A method of raising fly maggots with leftovers after cultivating housefly larvae with wheat bran
A technology of housefly larvae and leftovers, which is applied in the fields of application, animal feed, animal feed, etc., can solve the problems of no longer raising housefly larvae, etc., and achieve the effects of improving resource utilization efficiency, reducing production costs, and reducing labor costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 Effect of different proportions of NaOH on alkaline hydrolysis of leftovers
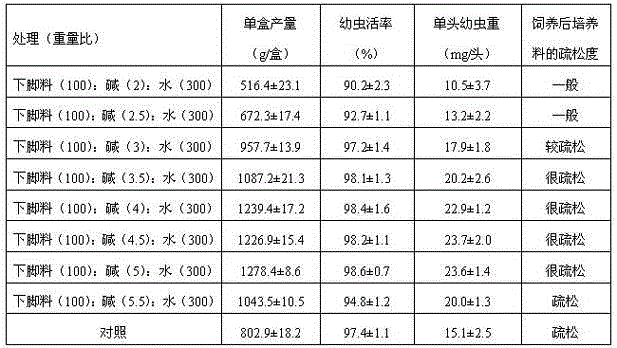
[0019] Dispose of the scraps as follows: Separate the scraps, alkali and water according to 100:2:300, 100:2.5:300, 100:3:300, 100:3.5:300, 100:4:300, 100:4.5: The weight ratio of 300, 100: 5: 300, 100: 5.5: 300 is subjected to alkaline hydrolysis treatment, and fermented at 30°C for 25 days. When the pH drops to 7, it is used to prepare feed for housefly larvae.
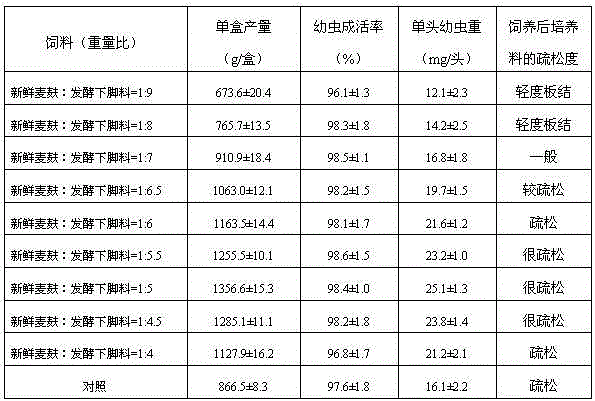
[0020] Feed preparation and feeding methods are as follows: Weigh 1.5kg of fresh wheat bran and 6.5kg of alkaline hydrolysis and fermentation scraps, mix them evenly, put them into a 68cm×45cm×18cm plastic box, and then receive 55,000 housefly eggs in each box. The larvae were reared at a temperature of 26°C and a humidity of 60%. After 4 days, the larvae were separated from the culture material, and the weight of the separated larvae and the weight of the single larvae were weighed. Repeat 6 times. 100% fresh wheat bran was ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2: Influence of water on the effect of alkaline hydrolysis of scraps
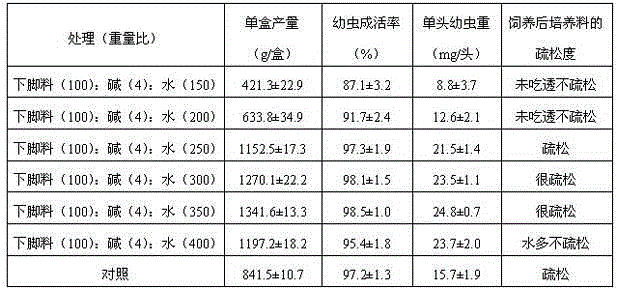
[0025] Dispose of leftovers as follows: Press 100:4:150, 100:4:200, 100:4:250, 100:4:300, 100:4:350, 100:4: The weight ratio of 400 is subjected to alkaline hydrolysis, and it is fermented at 30°C for 25 days. When the pH drops to 7, it is used to prepare housefly larva feed.
[0026] Feed preparation and feeding methods are as follows: Weigh 1.5kg of fresh wheat bran and 6.5kg of alkaline hydrolysis and fermentation scraps, mix them evenly, put them into a 68cm×45cm×18cm plastic box, and then receive 55,000 housefly eggs in each box. The larvae were reared at a temperature of 26°C and a humidity of 60%. After 4 days, the larvae were separated from the culture material, and the weight of the separated larvae and the weight of the single larvae were weighed. Repeat 6 times. 100% fresh wheat bran was used as a control (2.5kg fresh wheat bran per box, 5.5kg water). The results are shown in Table 2...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3: The influence of temperature on the fermentation of alkaline hydrolysis leftovers
[0031] The leftovers are treated as follows: the leftovers, alkali and water are subjected to alkaline hydrolysis treatment at a weight ratio of 100:4:300, and then fermented at 13, 18, 23, 28, 33, 38, and 43 ℃, and wait until the pH drops. At 7 o'clock, prepare housefly larva feed.
[0032] Feed preparation and feeding methods are as follows: Weigh 1.5kg of fresh wheat bran and 6.5kg of alkaline hydrolysis and fermentation scraps, mix them evenly, put them into a 68cm×45cm×18cm plastic box, and then receive 55,000 housefly eggs in each box. The larvae were reared at a temperature of 26°C and a humidity of 60%. After 4 days, the larvae were separated from the culture material. The weight of the larvae, the weight of a single larva and the survival rate of the larvae were measured. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0033] table 3.
[0034]
[0035] From the results in Table 3 above...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com