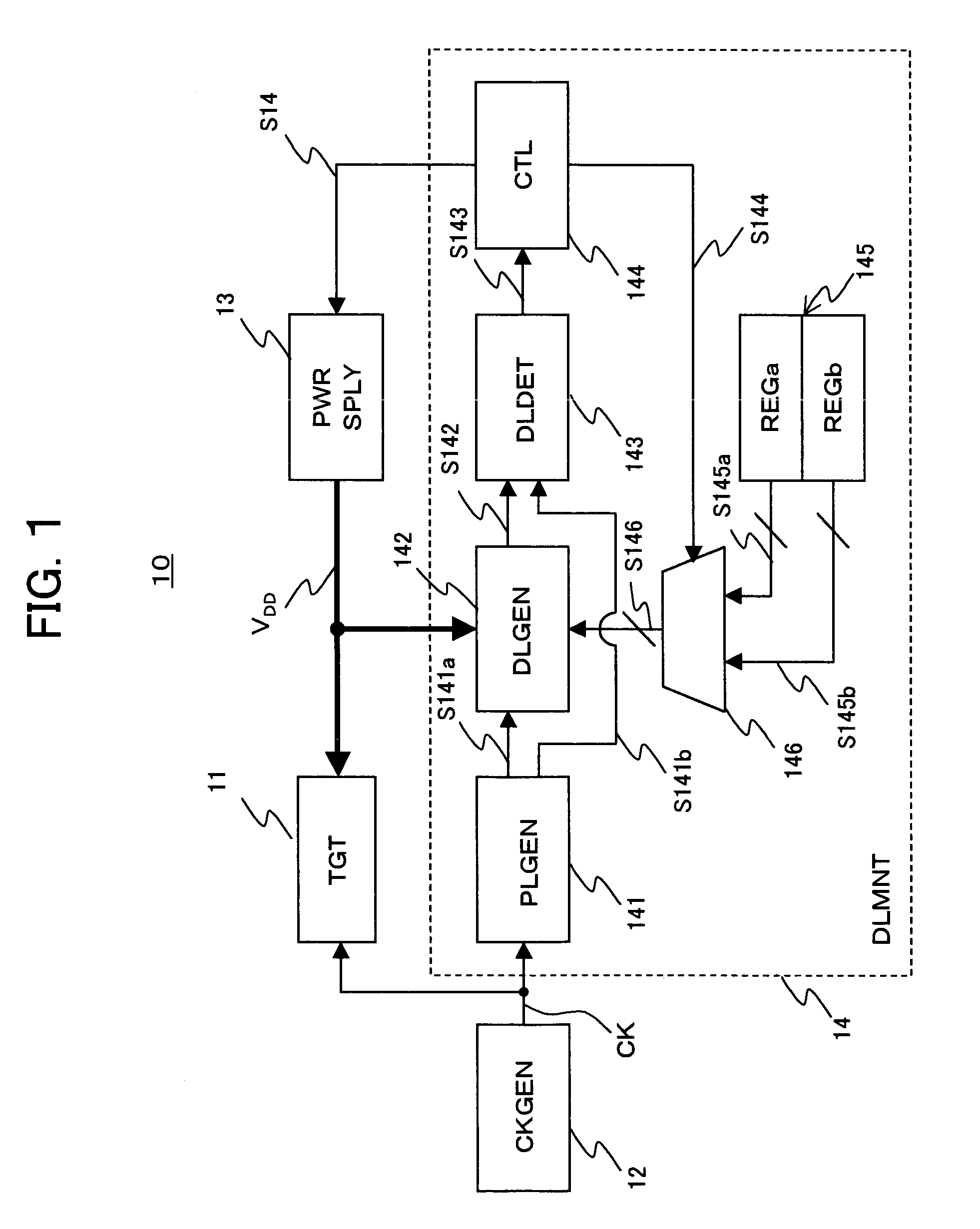
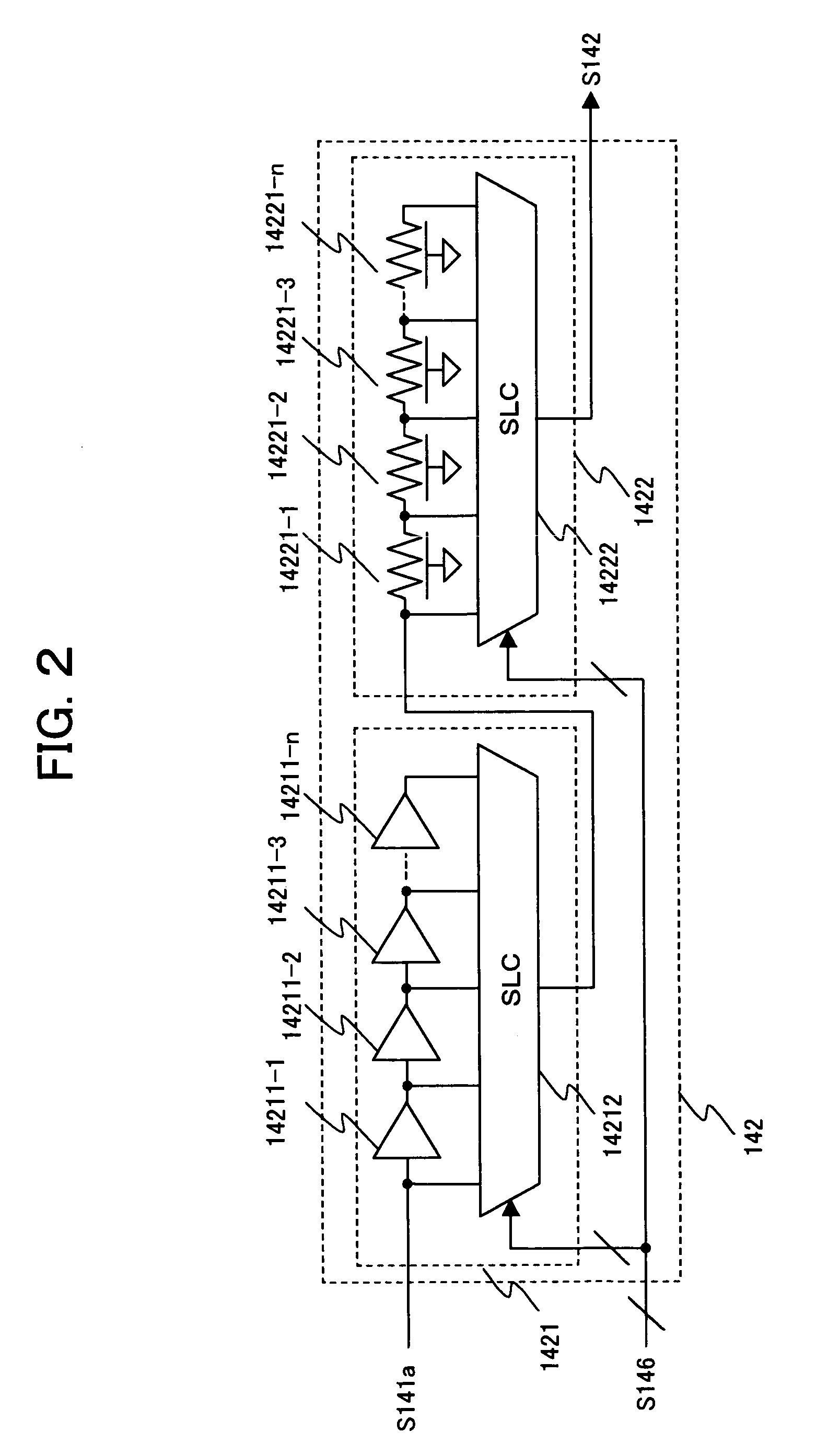
Semiconductor apparatus for monitoring critical path delay characteristics of a target circuit
InactiveUS7265590B2Flexible configurationImprove scalePulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringPropagation delayProcessor register
A semiconductor apparatus for flexibly and effectively configuring a delay monitor circuit without an increase in circuit scale includes a delay signal generation circuit for switching the configuration of delay element arrays based on first configuration information and second configuration information and propagating a delay element array wherein a pulse is switched, a register group having a first register for the first configuration information and a second register for second configuration information, a selector for outputting to the delay signal generation circuit the first configuration information and second configuration information in accordance with an instruction of a selection signal in a time sharing way, and a control circuit for controlling a power source voltage based on delay information of a delay element array and outputting to the selector a selection signal to select from the first configuration information and second configuration information in a time sharing way.
Owner:SONY CORP
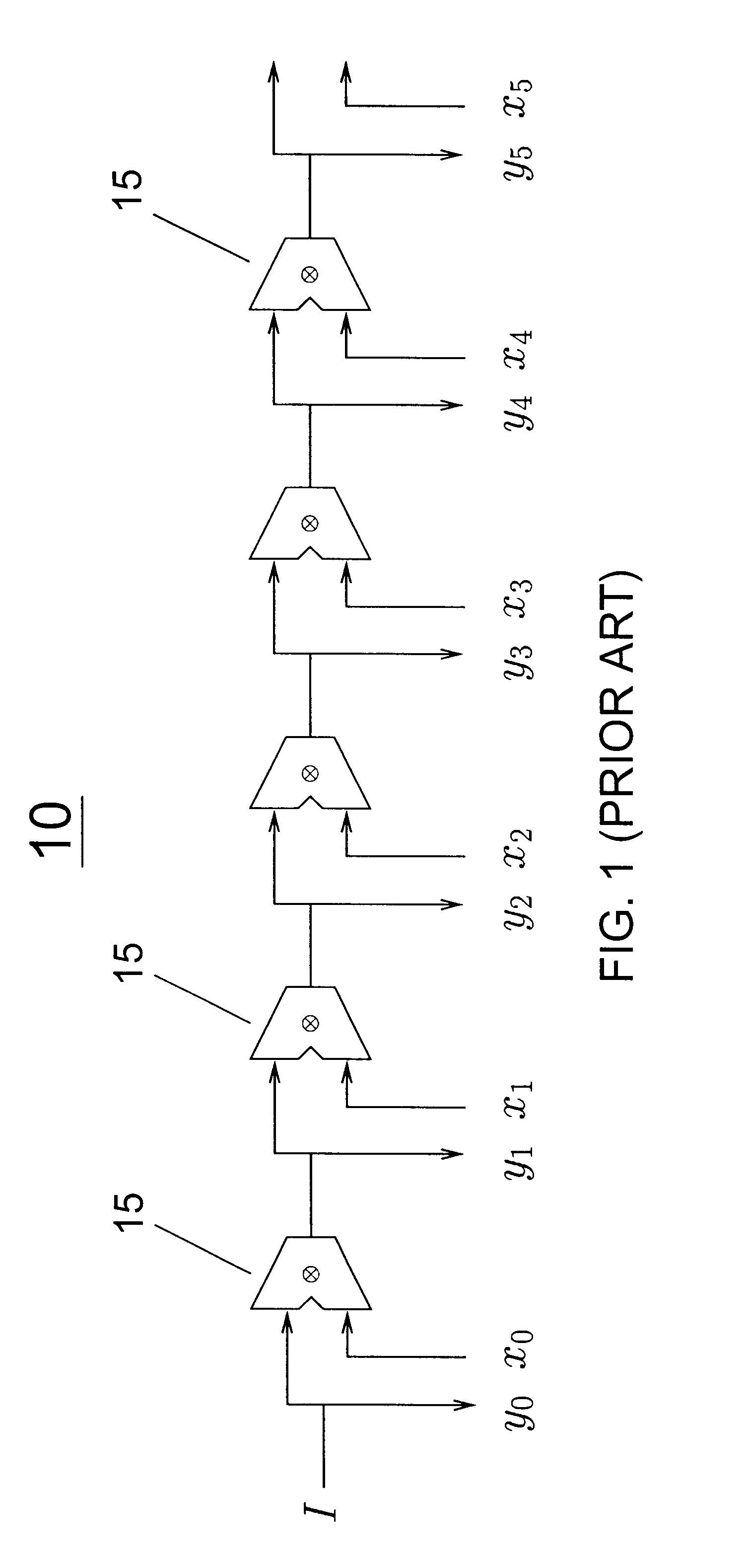
Efficient circuits for out-of-order microprocessors
InactiveUS20060015547A1Improve performanceAvoid performanceDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsExtensibilityScalar processor
The poor scalability of existing superscalar processors has been of great concern to the computer engineering community. In particular, the critical-path delays of many components in existing implementations grow quadratically with the issue width and the window size. This patent presents a novel way to reimplement these components and reduce their critical-path delay growth. It then describes an entire processor microarchitecture, called the Ultrascalar processor, that has better critical-path delay growth than existing superscalars. Most of our scalable designs are based on a single circuit, a cyclic segmented parallel prefix (cspp). We observe that processor components typically operate on a wrap-around sequence of instructions, computing some associative property of that sequence. For example, to assign an ALU to the oldest requesting instruction, each instruction in the instruction sequence must be told whether any preceding instructions are requesting an ALU. Similarly, to read an argument register, an instruction must somehow communicate with the most recent preceding instruction that wrote that register. A cspp circuit can implement such functions by computing for each instruction within a wrap-around instruction sequence the accumulative result of applying some associative operator to all the preceding instructions. A cspp circuit has a critical path gate delay logarithmic in the length of the instruction sequence. Depending on its associative operation and its layout, a cspp circuit can have a critical path wire delay sublinear in the length of the instruction sequence.
Owner:YALE UNIV
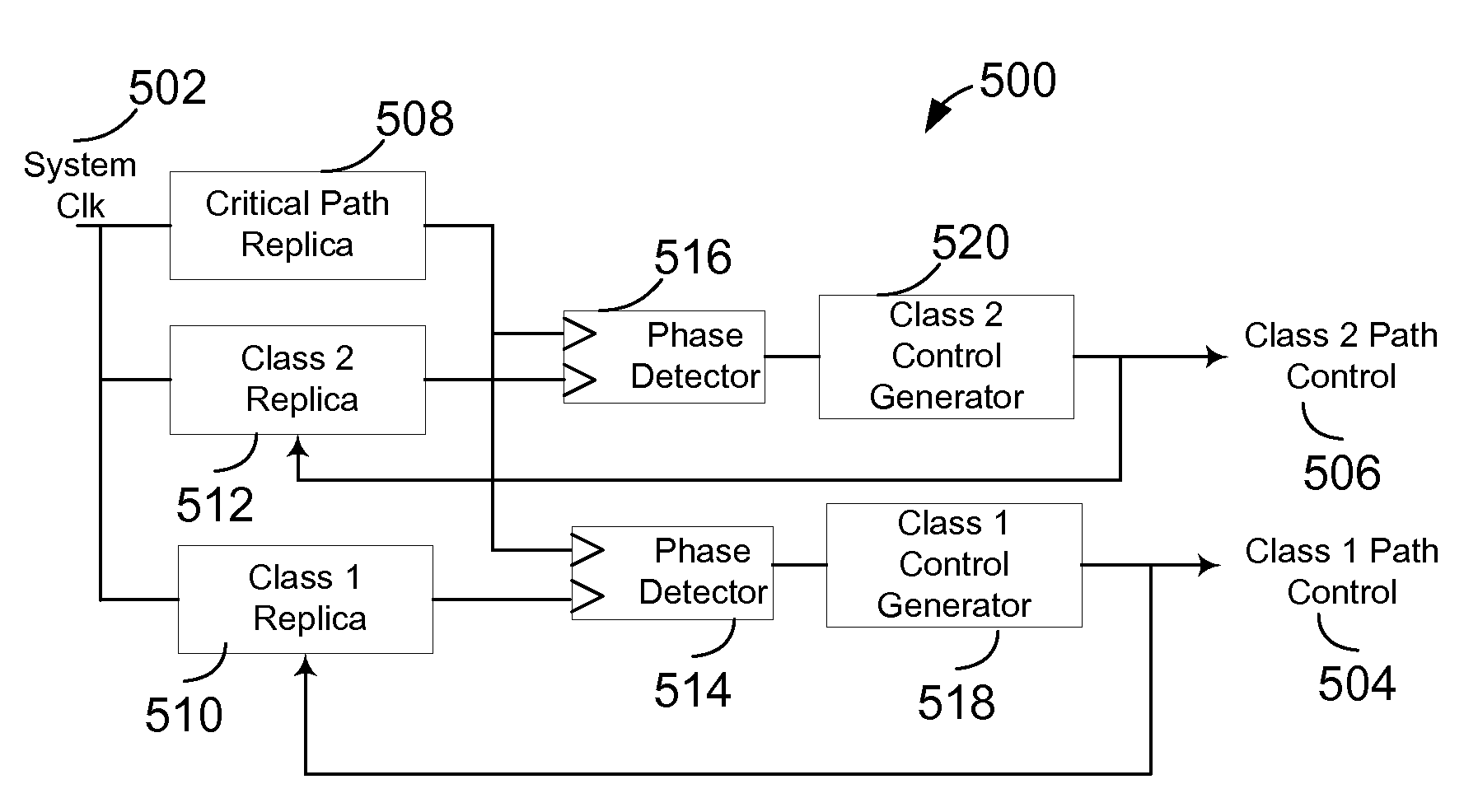
Systems and methods of reducing power consumption of digital integrated circuits
InactiveUS7557626B1Slow down propagation delayEasy to operateEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlEngineeringCritical path method
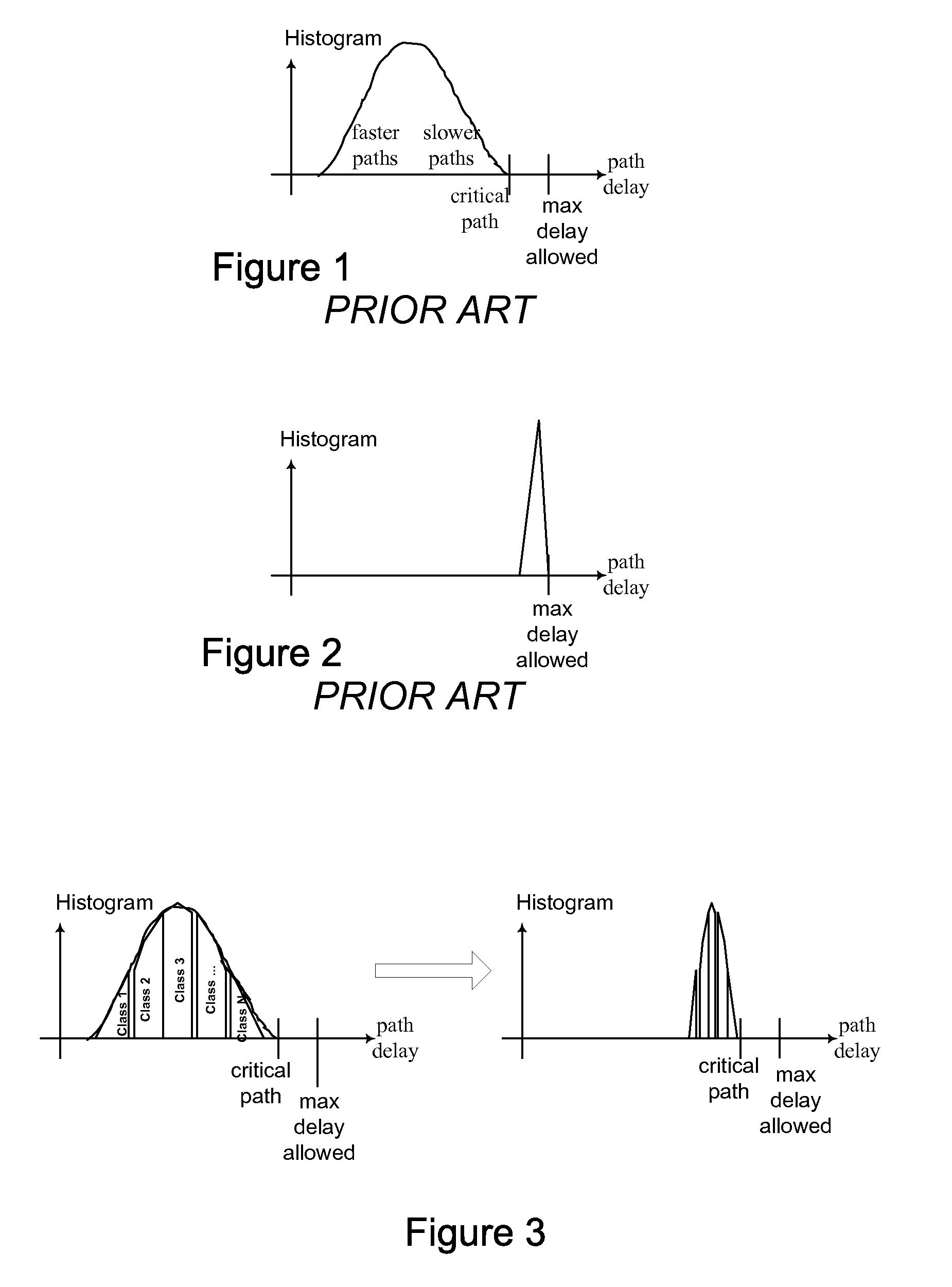
There exists a speed / power tradeoff in many digital logic circuits. In one embodiment, the tradeoff is used to reduce or minimize power dissipation by slowing down digital logic paths as system performance requirements allow. Relatively low power dissipation occurs when the histogram of logic path delays is packed towards the critical path delay, and the critical path delay is relatively close to the system clock period. In one embodiment, power is reduced by arranging path delays to be relatively slow. In one embodiment, the histogram of path delays is shaped by establishing classes of paths based on path delay, and individually controlling the classes to slow each class down, preferably relatively close to the delay of the critical path.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Distributed processing LDPC (low density parity check) decoder
ActiveUS7958429B2Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMultiplexerParity-check matrix
Distributed processing LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) decoder. A means is presented herein that includes an LDPC decoding architecture leveraging a distributed processing technique (e.g., daisy chain) to increase data throughput and reduce memory storage requirements. Routing congestion and critical path latency are also improved thereby. Each daisy chain includes a number of registers, and a number of localized MUXs (e.g., MUXs having merely 2 inputs each). The means presented herein also does not contain any barrel shifters, high fan-in multiplexers, or interconnection networks; therefore, the critical path is relatively short and it can also be pipelined to further increase data throughput. If desired, a communication device can include multiple configurations of such daisy chains to accommodate the decoding of various LDPC coded signals (e.g., such as for an application and / or communication device that must decoded LDPC codes using different low density parity check matrices).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
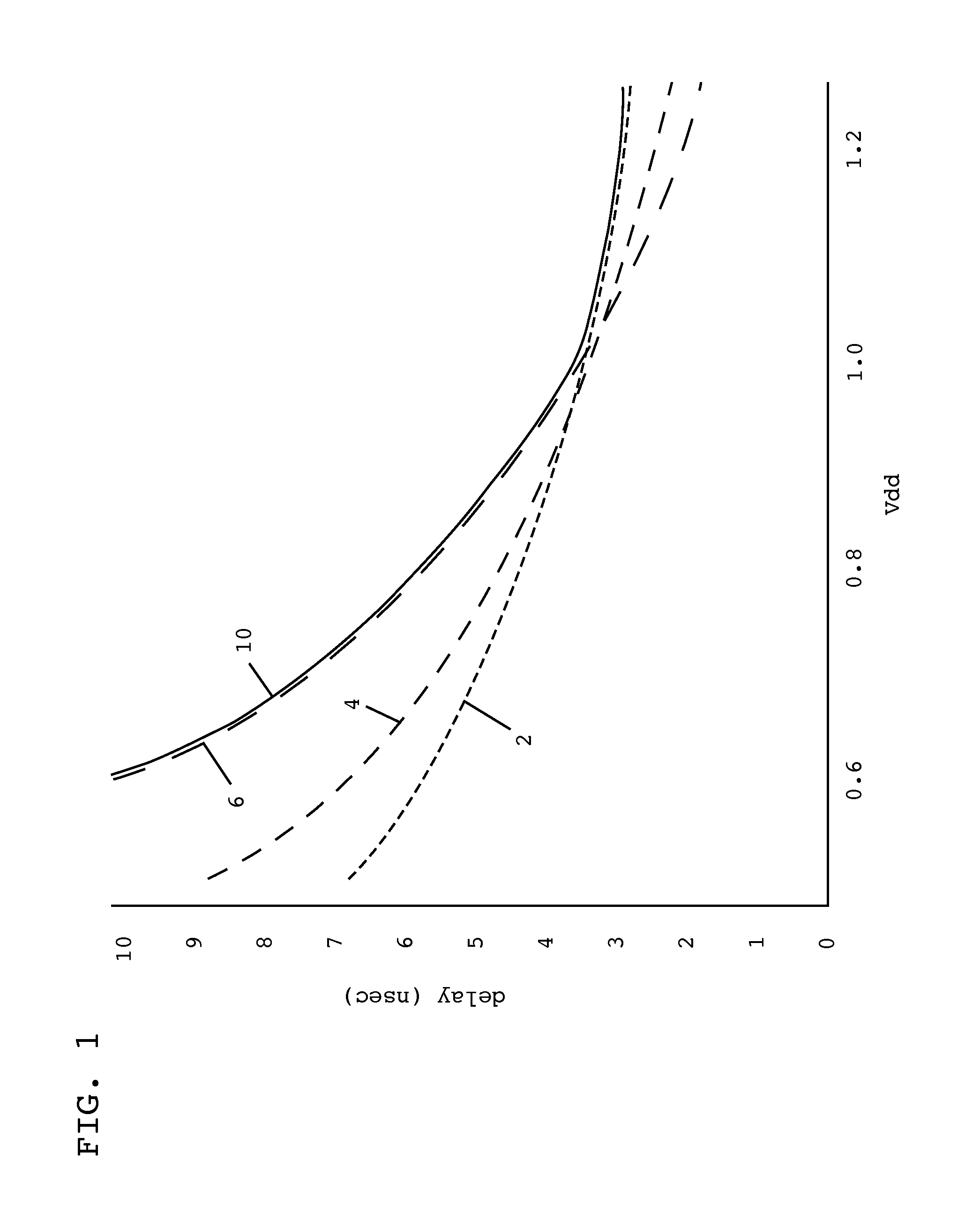
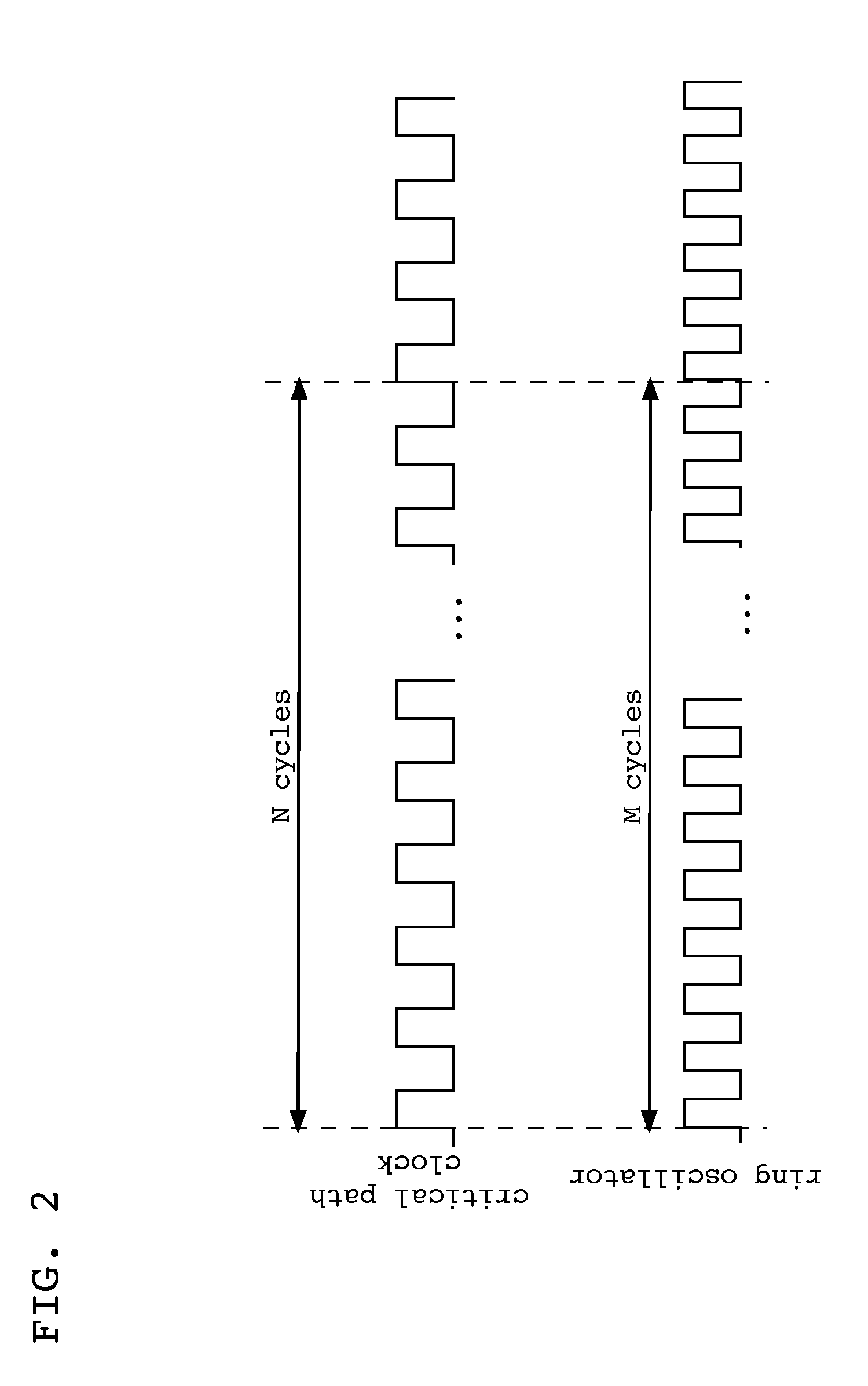
Critical path delay prediction
InactiveUS20130041608A1Voltage-current phase anglePulse characteristics measurementsCritical path delayRing oscillator
Embodiments of the invention provide a method, system, and program product for predicting a delay of a critical path. In one embodiment, the invention provides a method of predicting a delay of at least one critical path of an integrated circuit, the method comprising: determining a delay of at least one ring oscillator on the integrated circuit; and calculating a predicted delay for the at least one critical path delay based on a delay of components of the critical path at a corner condition, a wire delay of the at least one critical path, a delay of the at least one ring oscillator at a corner condition, and the determined delay of the at least one ring oscillator.
Owner:IBM CORP
Structure and circuit of logarithmic skip adder
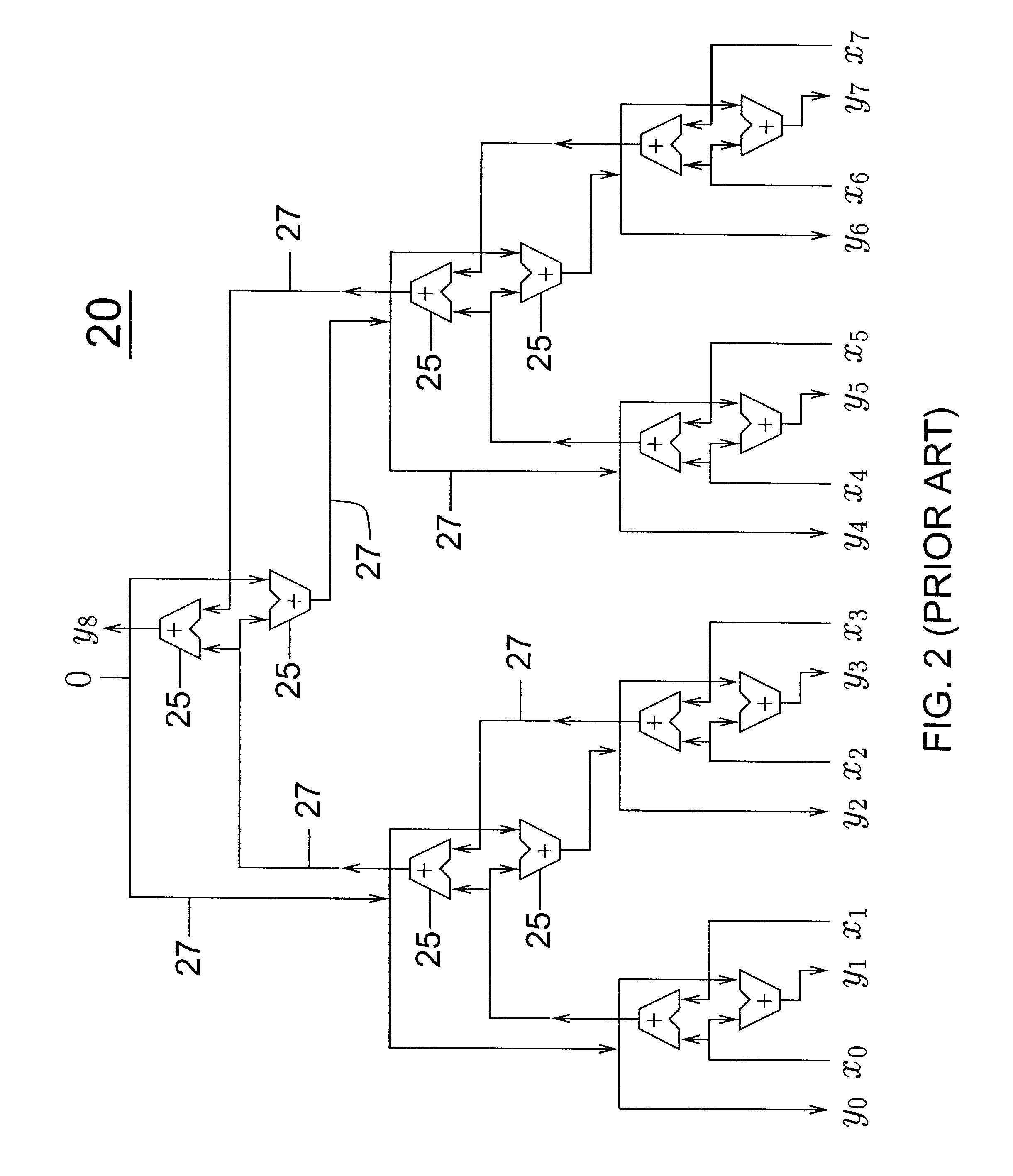
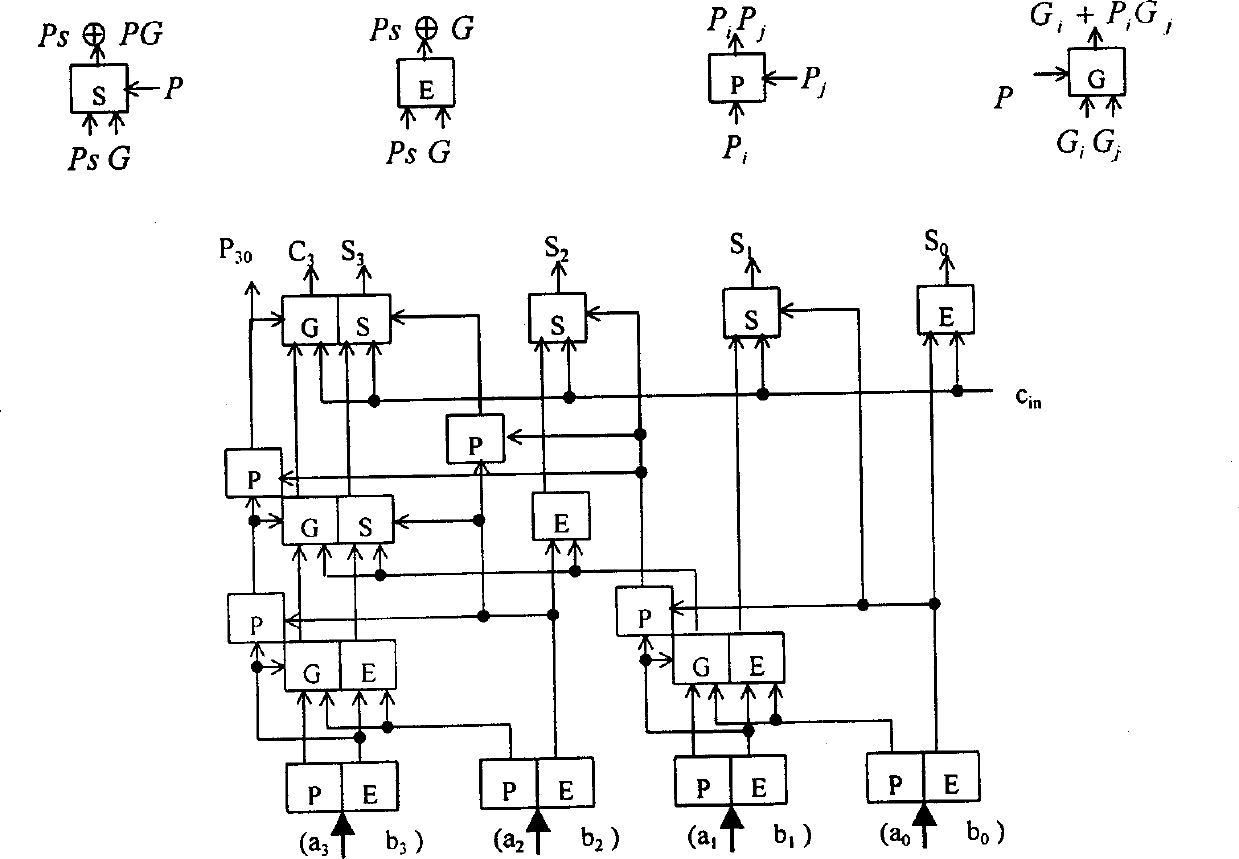
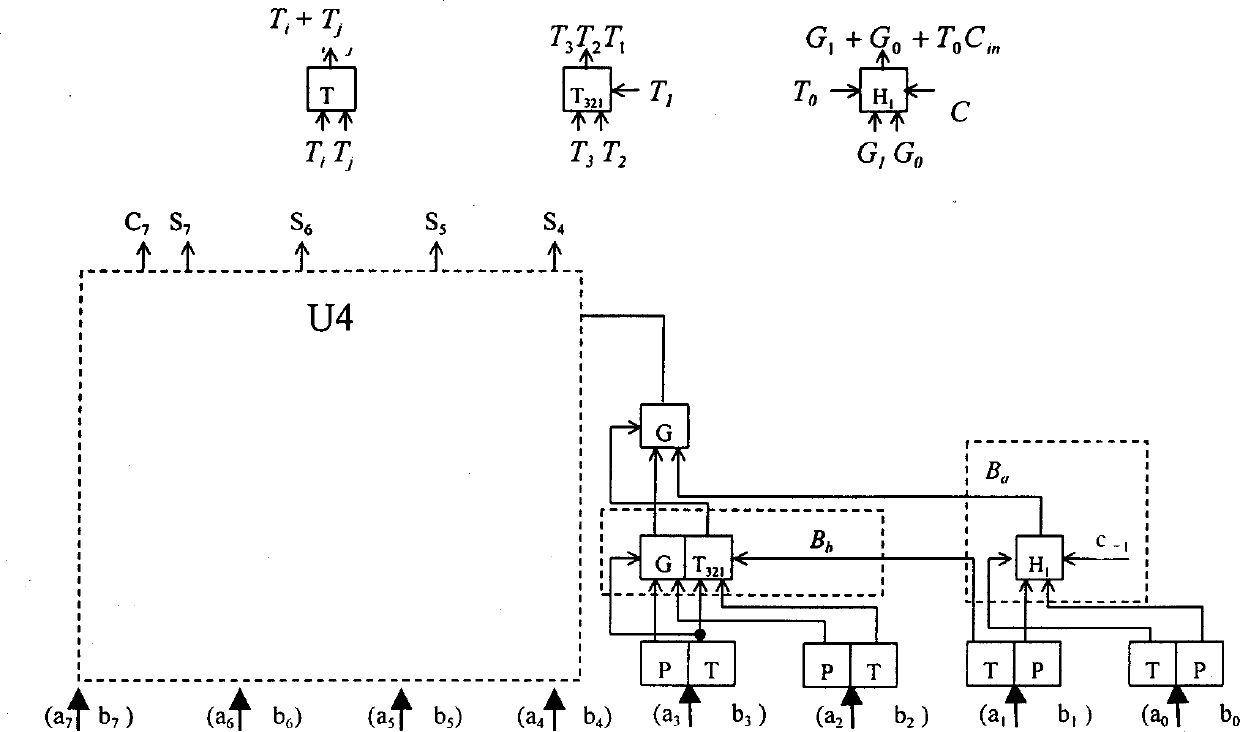
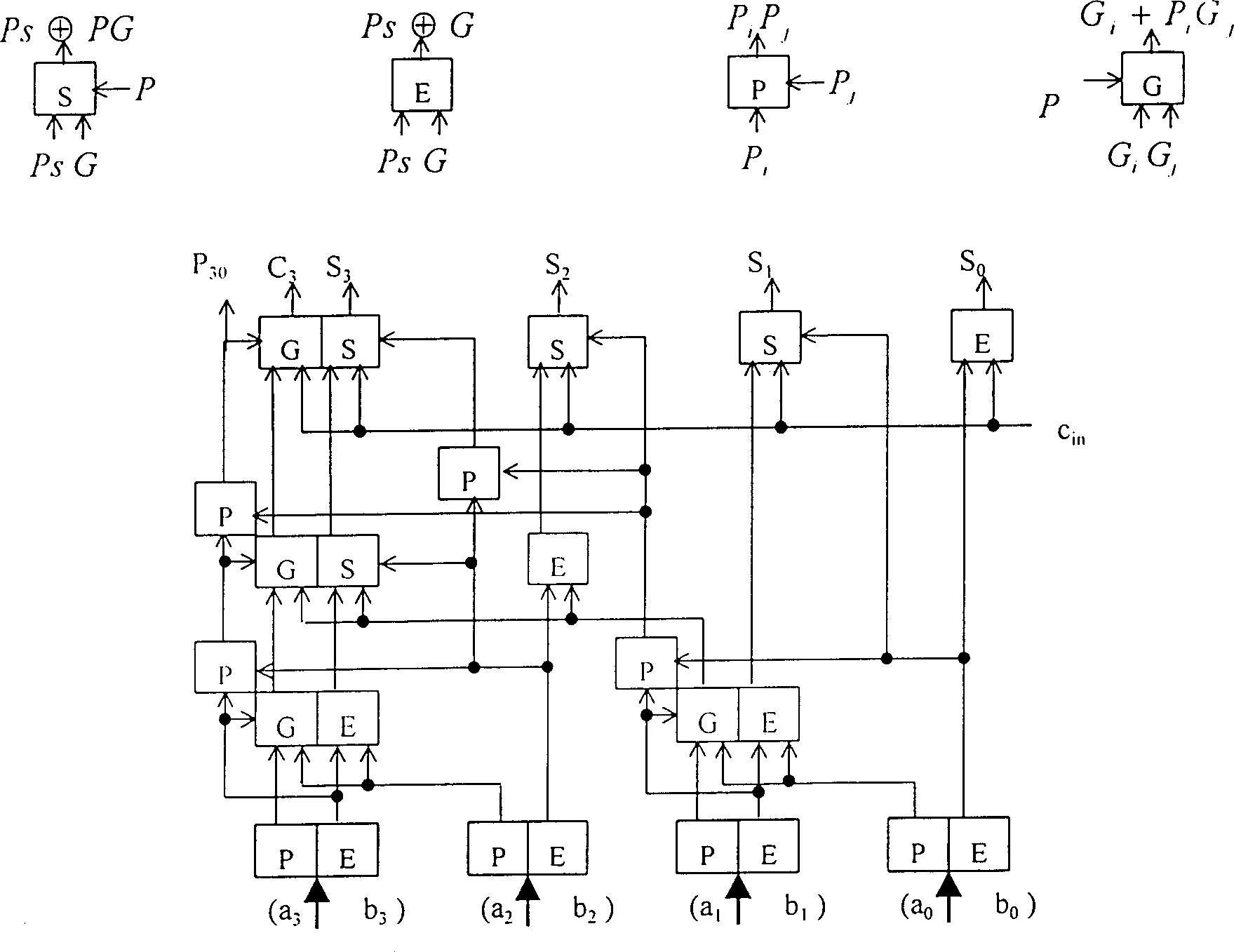
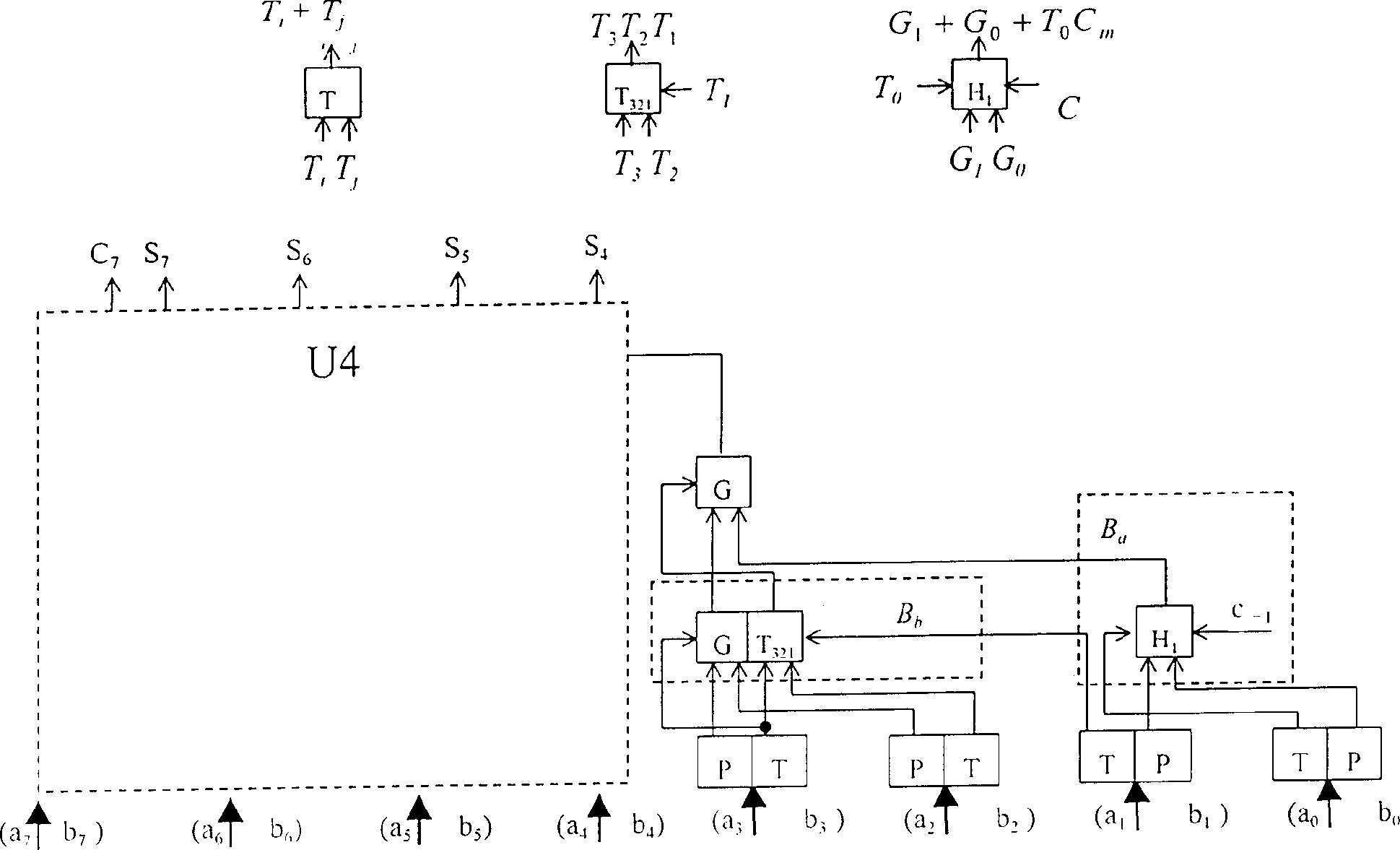
InactiveCN1360348AHigh speedReduce areaDigital data processing detailsSolid-state devices16-bitCritical path delay
The invention relates to a circuit of digital adder in binary. The carry skipping algorithm is used between grups and the ELM tree type adding structure is used inside group in the circuit. Adopting new carry combination structure makes the initial carry embed into the carry chain so as to realize transferring parallel carry within group. The relationship between the delay of key path and number of bits within group is logarithmic. The invented circuit structure has advantages of the adder produced with small area and quick speed, simple connecting wire, easy to be integrated. The invention can implement binary add operation in 32 bits and 16 bits effectively.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Approximate calculation-based polarization code belief propagation decoding method and decoder
ActiveCN108449091AReduce consumptionLimit decoding throughputError correction/detection using linear codesApproximate computingBelief propagation
The invention discloses an approximate calculation-based polarization code belief propagation decoding method and decoder. Approximate optimization treatment is executed for two types of decoding nodes in the conventional polarization code belief propagation decoder, thus, for the first type of node which realizes absolute value comparison operation of input data, when comparing input data absolute value size, only front section bits of the input data are compared, and bits of the back is ignored; and for the second type of node which realizes additive operation for the input data, a full adder and a full subtractor simultaneously perform operation for the absolute value of the input data, and a control number is generated according to an absolute value comparison result for performing screening, and a plus one unit in the operation only acts on the bits of the back part of the input data. According to the method and the decoder provided by the invention, key path delay and hardware consumption of the whole decoder are reduced by means of the approximate calculation. A simulation result shows that the method and the decoder provided by the invention can effectively reduce hardwareconsumption of the decoder and improve decoding efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
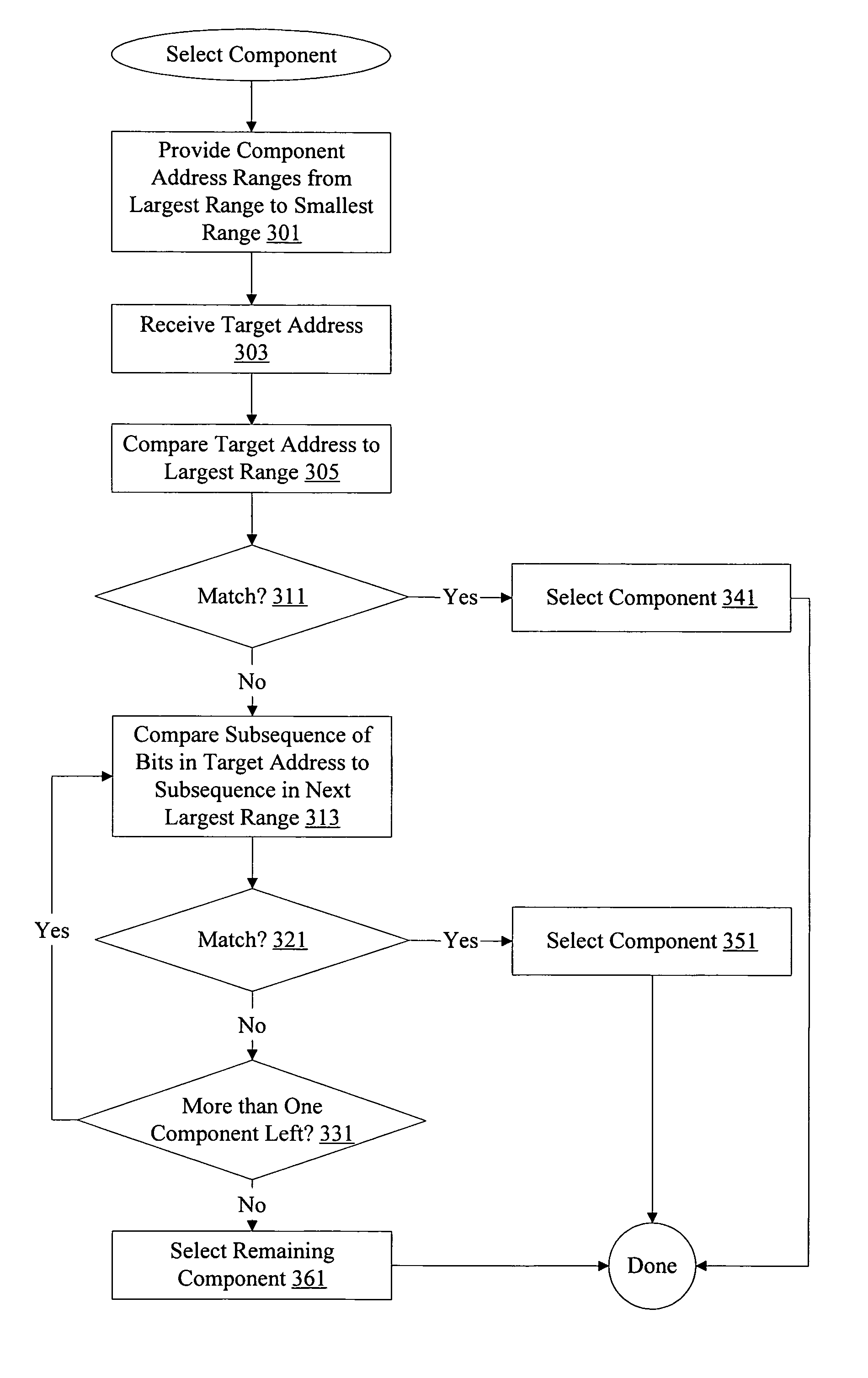
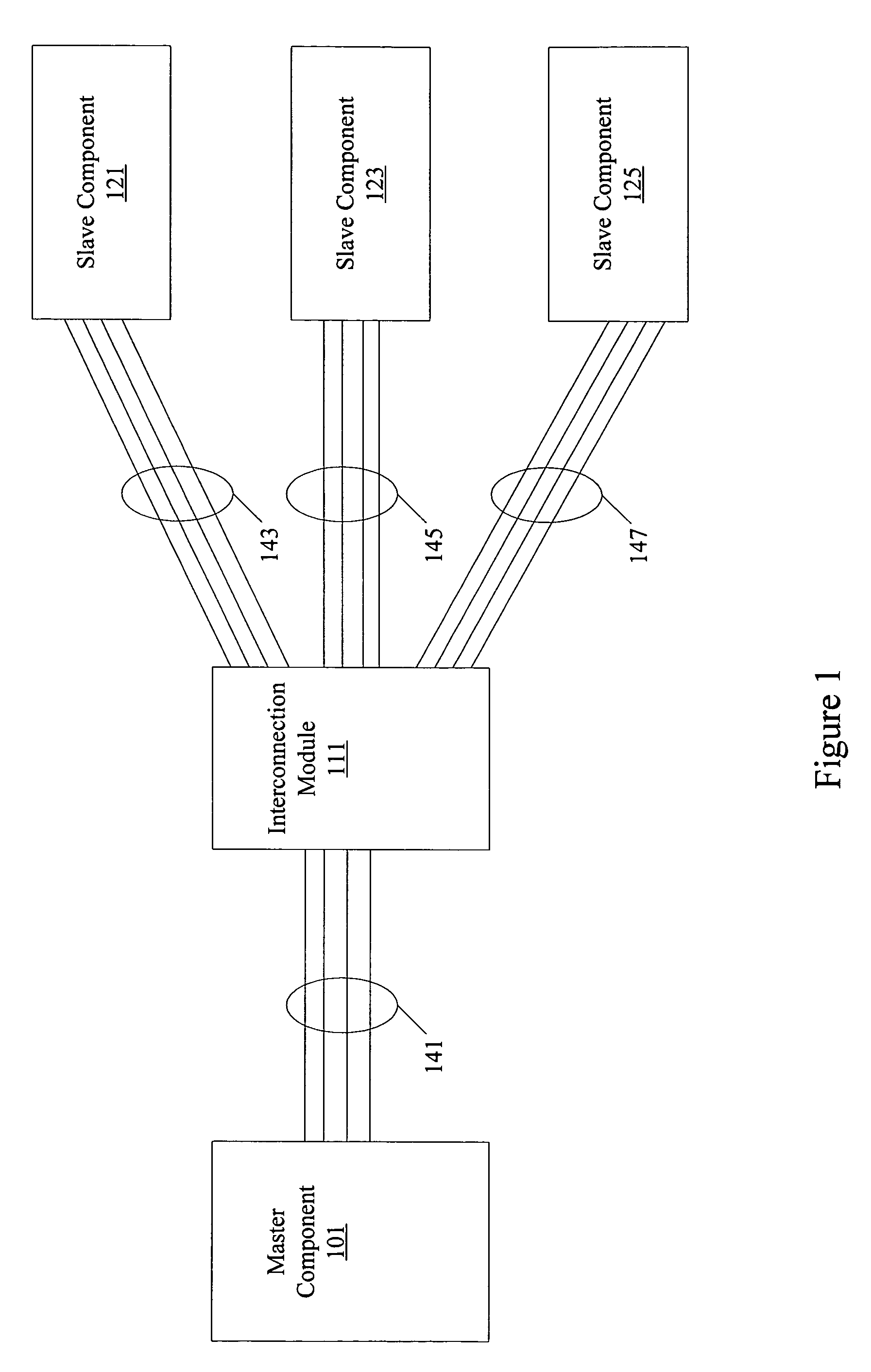
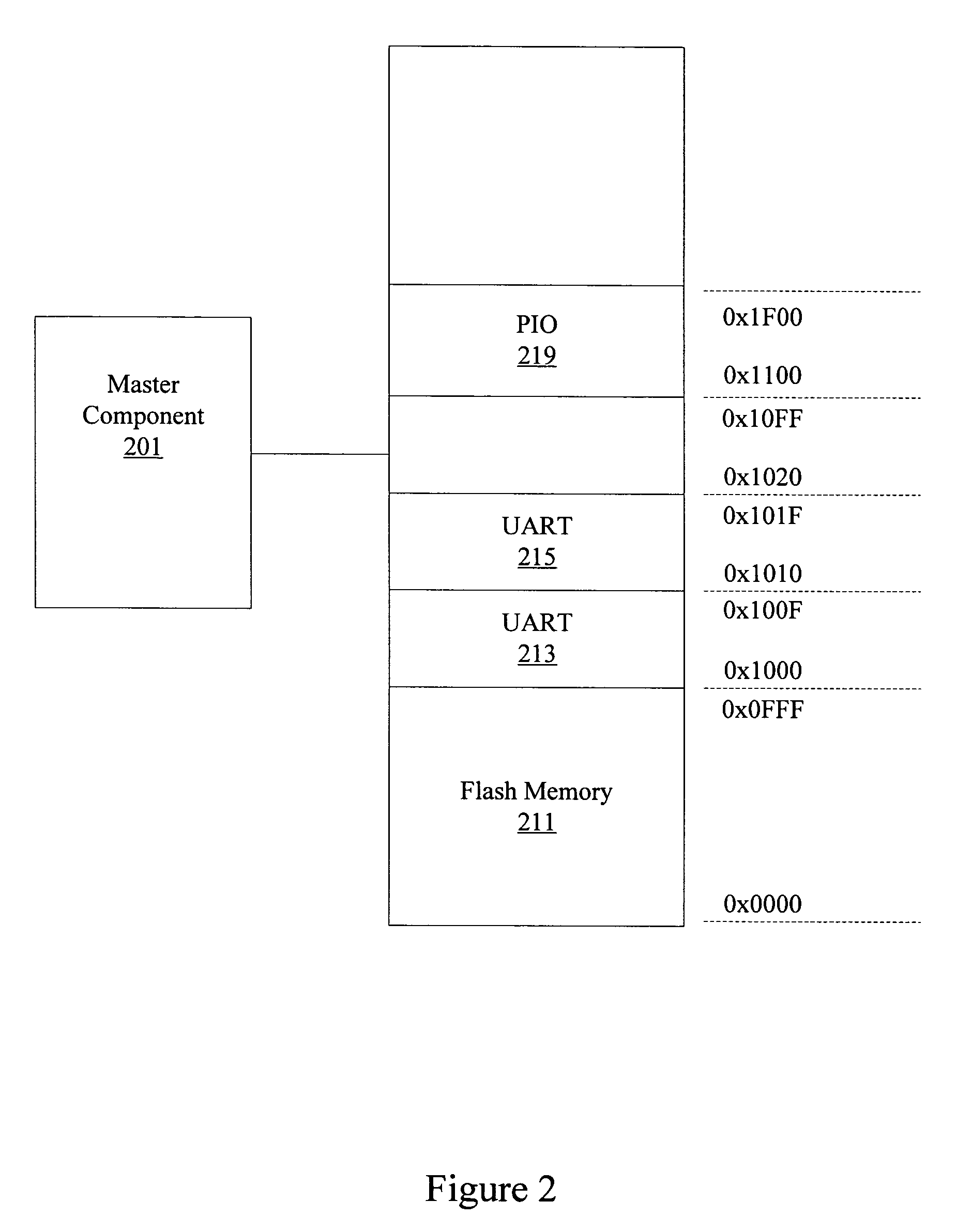
System memory map decoder logic
InactiveUS7809861B1Reduce degradationResource reducedInput/output processes for data processingData conversionComputer architectureMemory map
Methods and apparatus are provided optimizing system memory map decoder logic. A system is configured with multiple master and slave components. Using information known about the system configuration, optimized decoder logic can be configured. Critical path delay and system resource usage are reduced by optimizing decoder logic.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
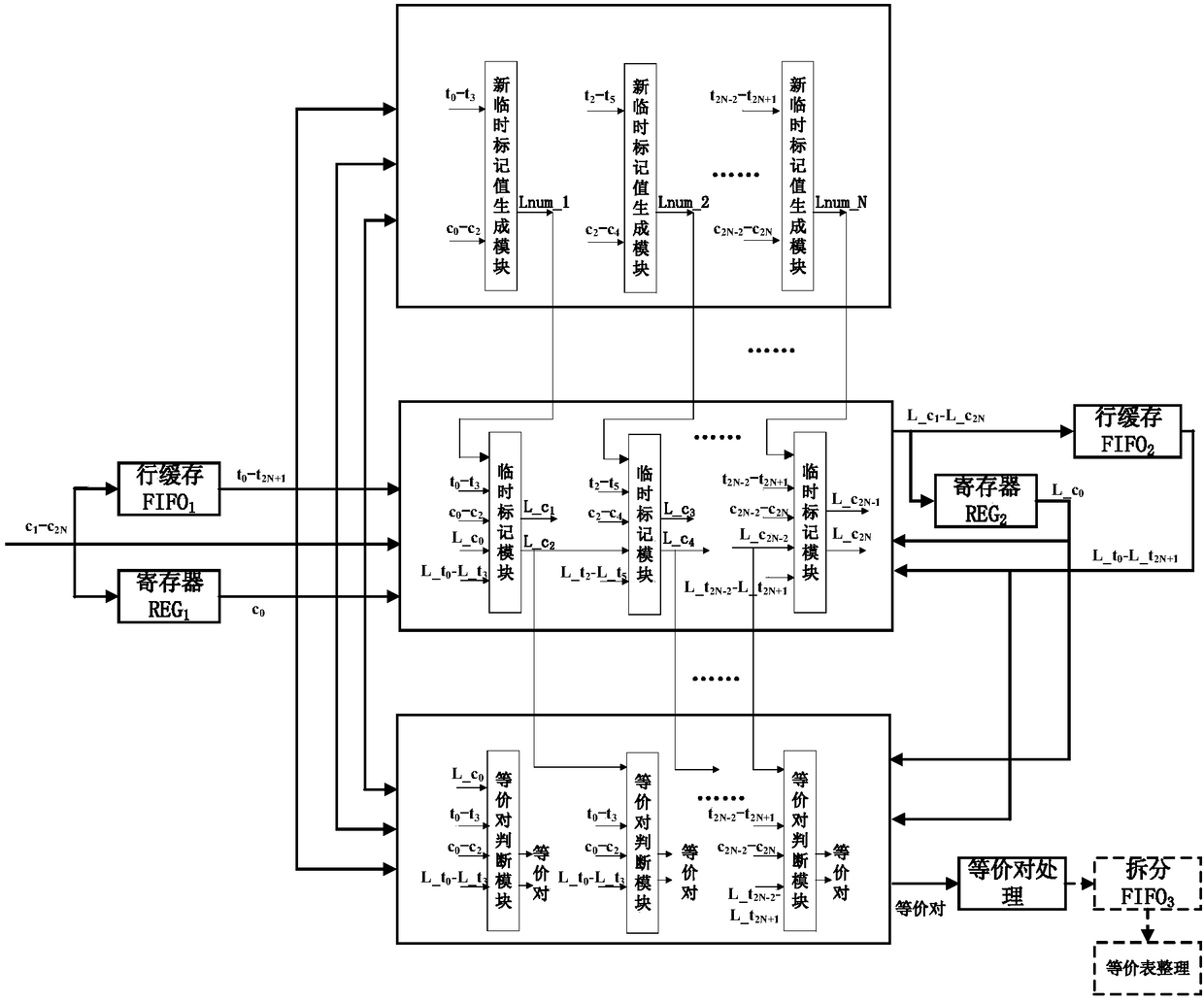
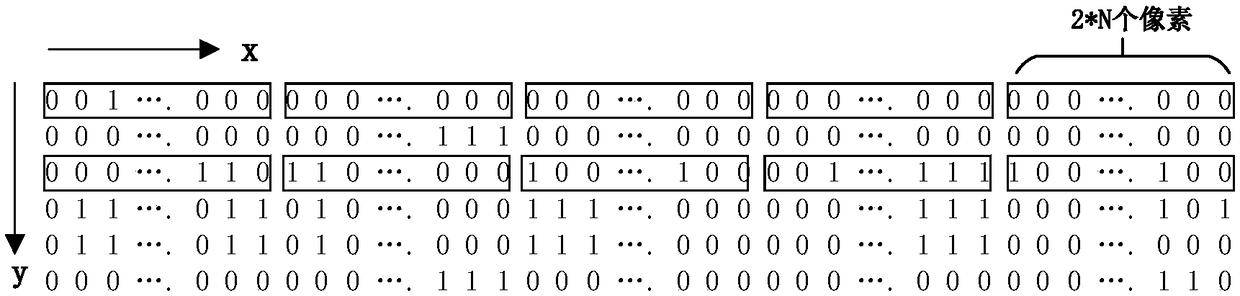
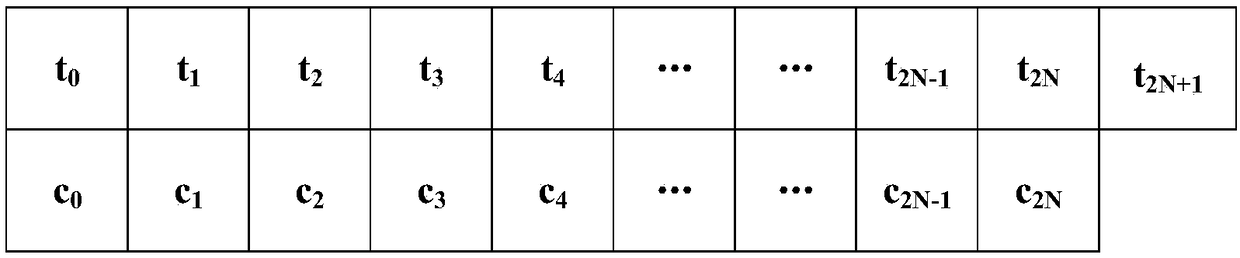
Multi-pixel parallel marking method and multi-pixel parallel marking system for marking binary images
ActiveCN108062759ALower latencySolve the problem of cascading multi-stage addersImage enhancementImage analysisPass rateComputer science
The invention discloses a multi-pixel parallel marking method and a multi-pixel parallel marking system for marking binary images. The system comprises a data module, a new temporary mark value generation module, a temporary marking module and an equivalent pair judgment module, wherein the data module is used for arranging images line by line by taking horizontally adjacent 2*N pixels as one unitpixel; one unit pixel includes horizontally adjacent N groups of pixels; the new temporary mark value generation module is used for generating new temporary mark values for all groups of pixels in parallel according to the N groups of pixels and the adjacent marked pixels thereof; the temporary marking module is used for assigning temporary mark values to the N groups of pixels in parallel according to the pixel values of the N groups of pixels and the adjacent pixels thereof; if the current group of pixels are not communicated with the adjacent marked pixels thereof, the new temporary mark value is assigned to the current group of pixels, and otherwise, the temporary mark value of the adjacent marked pixels is assigned to the current group of pixels; the equivalent pair judgment module is used for judging whether the two pixels with different temporary mark values are communicated with each other or not, and if so, the two temporary mark values form an equivalent pair. The method andthe system reduce the delay of a critical path, and are high in data passing rate and short in time consumption.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Semiconductor device
InactiveCN101086514ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementStatic storageDevice materialCritical path method
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
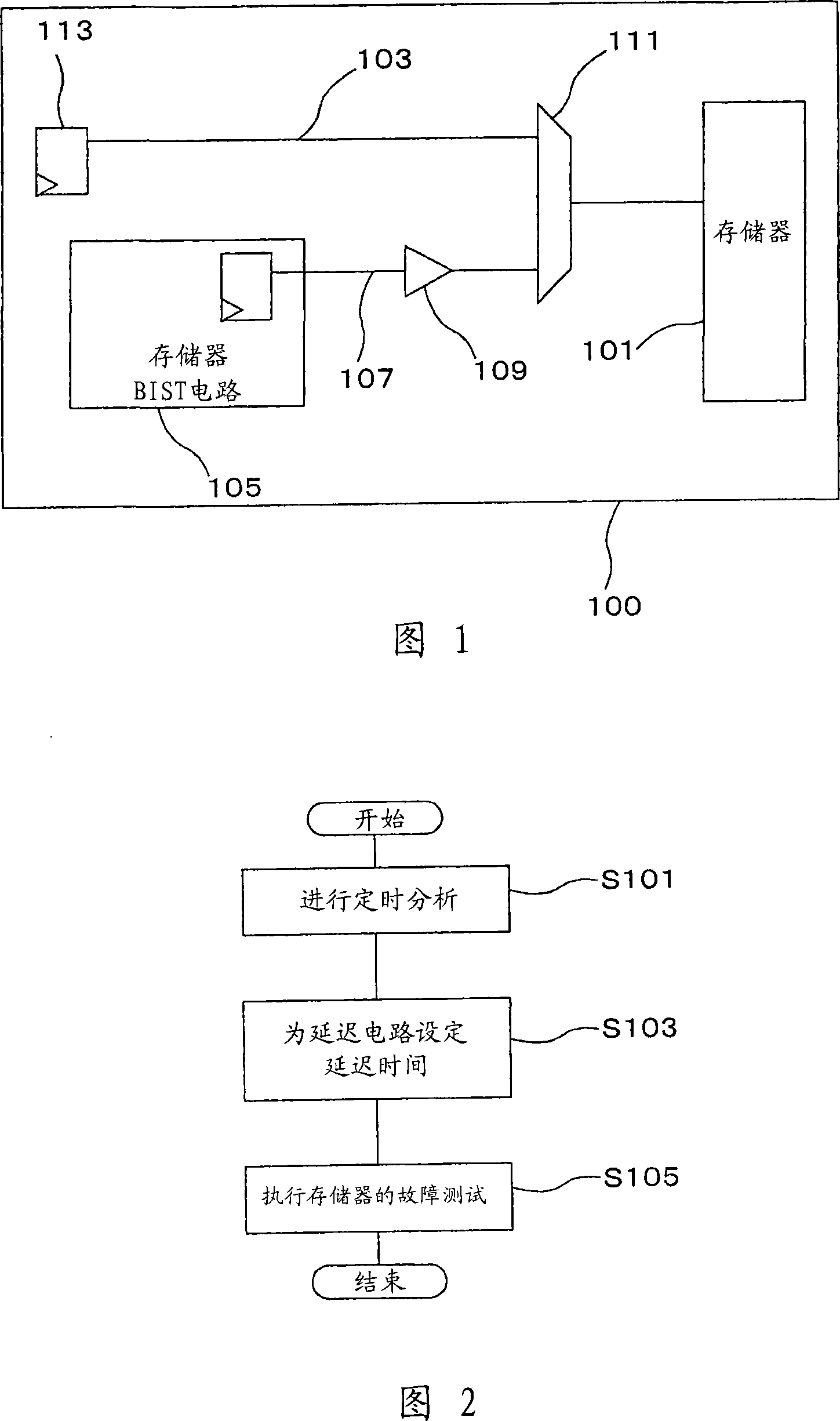
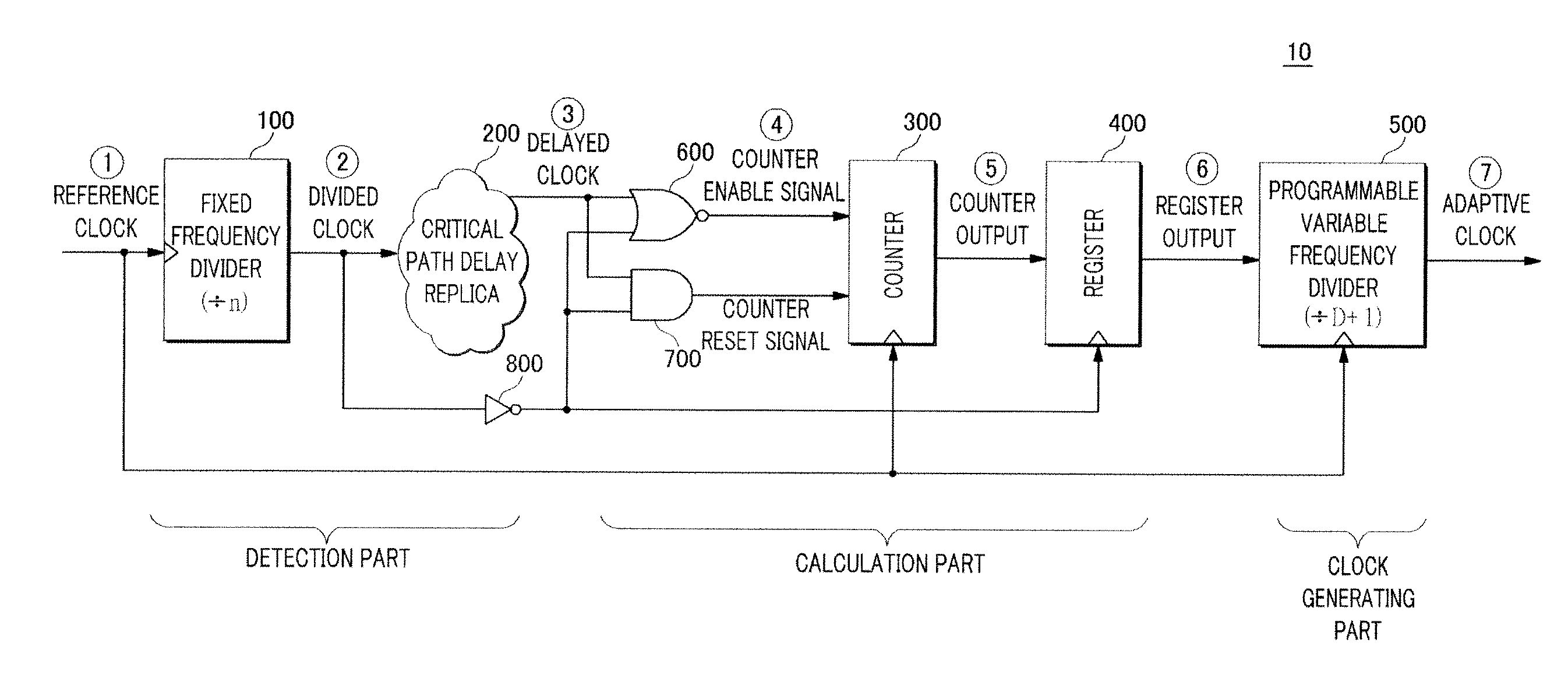
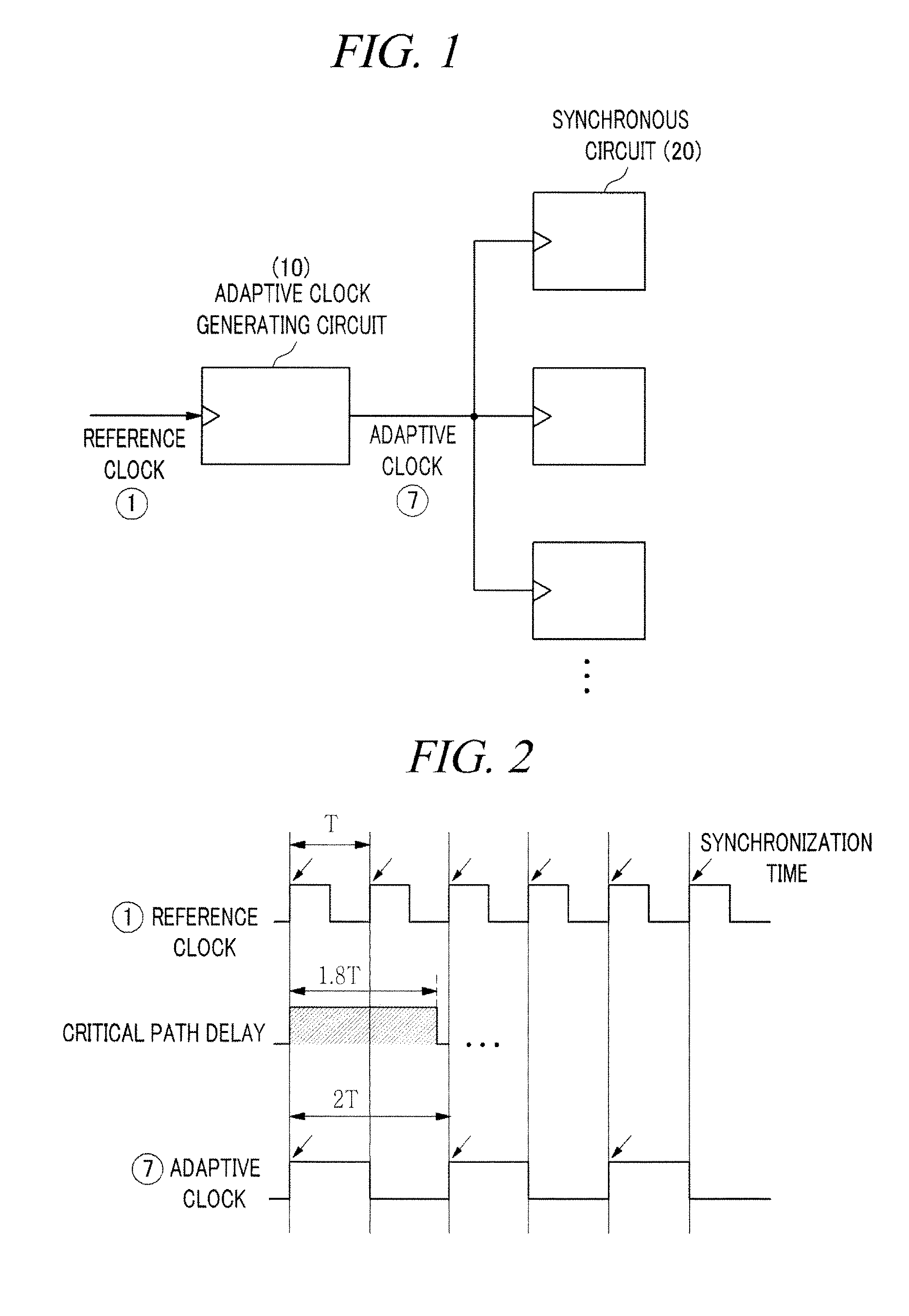
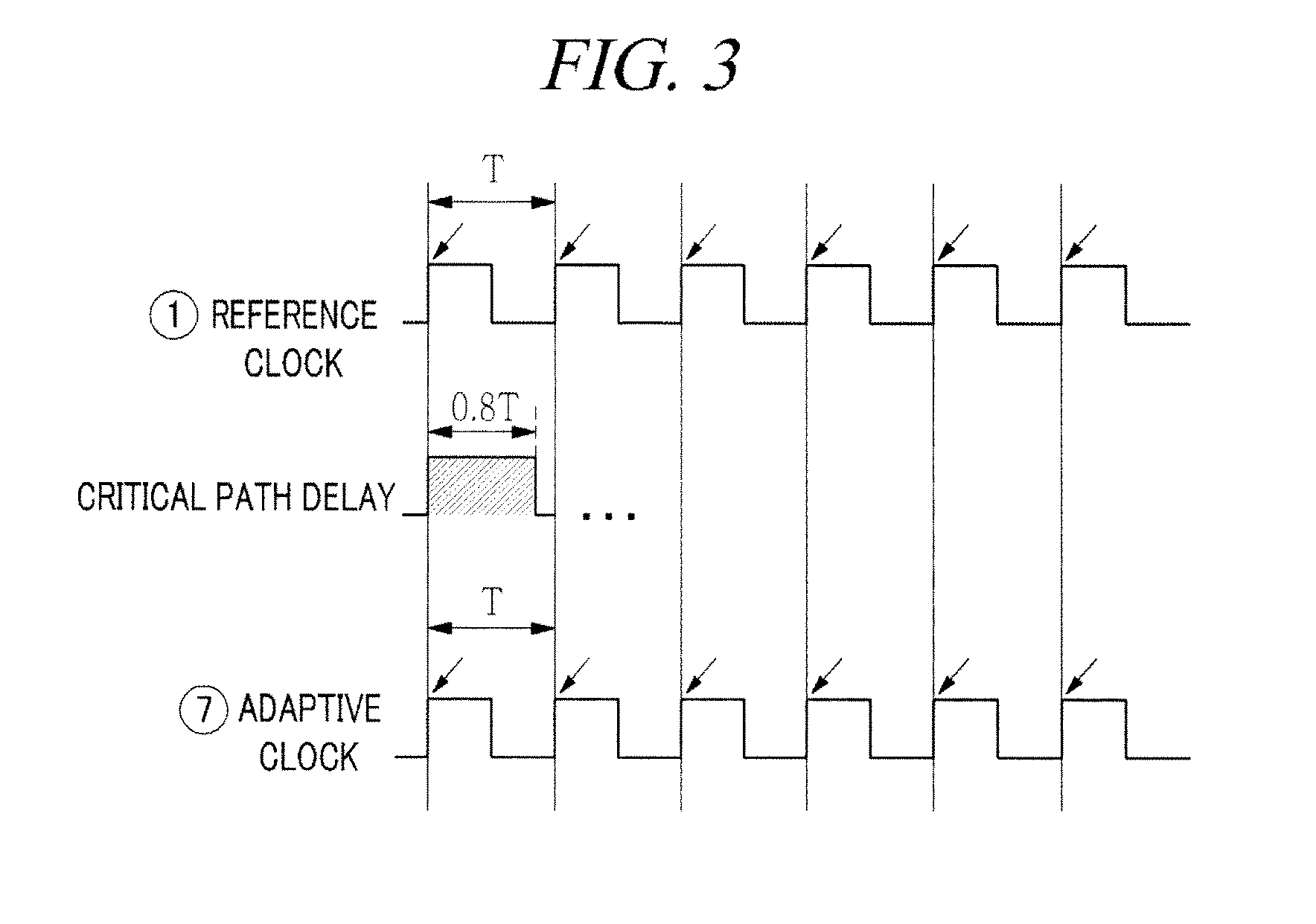
Adaptive clock generating apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS20130222018A1Avoid mistakesMinimize energy consumptionPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsSelf adaptiveComputer science
An adaptive clock generating apparatus is provided. The apparatus includes a fixed frequency divider, a replica, a counter, a variable frequency divider. The adaptive clock generating apparatus generates a clock whose period varies along with changes in the critical path delay of a synchronous circuit.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
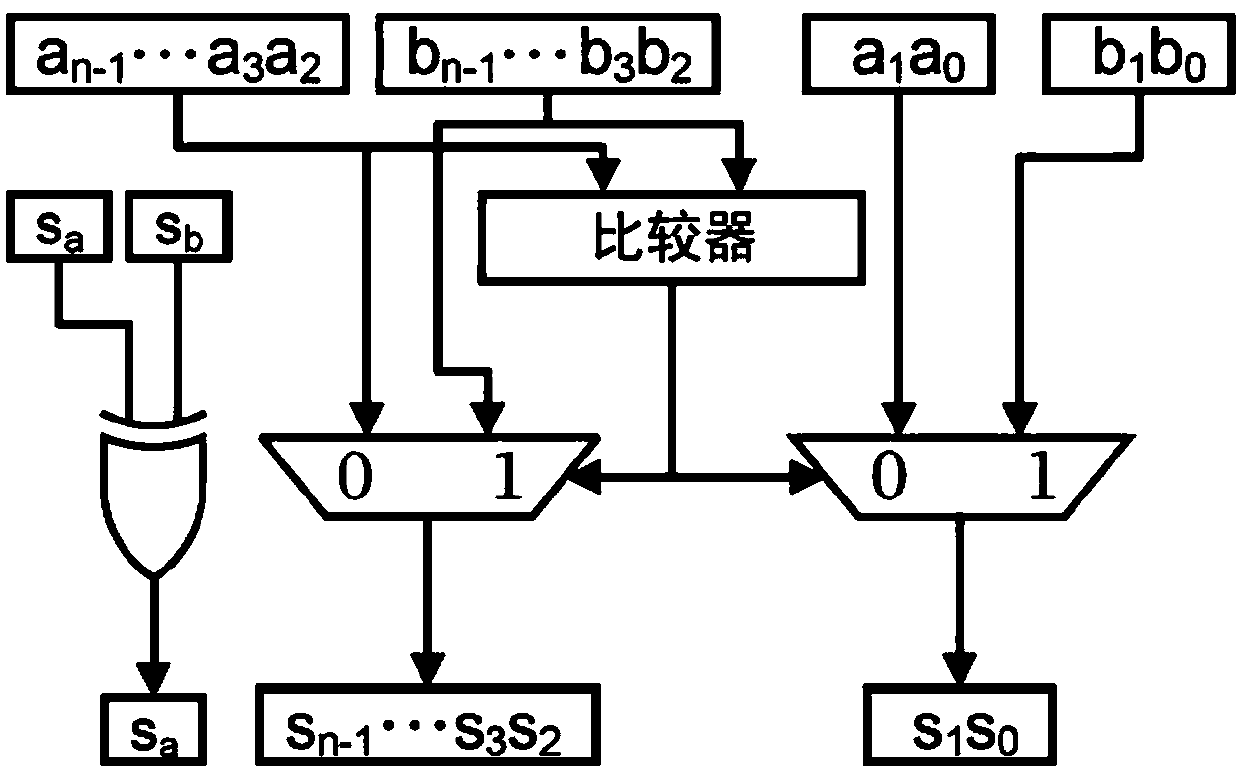
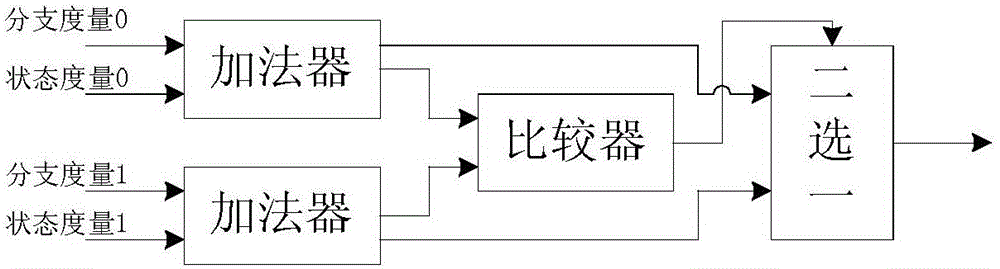
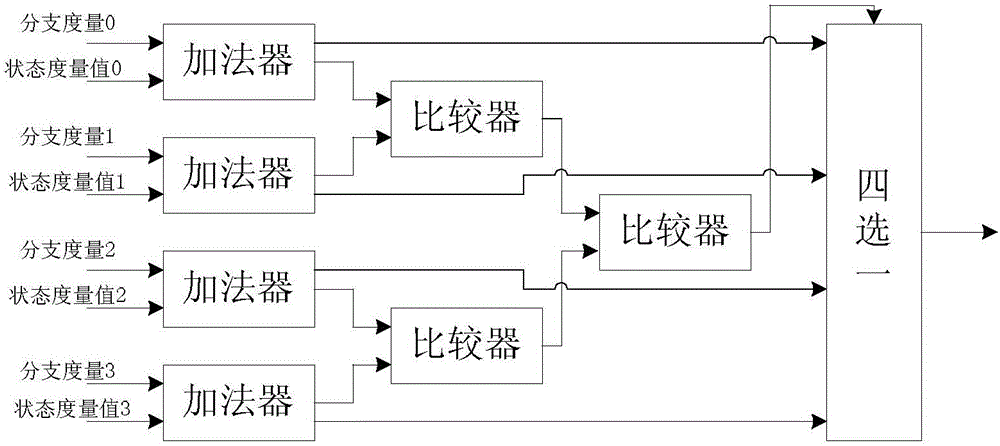
Addition comparison selection calculation method and addition comparison selection calculation device in radix-4 algorithm
ActiveCN105162474ALower latencyIncrease decoding rateError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesComputer scienceCalculation methods
The invention discloses an addition comparison selection calculation method in a radix-4 algorithm. The addition comparison selection calculation method comprises the following steps: adding a branch measurement value to a corresponding state measurement value to obtain four temporary state measurement values; pairwise comparing the four temporary state measurement values, and simultaneously, respectively subtracting a certain state measurement value at a previous time from the four temporary state measurement values so as to obtain statute operated state measurement values; and selecting the maximal / minimal value in the four statute operated state measurement values as new state measurement values according to a comparison result. The invention further discloses an addition comparison selection calculation device in the radix-4 algorithm. According to the invention, the critical path delay of a decoding unit can be reduced; the decoding rate can be increased; and thus, the decoding performance of the whole system can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING SMART LOGIC TECH CO LTD
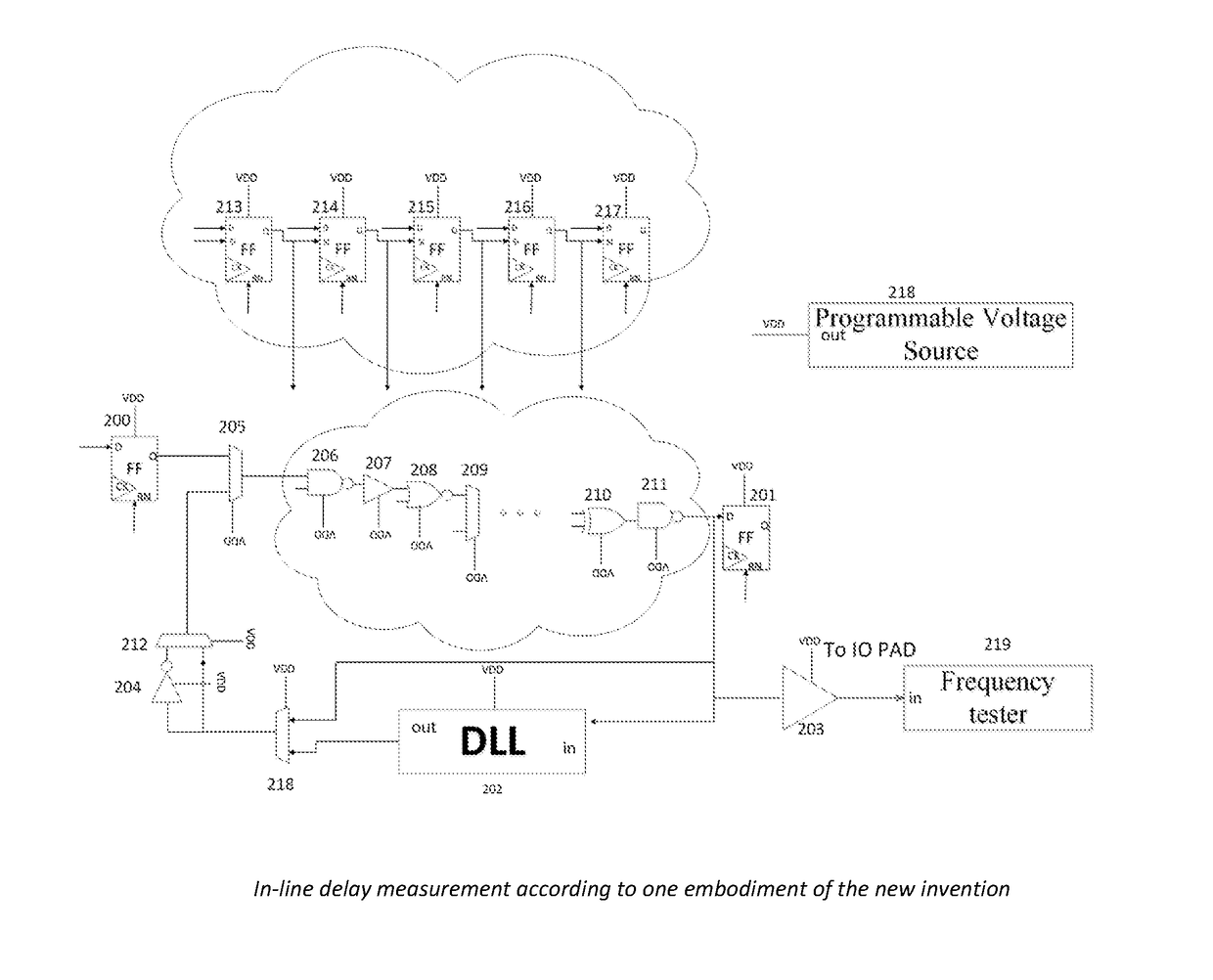
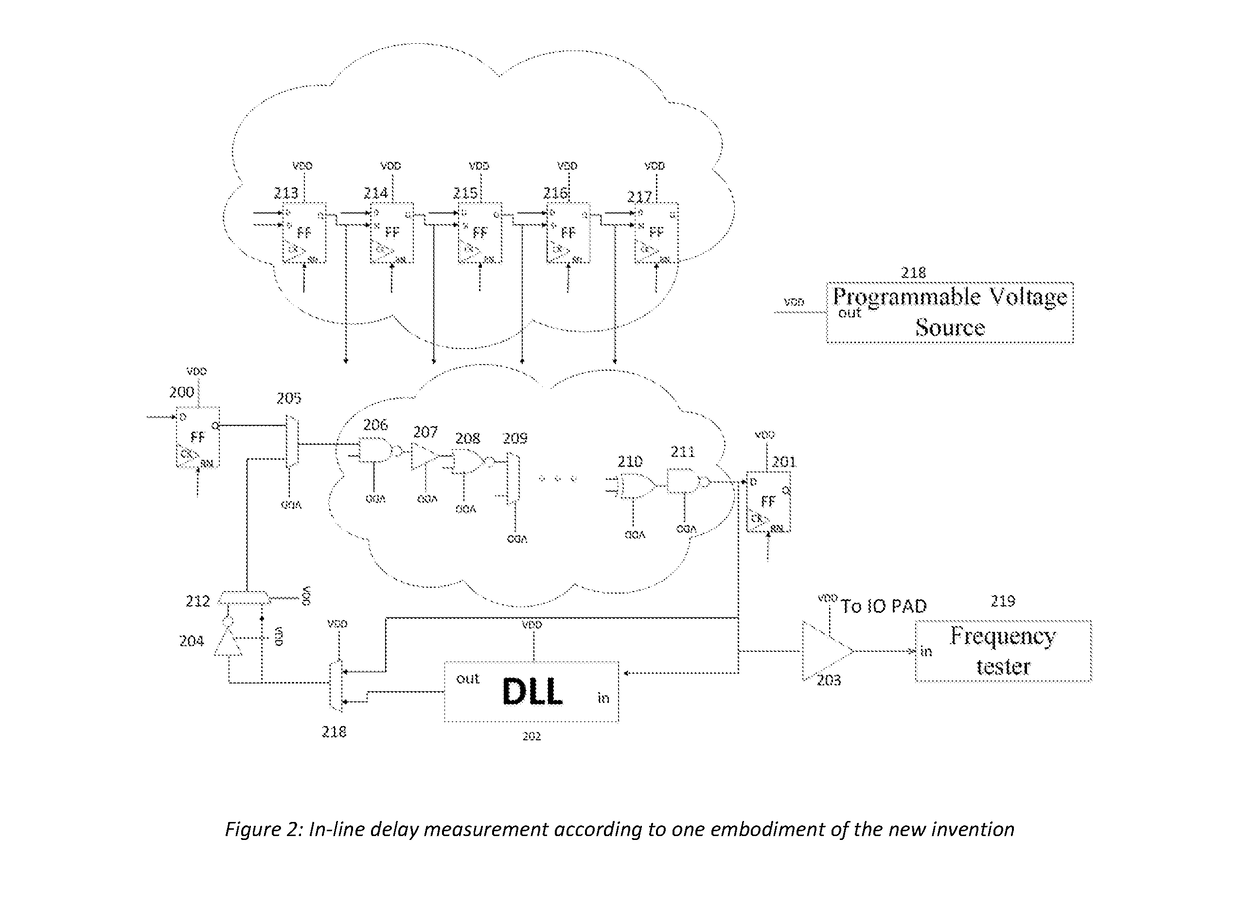
In line critical path delay measurement for accurate timing indication for a first fail mechanism
ActiveUS9882564B1Easy to useImprove powerPower consumption reductionDelay line applicationsLogic cellCritical path method
A method for implementing a programmable critical delay path measurement in-line with the critical path logic cells. Additionally, the delay measurement creates a code to be used with a programmable DLL which indicates the delay of the measured critical path. This code can also be used by an off line First Fail Circuit which can mimic the delay of the critical path and give an indication of the critical path delay. The target of this invention is to create a method to optimize the required operating voltage of an integrated circuit per specific speed requirement, overcoming different process variations, temperatures changes and in die variations.
Owner:NXP ISRAEL LTD
Reconfigurable LT code decoding system and decoding method
InactiveCN106850133ALower latencyDegree value decreasedError preventionOther decoding techniquesTheoretical computer scienceCoding decoding
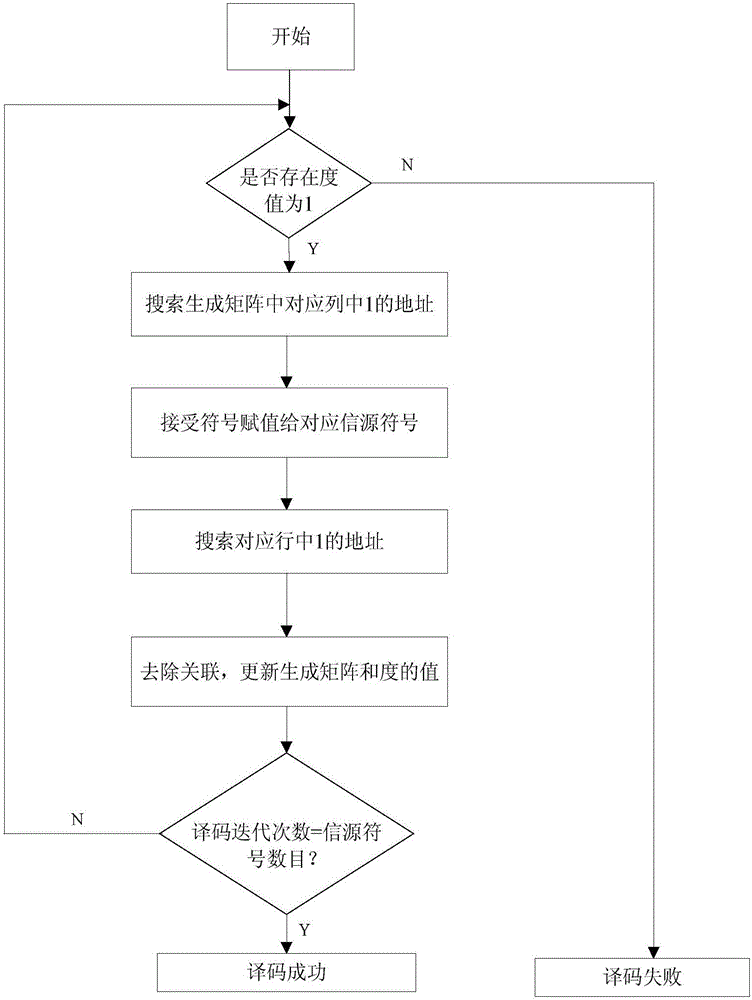
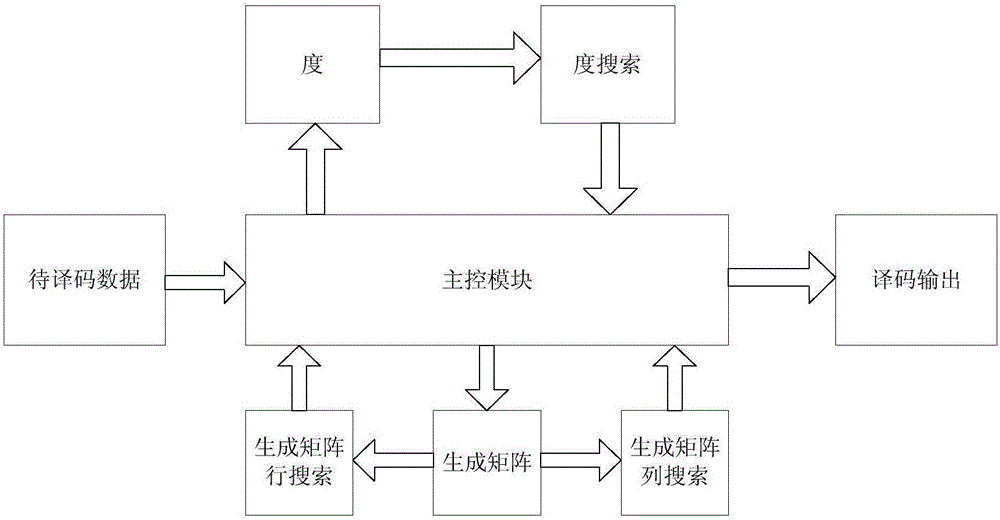
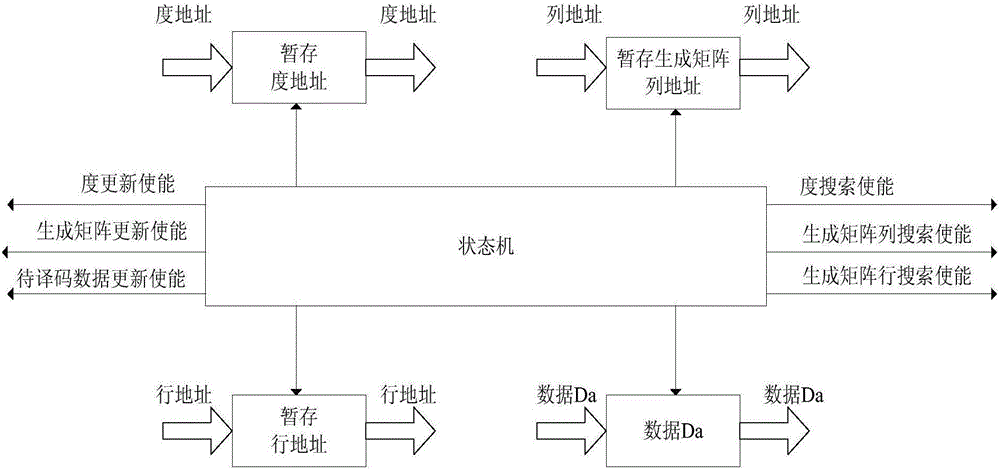
The invention discloses a reconfigurable LT code decoding system, comprising a main control module, a degree module, a degree searching module, a to-be-decoded data module, a generated matrix module, a generated matrix column searching module, a generated matrix row searching module and a decoding output module. The invention further discloses a reconfigurable LT code decoding method, comprising searching for data with a degree value being 1 at first, then searching for a corresponding column of a generated matrix, decoding the data with a degree value being 1, then searching for a corresponding row in the generated matrix and updating the same, and reducing a corresponding degree value. The decoding is finished by repeatedly executing the processes, critical path delay is effectively reduced, a decoding speed of an integral LT code is convenient to choose, and better flexibility is realized in the aspects of hardware realizing complexity and a decoding speed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
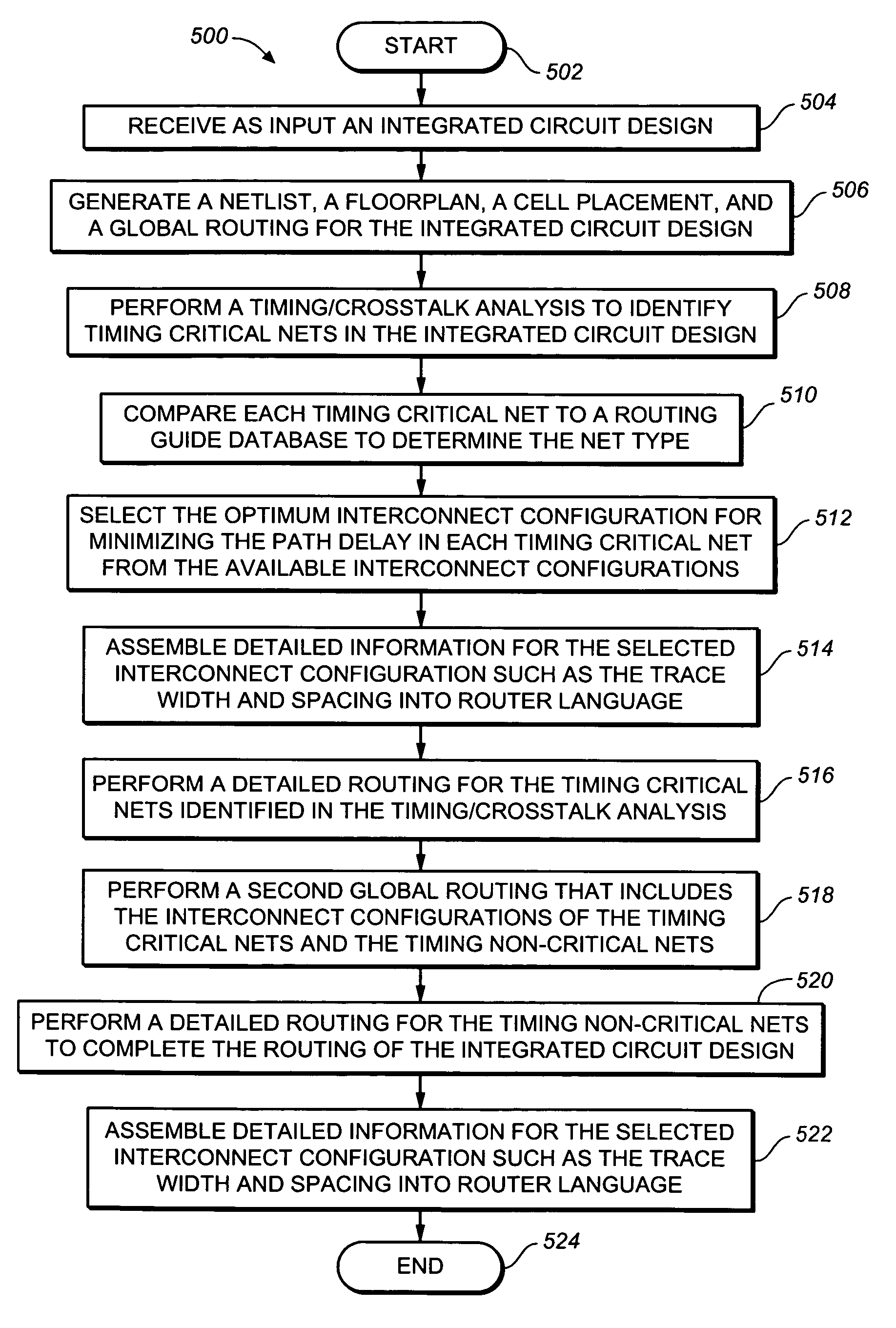
Method of optimizing critical path delay in an integrated circuit design
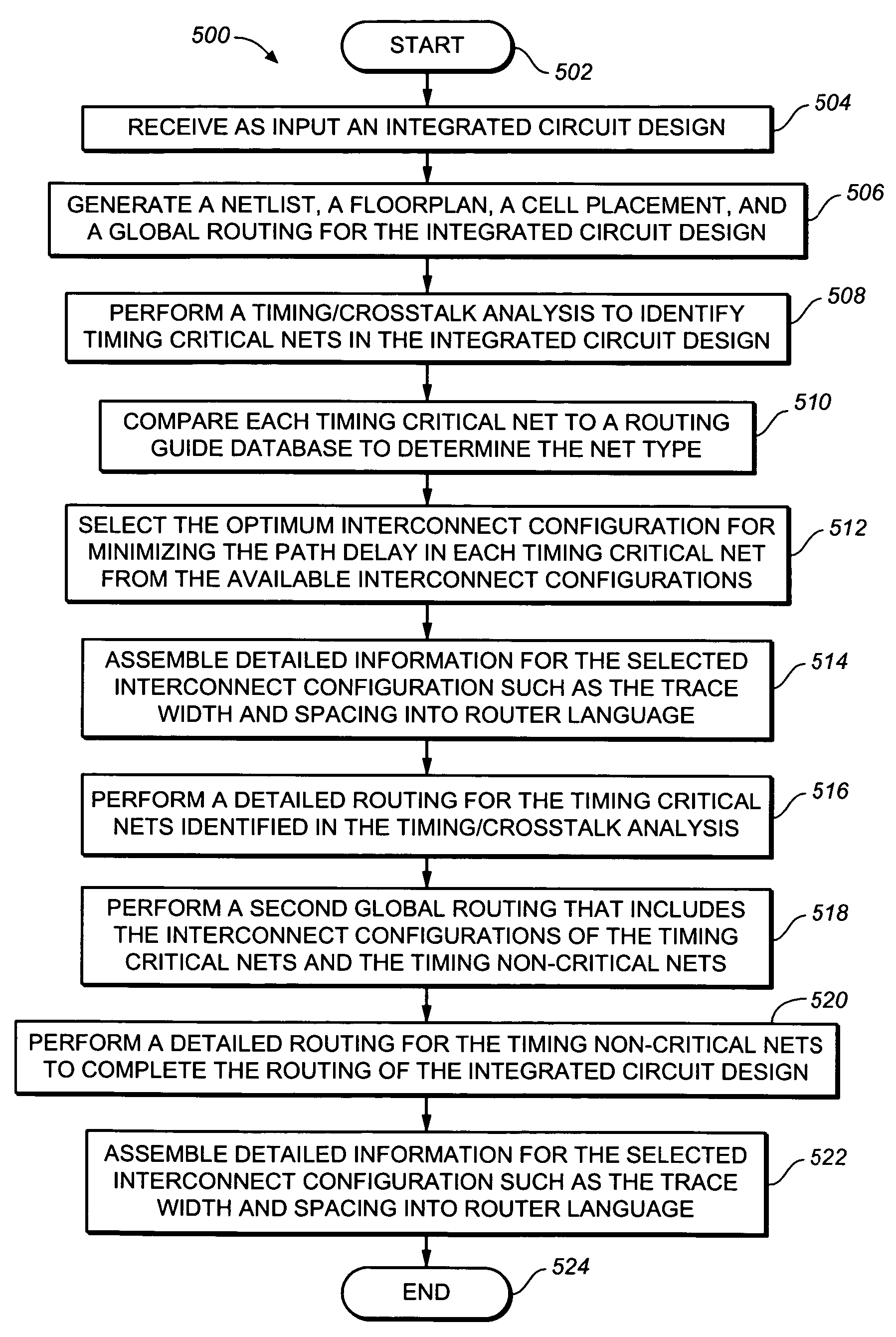
ActiveUS7181712B2Minimize delayComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCircuit designCrosstalk
A method and computer program product for optimizing critical path delay in an integrated circuit design include steps of: (a) receiving as input an integrated circuit design; (b) performing a timing / crosstalk analysis to identify each timing critical net in the integrated circuit design; (c) selecting an optimum interconnect configuration for minimizing path delay in each timing critical net; (e) performing a detailed routing that includes the selected optimum interconnect configuration for each timing critical net; and (f) generating as output the detailed routing.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Method for hierarchically identifying circuit gate based on workload
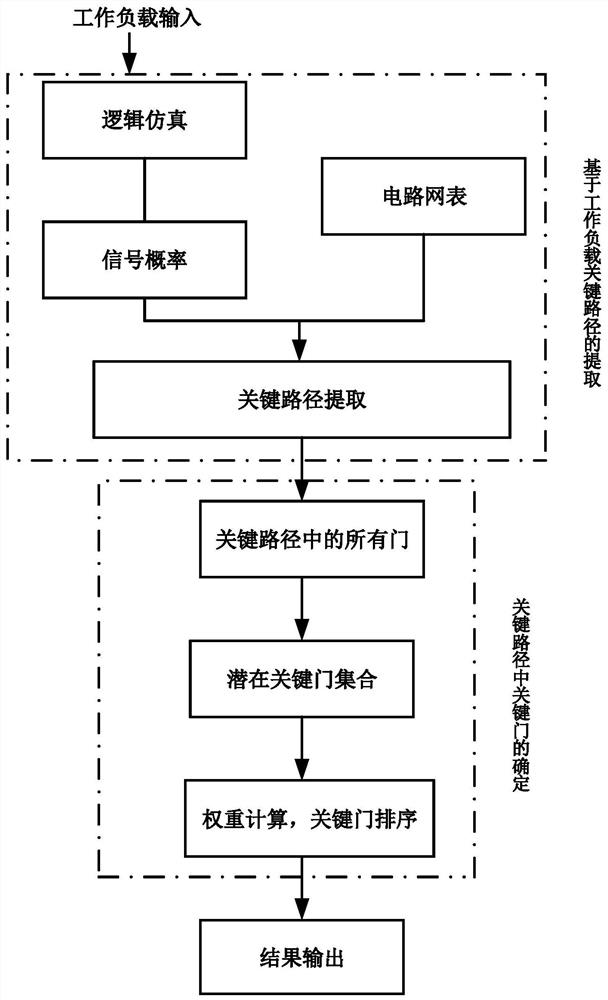
PendingCN111651946AAccurate and effective extractionAvoid duplicationConstraint-based CADCAD circuit designBatch processingHemt circuits
The invention discloses a method for hierarchically identifying a circuit gate based on a workload, and belongs to the field of high reliability of high-performance processors. The method comprises: obtaining a workload signal, and, in a signal probability extracting stage, reading a circuit net list and design constraints, obtaining path delay of a circuit, and obtaining a potential critical path. The method comprises the signal probability extracting stage, a parameter analysis and calculation stage and a hierarchical identification gate determination stage. The parameter analysis and calculation stage is used for calculating the maximum critical path delay which can be borne by the circuit path and is obtained by aging delay degradation under the effect of the NBTI; and the hierarchicalidentification gate determination stage, which is used for determining a gate with relatively high aging sensitivity in the critical path, and proposing a new weight calculation method, and sorting the determined circuit gates according to the weights so as to perform hierarchical batch processing on the gate circuit. The method can be integrated in the ASIC design process, the aging critical path and the aging critical door can be effectively identified, the complexity of replacing the door in the critical path in a traditional method is reduced, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-performance approximate full adder gate-level unit
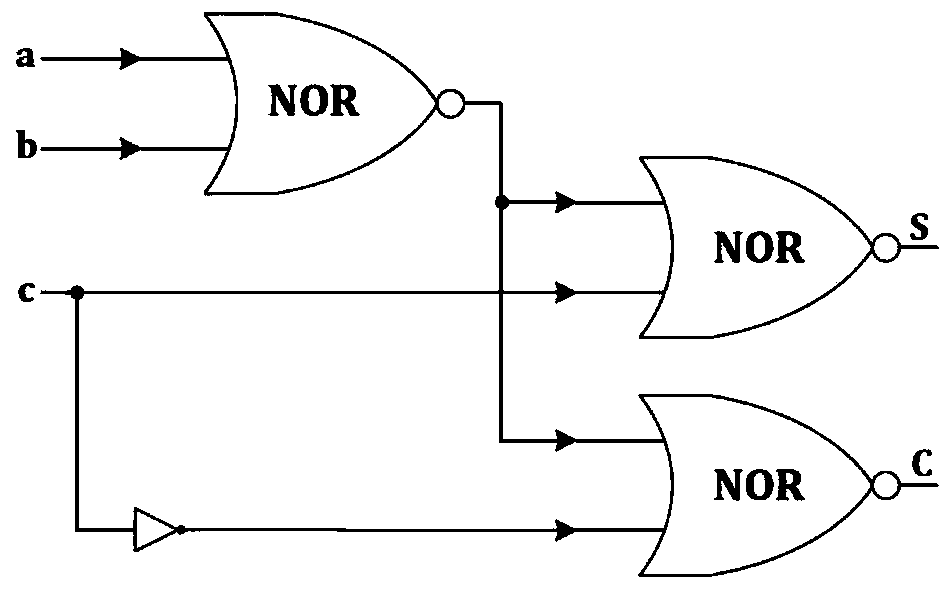
ActiveCN111313890ASmall footprintReduce in quantityPower reduction in field effect transistorsExclusive-OR circuitsCircuit complexityNOR gate
The invention discloses a high-performance approximate full adder gate-level unit, which comprises a first NOR gate, a second NOR gate, a third NOR gate and a NOT gate, the first input end of the first NOR gate is an addend input end, the second input end is an addend input end, and the output end is connected with the first input end of the second NOR gate and the first input end of the third NORgate; the second input end of the second NOR gate is a low carry input end, and the output end of the second NOR gate is the sum output end of the gate-level unit; the second input end of the secondNOR gate is further connected with the input end of the NOT gate, the output end of the NOT gate is connected with the second input end of the third NOR gate, and the output end of the third NOR gateis the high carry output end of the gate-level unit. Compared with an accurate full adder, the full adder has the advantages that the performance is improved by 50 percent in the aspect of key path delay, and the circuit complexity is reduced by 58 percent.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method of optimizing critical path delay in an integrated circuit design
ActiveUS20060090145A1Minimize delayComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCircuit designCrosstalk
A method and computer program product for optimizing critical path delay in an integrated circuit design include steps of: (a) receiving as input an integrated circuit design; (b) performing a timing / crosstalk analysis to identify each timing critical net in the integrated circuit design; (c) selecting an optimum interconnect configuration for minimizing path delay in each timing critical net; (e) performing a detailed routing that includes the selected optimum interconnect configuration for each timing critical net; and (f) generating as output the detailed routing.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Structure and circuit of logarithmic skip adder
InactiveCN1164988CHigh speedReduce areaDigital data processing detailsSolid-state devices16-bitCritical path delay
The invention relates to a circuit of digital adder in binary. The carry skipping algorithm is used between grups and the ELM tree type adding structure is used inside group in the circuit. Adopting new carry combination structure makes the initial carry embed into the carry chain so as to realize transferring parallel carry within group. The relationship between the delay of key path and number of bits within group is logarithmic. The invented circuit structure has advantages of the adder produced with small area and quick speed, simple connecting wire, easy to be integrated. The invention can implement binary add operation in 32 bits and 16 bits effectively.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com