Permanent-magnet type rotating electrical machine
A technology of rotating electrical machines and permanent magnets, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult processing of magnetic steel plates, difficulty in improving the accuracy of the outer diameter of the rotor core, etc., to maintain accuracy and reduce torque ripple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
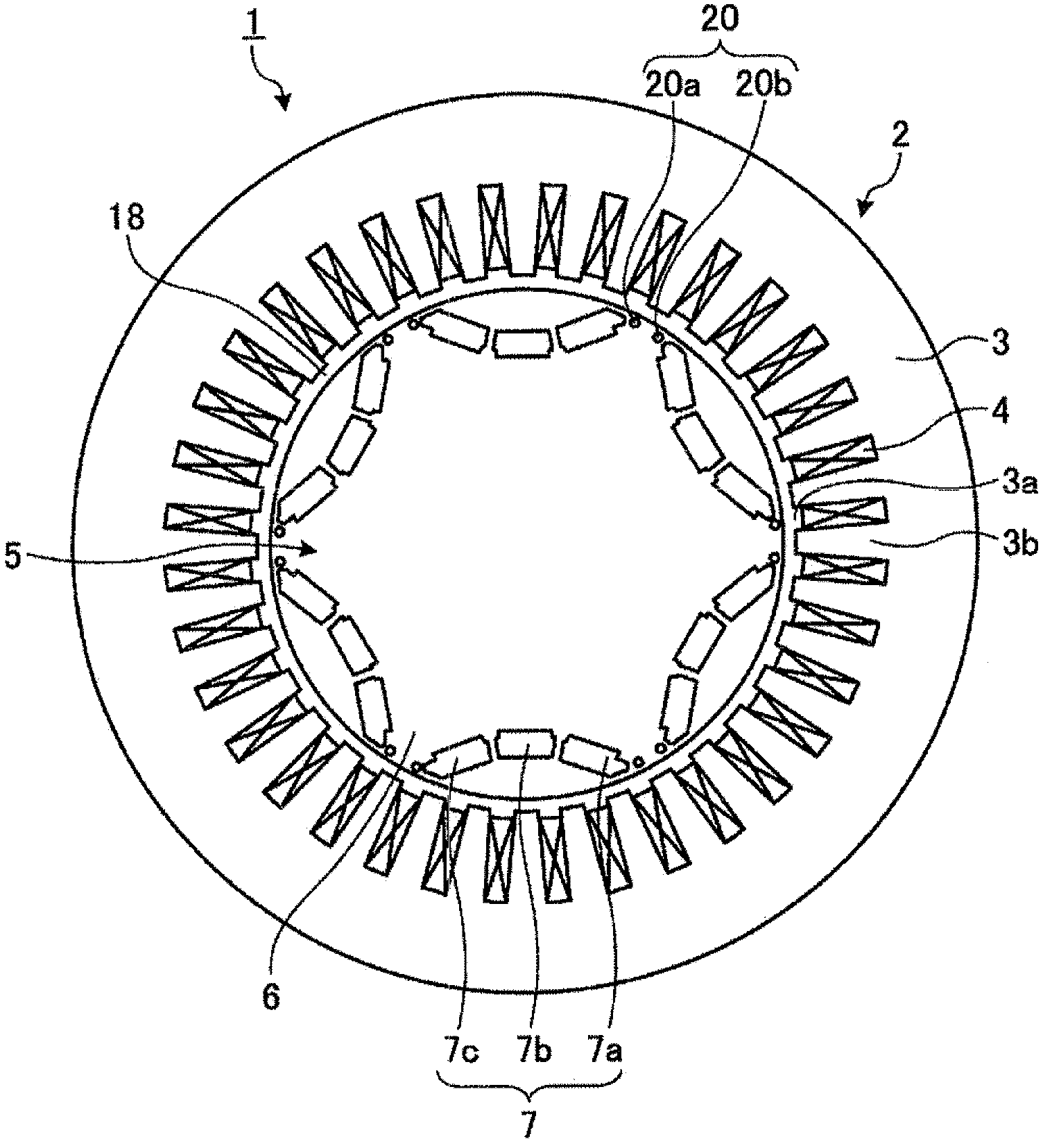
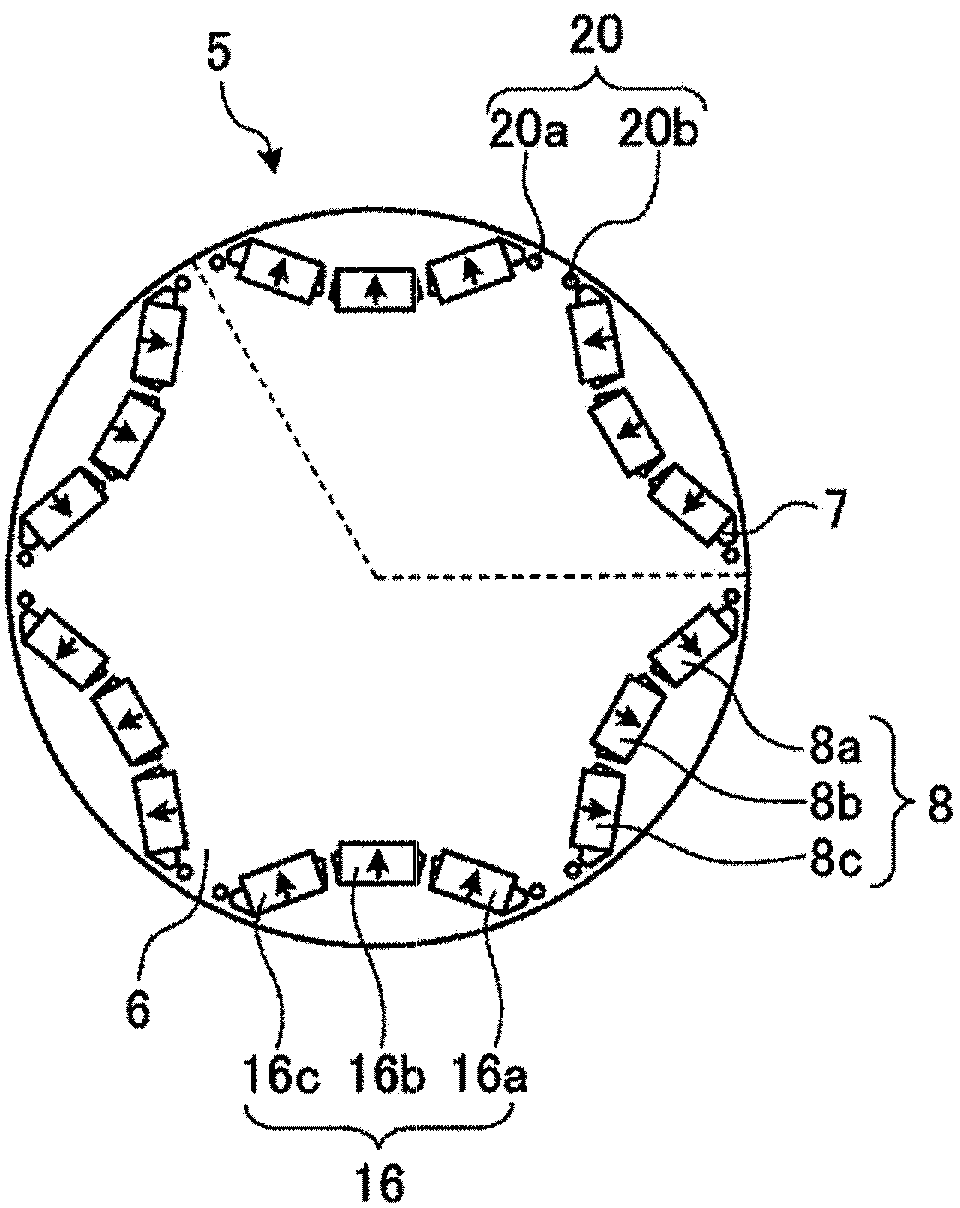
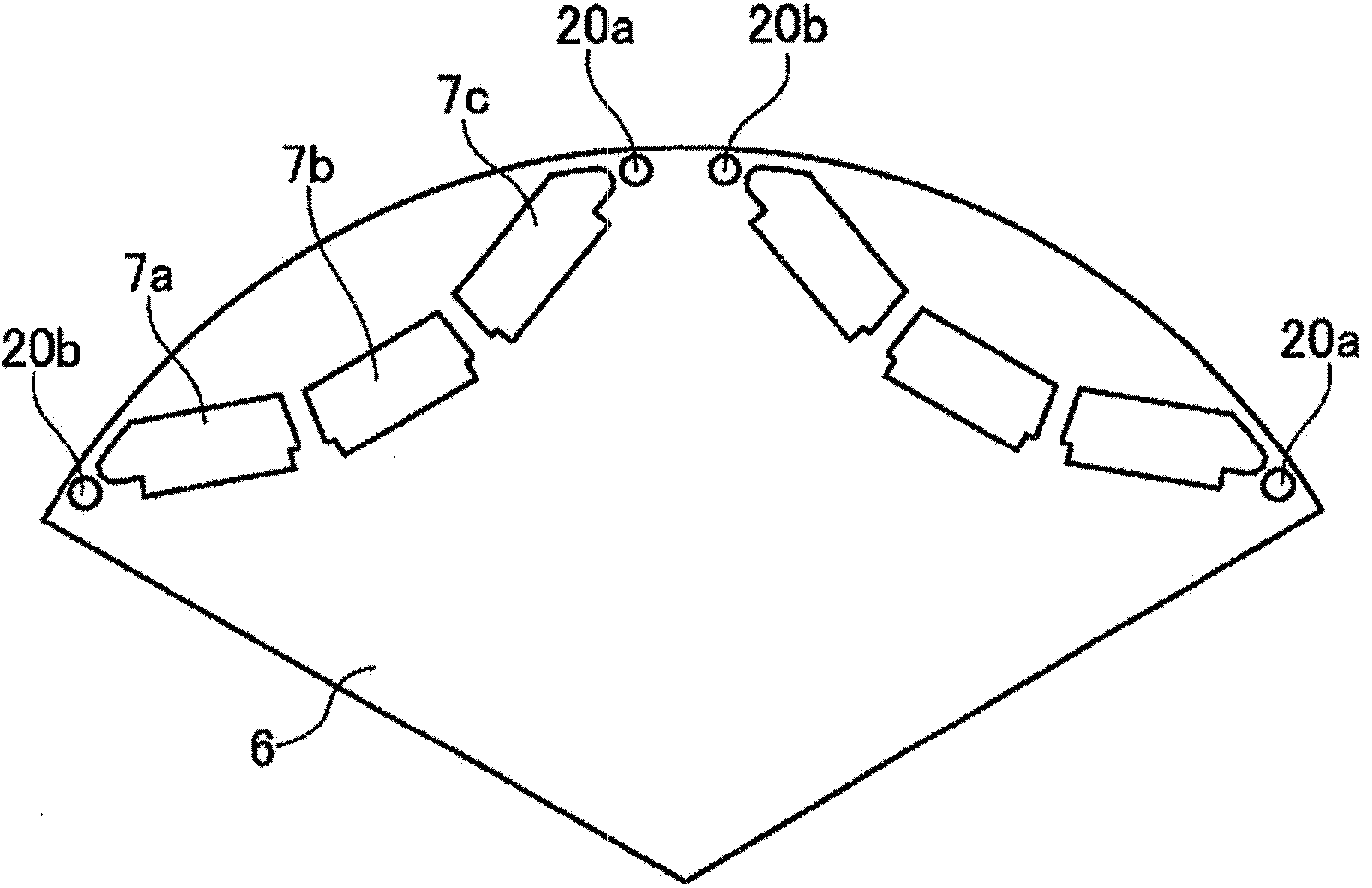
[0028] figure 1 Is a cross-sectional view of a permanent magnet type electric motor as an example of the permanent magnet type rotating electric machine according to the first embodiment, figure 2 Is a schematic cross-sectional view of the rotor showing the magnetic pole structure of the permanent magnets embedded in the rotor, image 3 Yes figure 2 A partial enlarged view of the part shown by the dotted line in the case where no permanent magnet is inserted, Figure 4 Is in the case of inserting permanent magnets and image 3 The corresponding partial enlarged view.
[0029] The permanent magnet motor 1 according to the first embodiment has a stator 2 and a rotor 5. The stator 2 has a stator core 3 formed in a cylindrical shape. On the inner peripheral side of the stator core 3, for example, 36 teeth 3b are formed at equal angular intervals at intervals to form 36 slits 3a. In addition, the stator coil 4 is wound and housed in the slit 3a so as to have a fixed number of teeth 3...
Embodiment approach 2
[0047] In the first embodiment, a pair of magnetic flux control holes 20a, 20b capable of reducing torque ripple are provided in the inter-pole part of the rotor, but these magnetic flux control holes 20a, 20b may be such as Figure 8 The riveting structure as shown. Figure 8 It is an axial cross-sectional view of a magnetic flux control hole formed by a riveting structure.
[0048] In addition, Picture 9 It is a graph (simulation result) showing the relationship between the center distance of the magnetic flux control hole 20 formed by the riveting structure and the amplitude of the torque ripple. In addition, the relationship between the horizontal axis and the vertical axis and the diameter of the magnetic flux control hole 20 as a parameter are the same as those in the first embodiment.
[0049] Such as Picture 9 As shown, regardless of the size (diameter) of the magnetic flux control holes 20, the value (m / τ) obtained by normalizing the center distance m between the magnetic...
Embodiment approach 3
[0053] Picture 10 A schematic cross-sectional view showing a partial structure of the rotor core of the permanent magnet type rotating electrical machine according to the third embodiment. In the first and second embodiments, three permanent magnets are arranged in a substantially U-shape for each pole, but in this embodiment, as Picture 10 As shown, two permanent magnets are arranged in a V shape for each pole, and the same magnetic flux control holes 20a and 20b as in the first embodiment are provided in the inter-pole part.
[0054] In addition, Picture 11 It is a graph (simulation result) showing the relationship between the center distance of the magnetic flux control holes 20 and the amplitude of the torque ripple in the rotor structure according to the third embodiment. In addition, the relationship between the horizontal axis and the vertical axis and the diameter of the magnetic flux control hole 20 as a parameter are also the same as those in the first embodiment.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com