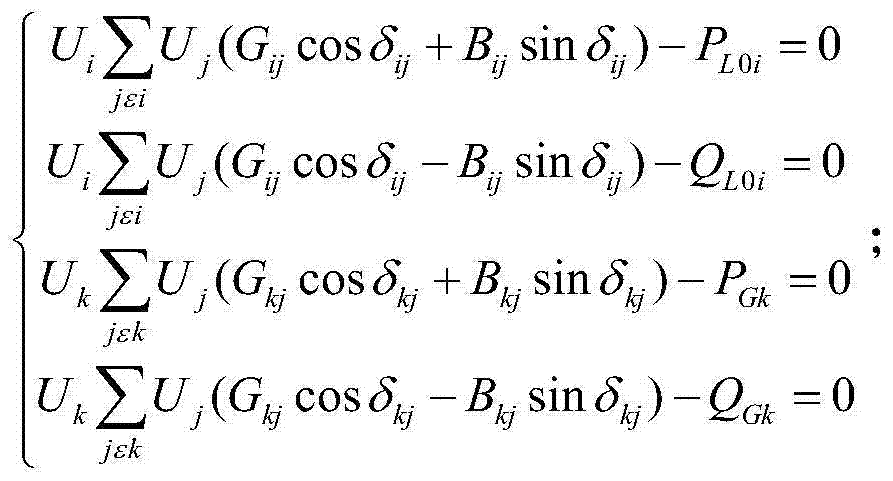Method for optimizing grid-connected unit excitation difference adjustment coefficient based on minimum overall network loss
A technology with the smallest adjustment coefficient and net loss, applied in the direction of single-network parallel feeding arrangement, etc., can solve problems such as large randomness and lack of theoretical calculations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
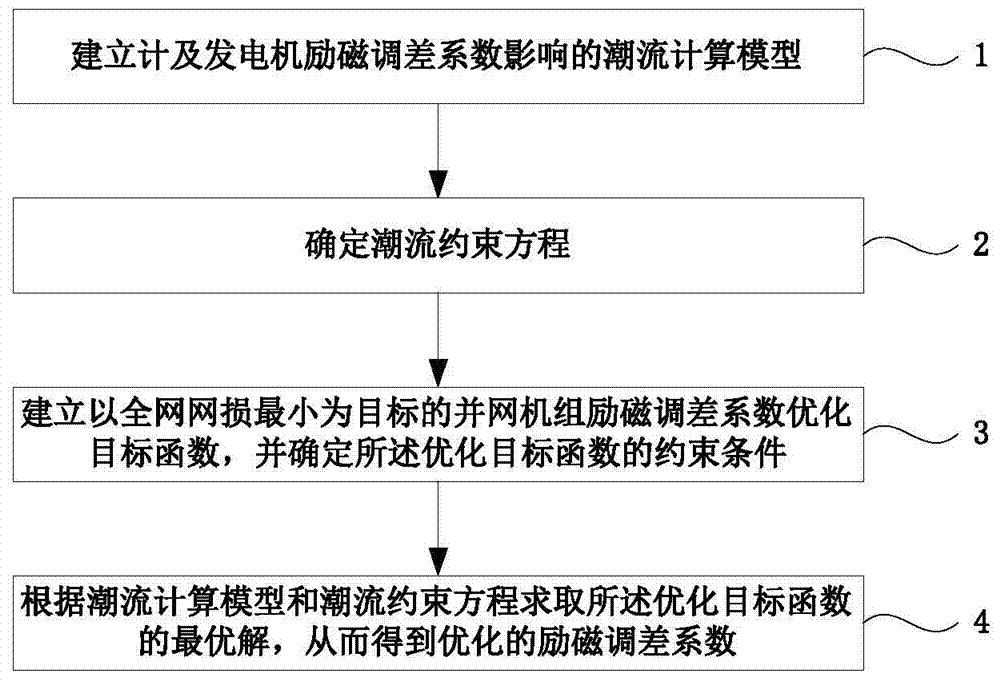
[0046] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the optimization method for the excitation adjustment coefficient of the grid-connected unit based on the minimum network loss of the whole network, as shown in figure 1 As shown, the optimization method provided by the present invention includes:
[0047] Step 1: Establish a power flow calculation model that takes into account the influence of generator excitation adjustment coefficient.
[0048] The relationship between generator terminal voltage and output reactive power is shown in formula (1):
[0049] Q G = 1 R ( U G 0 U G - U G 2 ) - - - ( 1 )
[0...
Embodiment 2
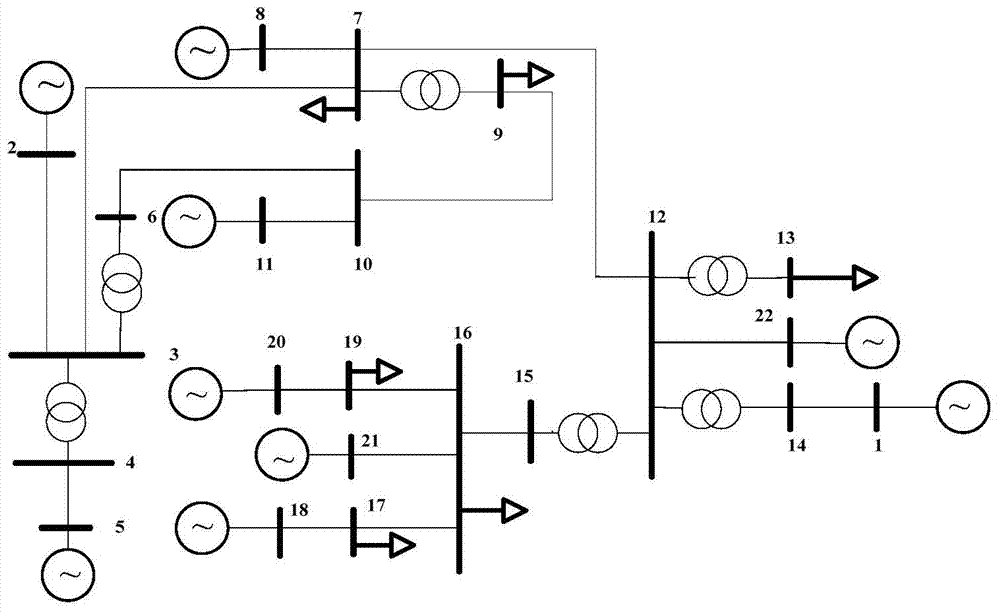
[0075] figure 2 It is a simplified diagram of a certain provincial power grid provided by the embodiment, which includes 22 nodes, among which nodes 1, 5, 8, 20 and 21 are generator nodes.
[0076] First, determine the value of each variable, including the node admittance matrix, the no-load voltage U of the generator node G0k , The active power P of the load node L0i and the reactive power Q at the load node L0i .
[0077] Secondly, given the generator active power P Gk , Excitation adjustment coefficient R k , node voltage amplitude U j and node voltage phase angle δ j initial value.
[0078] Finally, using the optimization objective function established by the present invention, combined with constraints, in MATLAB software, iteratively solved with the help of a numerical solution algorithm, and the results are shown in the following table.
[0079]
[0080] It can be seen from the above table that after optimization, the variation coefficient of generator 1 is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com