Method for coagulation related function detection by EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) anticoagulation
A technology related to function and function detection, applied in measurement devices, biological tests, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problem of inability to detect blood coagulation function detection by platelet aggregation function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
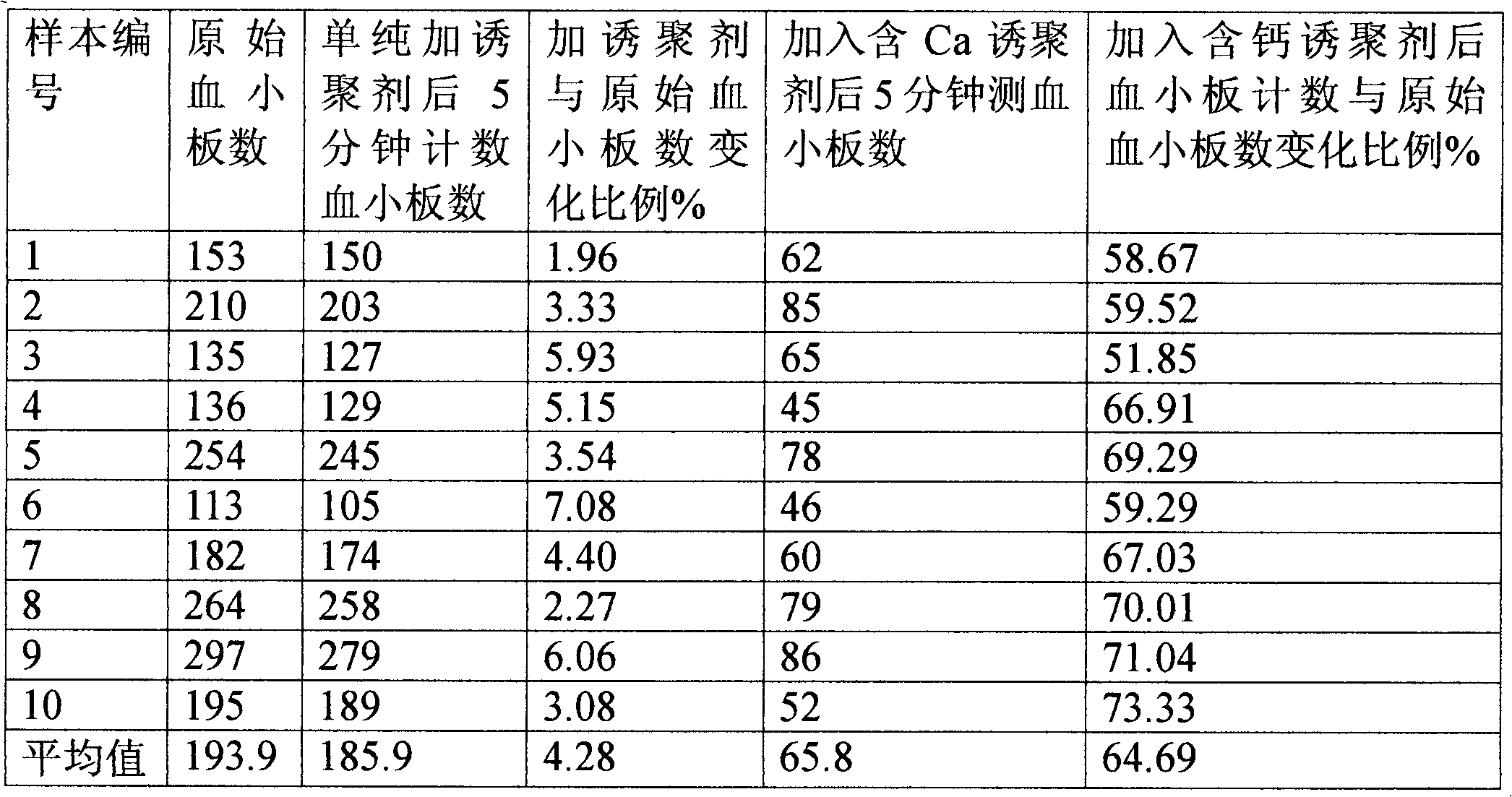
[0004] Taking platelet counting method to detect platelet aggregation function as an example, the specific operation process of this method is: when collecting fresh blood samples, prepare anticoagulant blood according to the conventional ratio (add 0.8mgEDTA per 1ml whole blood), and then use this EDTA anticoagulant blood Perform platelet count to obtain the original number of platelets in the blood sample, then add calcium ion-containing aggregation inducer to the blood sample, and the final content of added calcium chloride is >2.0mmol / L. In normal blood samples, platelets begin to aggregate after adding calcium-containing aggregation inducers, and the platelet aggregation rate can be judged by detecting the number of aggregated platelets, and platelet aggregation does not occur in normal blood samples without adding calcium ions and simply adding aggregation inducers. It shows that conventional EDTA anticoagulant blood has no aggregation function under the condition of not ...
specific Embodiment 2
[0011] Five parts of EDTA anticoagulant blood collected were prepared into plasma, and each part was divided into two parts at the same time to form two groups. One group was added with calcium chloride-containing PT (prothrombin time test) reagent, and the other group was added with the same amount Does not contain calcium PT (prothrombin time test) reagents, etc. Two groups of samples were added with PT (prothrombin time test) reagent for 5 minutes to observe the plasma coagulation status of the two groups. The result statistics are as follows:
[0012] Table 2 Observation table for the number of platelets obtained by using EDTA anticoagulated blood samples plus PT (prothrombin time test) reagent
[0013] Numbering
[0014] *Indicating that EDTA anticoagulant plasma can restore blood coagulation function after adding calcium. That is, EDTA anticoagulant blood can be tested for blood coagulation function after adding calcium ions.
specific Embodiment 3
[0015] Calcium ions were added to EDTA anticoagulated whole blood, and the blood samples were all coagulated to varying degrees after standing still for 10 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com