Method for hierarchically identifying circuit gate based on workload
A work load and circuit identification technology, applied in the direction of constraint-based CAD, CAD circuit design, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem of circuit inapplicability, not considering the aging state of the circuit, etc., to improve work efficiency and avoid duplication. The effect of processing and good guiding significance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] This embodiment provides a method for hierarchically identifying circuit gates based on workload, the method including:
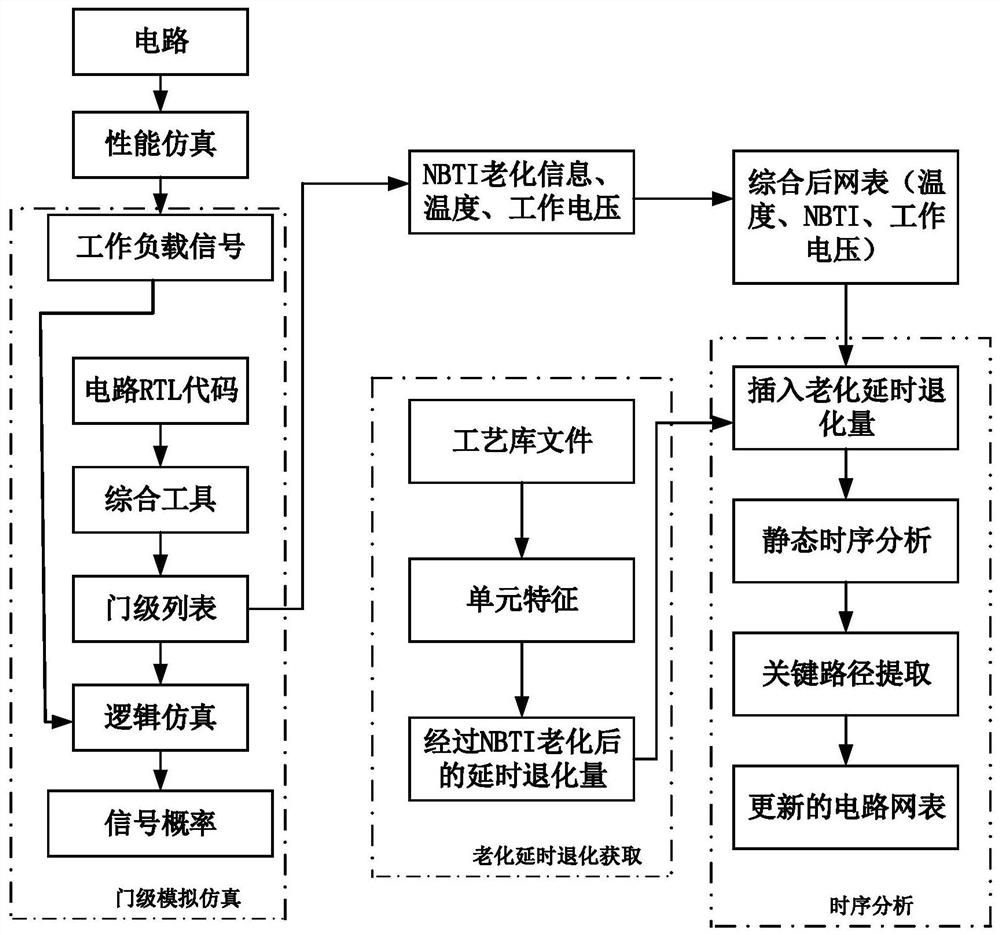
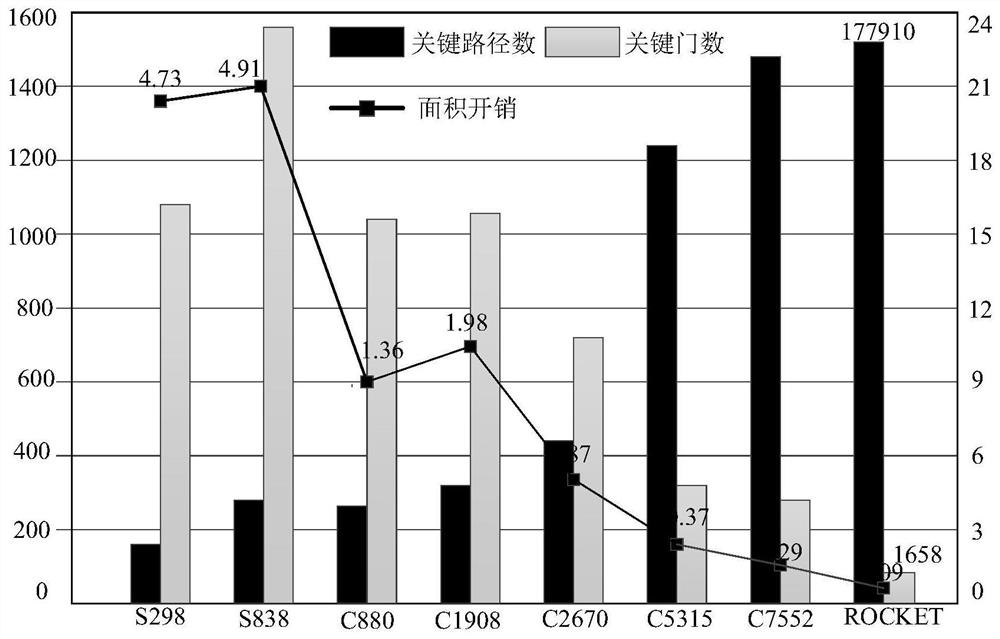
[0048] S1 performs static timing analysis according to the circuit netlist and constraint files, and obtains the original delay value set of the timing path inside the circuit, which is defined as the original delay set D p ={d p1 , d p2 ,...,d pj ,...,d pn}, where n represents the number of original paths. And sort the original delay sequence of the circuit to find out the maximum delay T of the circuit without considering the aging delay max ; The original delay value is the sum of the delays of each aging gate circuit;
[0049] S2 traverses the original delayed collection D p , if d pj ×(1+R%)>T max , then define d pj The corresponding path is a potential path considering the aging condition, which is written into the potential critical path set RCP until the original delay set D p End the traversal when it is empty; among them, R% takes...
Embodiment 2
[0061] This embodiment provides a practical application of a method for hierarchically identifying circuit gates based on workload. The method includes:
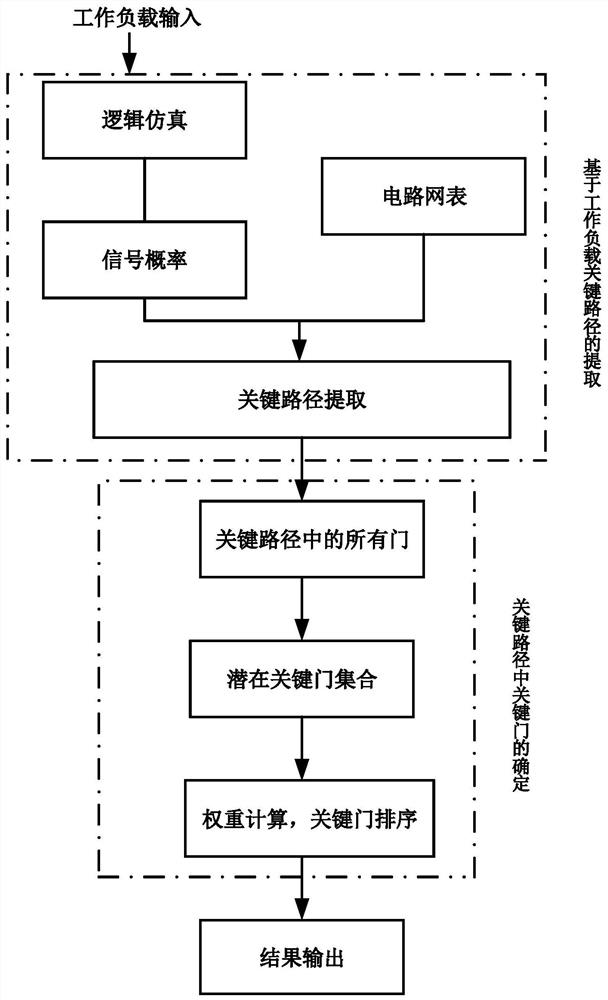
[0062] Step 1: Obtain the workload signal and extract the probability of the workload signal;
[0063] For the design of microprocessors, use a performance simulator to extract the workload; for example, use a performance simulator to extract the input patterns of the different functional blocks of the processor of the target application.
[0064] For other designs, such as ASICs, high-level (system-level) simulation vectors can be used for performance analysis. That is, profiling data containing system-level workload-related data is provided to step 2 for further processing for timing analysis.
[0065] With this approach, a link is established between system-level workload dependencies (that is, occur at runtime) and timing analysis at design time.
[0066] Step 2: The information obtained from the system-level workload ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com