Fragmented-file storage method based on distributed storage system
A distributed storage and file storage technology, which is applied in the direction of memory system, memory address/allocation/relocation, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problem of low efficiency of fragmented file processing, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency and improving utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
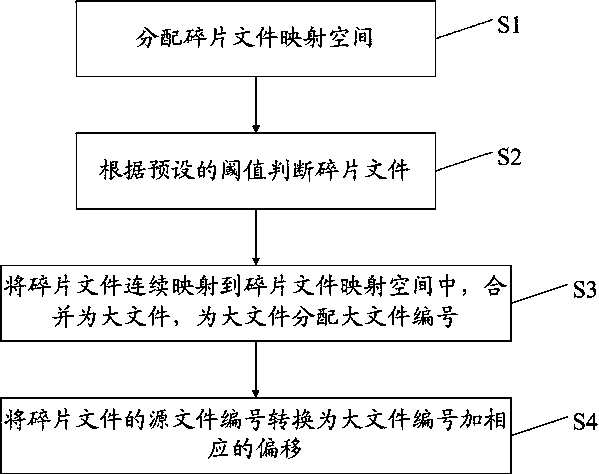
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for storing fragmented files based on a distributed storage system, comprising the following steps:
[0040] Step S1, allocate a fragmented file mapping space in the memory of the storage node, and the fragmented file mapping space is continuous.
[0041] Step S2, in the storage node, judge several source files according to the preset threshold value, if the size of a certain source file is smaller than the threshold value, then the source file is a fragment file, and obtain several fragment files after judgment; wherein, each Each source file is preset with a corresponding source file number.
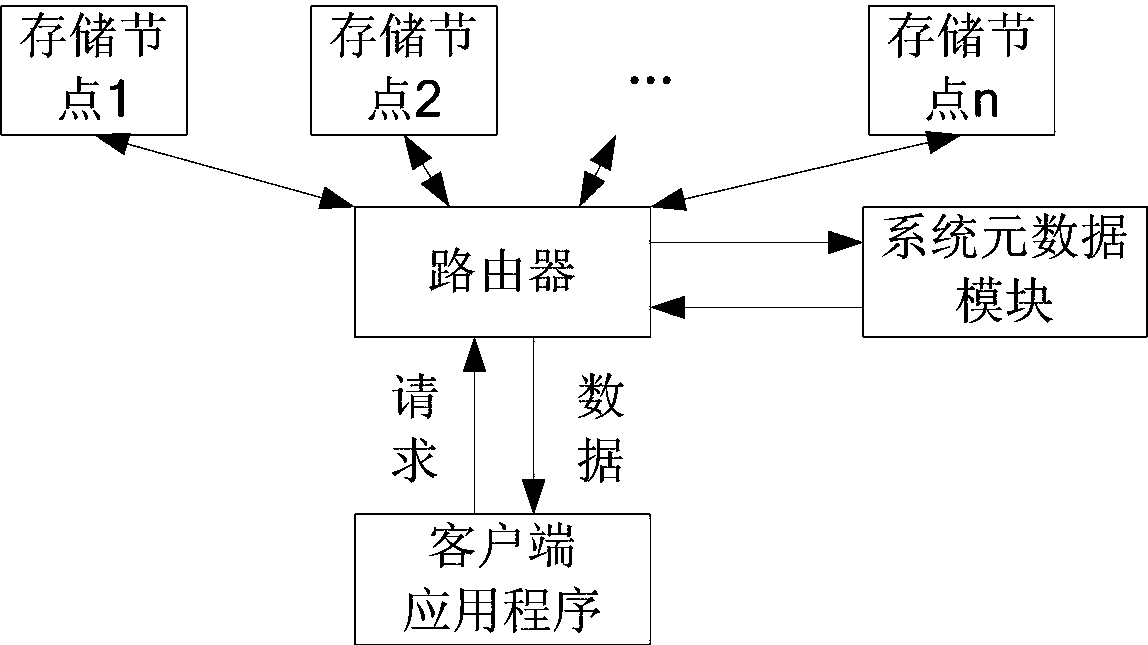
[0042] Wherein, the source file refers to the file uploaded by the client application program to the storage node through the router. The source file number is assigned by the router when the source file is uploaded by the router. A request table is set in the router, and the request table is used to record th...
Embodiment 2
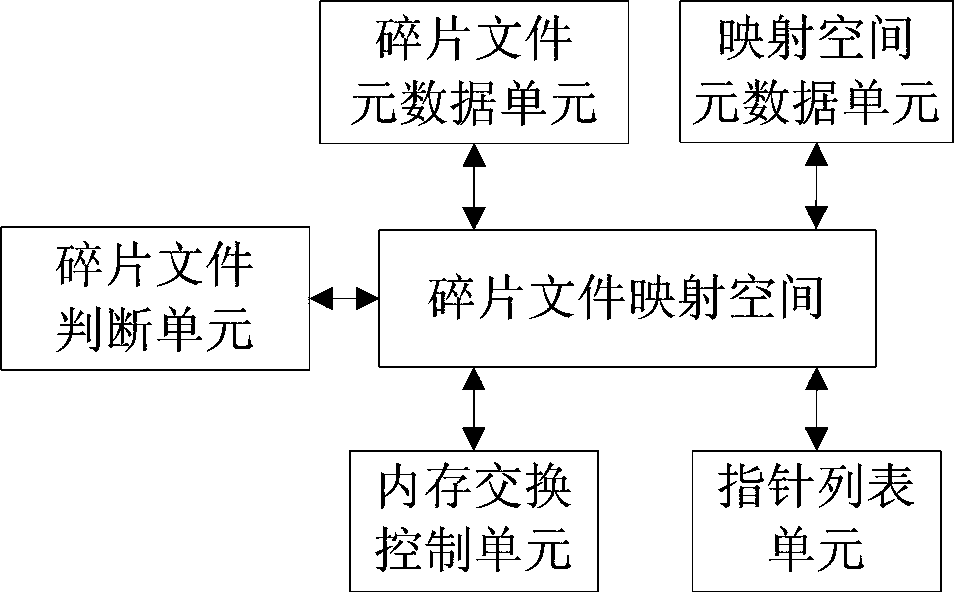
[0056] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the fragmented file mapping space adopts non-swap memory. Due to the use of non-swappable memory, the fragmented file mapping space will not automatically release the content in the space, and some swap methods need to be set to realize the exchange of files between the fragmented file mapping space and the disk.
[0057] The priority is preset for each large file, and the exchange of large files between the fragmented file mapping space and the disk is determined according to the priority. The priority may be set according to the following criteria: the frequency of file access, or the time of the last access, or the weighting of historical access records; but not limited thereto, other criteria may also be used. Take the standard of the frequency of file access as an example, if a large file has more access times, the priority of the large file is higher, otherwise, the priority is lower; large files with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com