Resistance change element and manufacturing method therefor
A technology of variable resistance element and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of electric components, electric solid-state devices, circuits, etc., and can solve the problems that the operation characteristics impair the operation stability and reliability of semiconductor storage devices, and hinder the miniaturization and large-capacity of storage devices, etc. , to achieve the effect of miniaturization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0083] [Structure of variable resistance element]
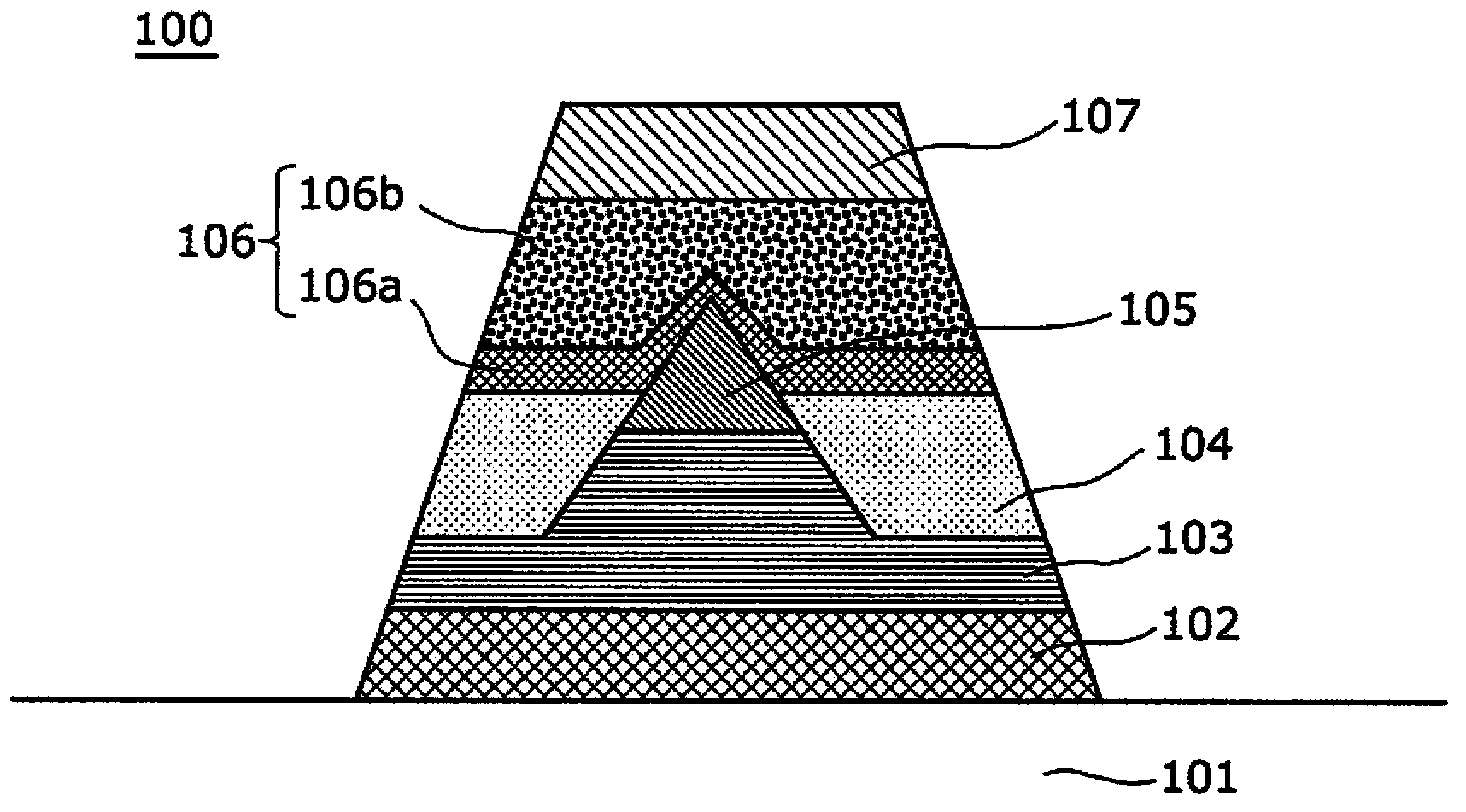
[0084] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view showing a configuration example of the variable resistance element 100 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0085] Such as figure 1 As shown, the variable resistance element 100 includes a substrate 101; an adhesive layer 102 (10-20 nm in thickness) formed on the substrate 101 and made of titanium nitride (TiN); formed on the adhesive layer 102, made of titanium aluminum nitride (TiAlN) truncated conical conductive layer 103 (thickness 50-100nm); conical (needle)-shaped second electrode 105 formed on the conductive layer 103; formed on the second electrode 105 covering the second electrode 105 The second variable resistance layer 106a (thickness 2-10nm); the interlayer insulating layer 104 formed on the conductive layer 103 and the second electrode 105 covering the conductive layer 103 and the part of the second electrode 105 excluding the needle-shaped part; ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0109] [Structure of variable resistance element]
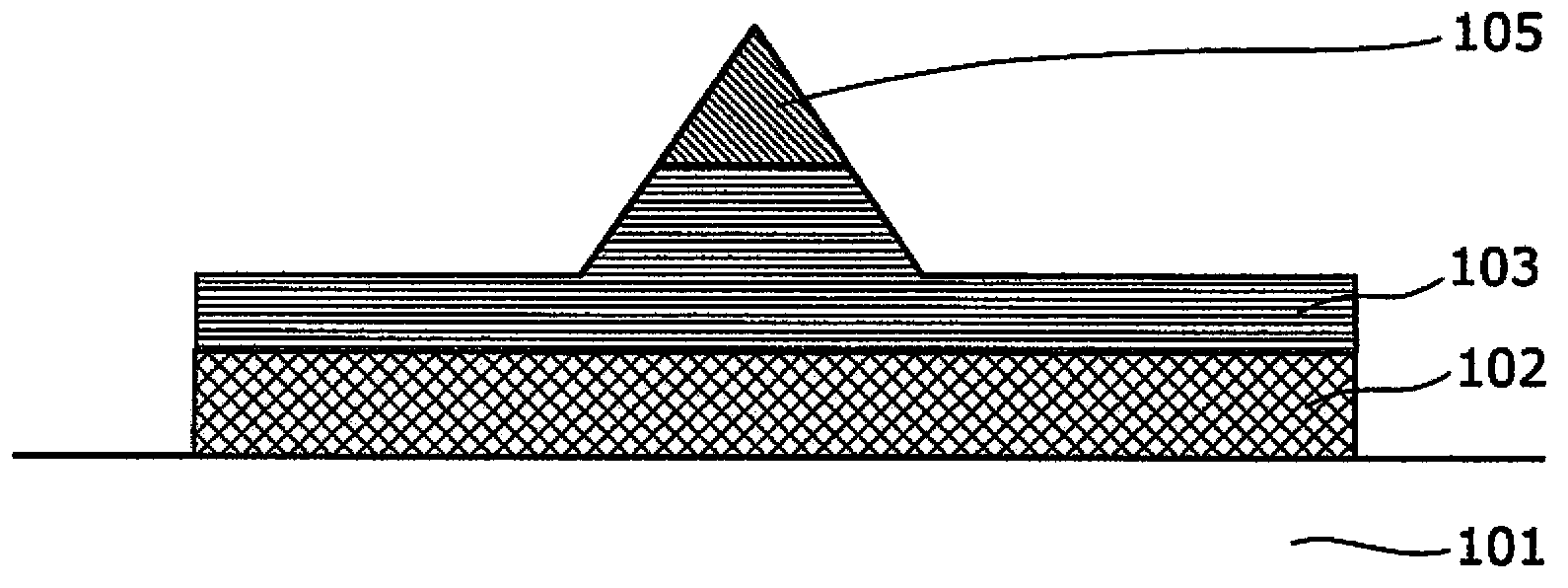
[0110] image 3 It is a cross-sectional view showing a configuration example of the variable resistance element 300 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0111] Such as image 3 As shown, the variable resistance element 300 includes: a substrate 301; an adhesive layer 302 (10-20 nm in thickness) formed on the substrate 301 and made of titanium nitride (TiN); a first electrode 307 (5-100 nm in thickness), It is formed on the adhesive layer 302 and is composed of tantalum nitride (TaN); the first variable resistance layer 306b (thickness 18-95nm) is formed on the first electrode 307; the interlayer insulating layer 304 is formed on the adhesive layer 302, On the laminated structure composed of the first electrode 307 and the first variable resistance layer 306b and the substrate 301; a spacer (spacer) 309 is formed on the upper surface of the first variable resistance layer 306b that penetrates the interlayer ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com