Parallel message routing detection method
A detection method and message technology, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency and inability to detect the packet loss rate of intermediate nodes, achieve low efficiency, realize parallel routing detection, and speed up detection. The effect of efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
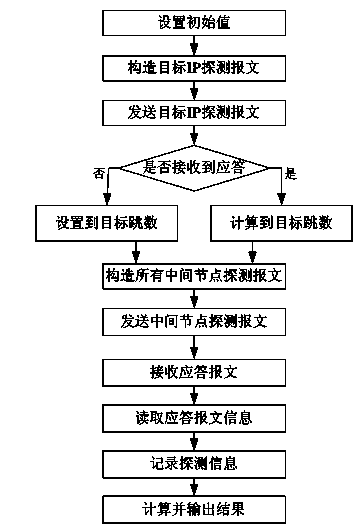
[0026] A parallel message routing detection method, characterized in that:
[0027] Step 1: Set a detected IP address A, set the number k of each type of message sent, k=1~100, set an array structure D including 32*k records, each record of the array structure D includes The TTL number of the sent message, the time stamp of the sent message, the time stamp of the received response message, the identification number of the sent message and the source IP address of the response message, enter step 2;
[0028] Step 2: an ICMP message with detected IP address A as the target address is set, the TTL field of the IP message header of the ICMP message is set to 64, and the ICMP message is sent by the measurement point to the target address, Go to step three;
[0029] Step 3: If the response message of the ICMP message is received, then measure the value TL of the TTL field of the IP header in the received response message, and enter step 4; if the response message is not received, s...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A parallel message routing detection method, characterized in that:
[0039] Step 1: The IP address of the measurement point is 101.4.116.222, set a detected IP address 121.194.0.239, set the number k of each type of message sent, k=3, and set an array structure including 32*k records D, each record of the array structure D includes the TTL number of the sent message, the timestamp of the sent message, the timestamp of the received response message, the identification number of the sent message and the source IP address of the response message, and enter step 2 ;
[0040] Step 2: set an ICMP message with the detected IP address 121.194.0.239 as the target address, the TTL field of the IP message header of the ICMP message is set to 64, and the ICMP message is sent to the target address by the measurement point text, go to step 3;
[0041] Step 3: after receiving the response message of the ICMP message, measure the value TL of the IP header TTL field in the received r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com