Intraocular foreign body forceps
An intraocular foreign body and tweezers technology, applied in the field of intraocular foreign body tweezers, can solve the problems of increasing the risk of endophthalmitis, increasing the retina, and long operation time, reducing the risk and complications of surgery, overcoming the instability of foreign bodies, and improving The effect of surgical success
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
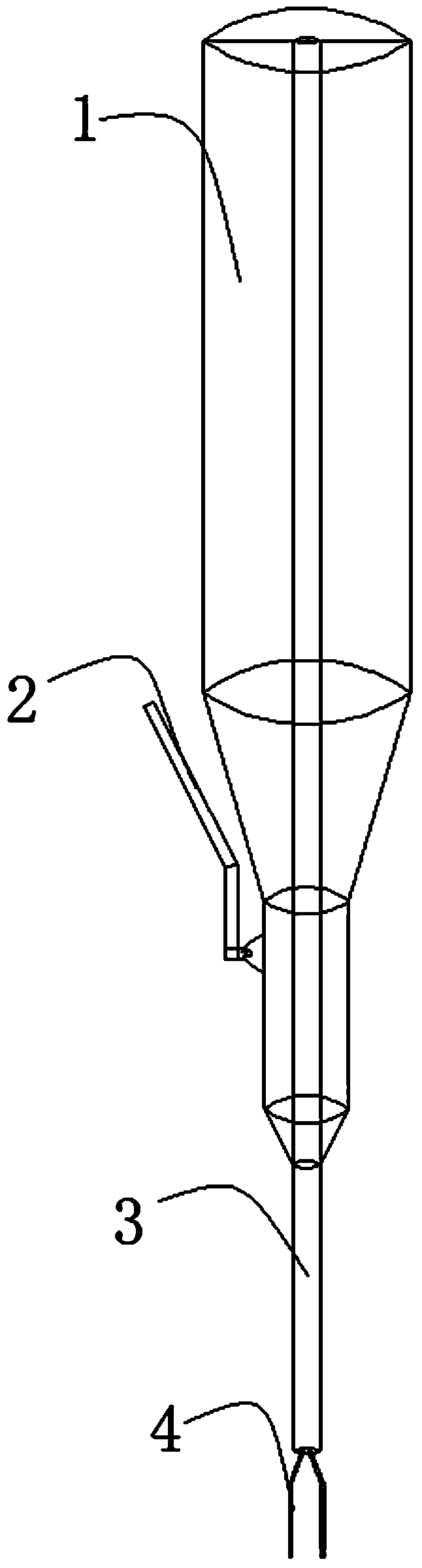
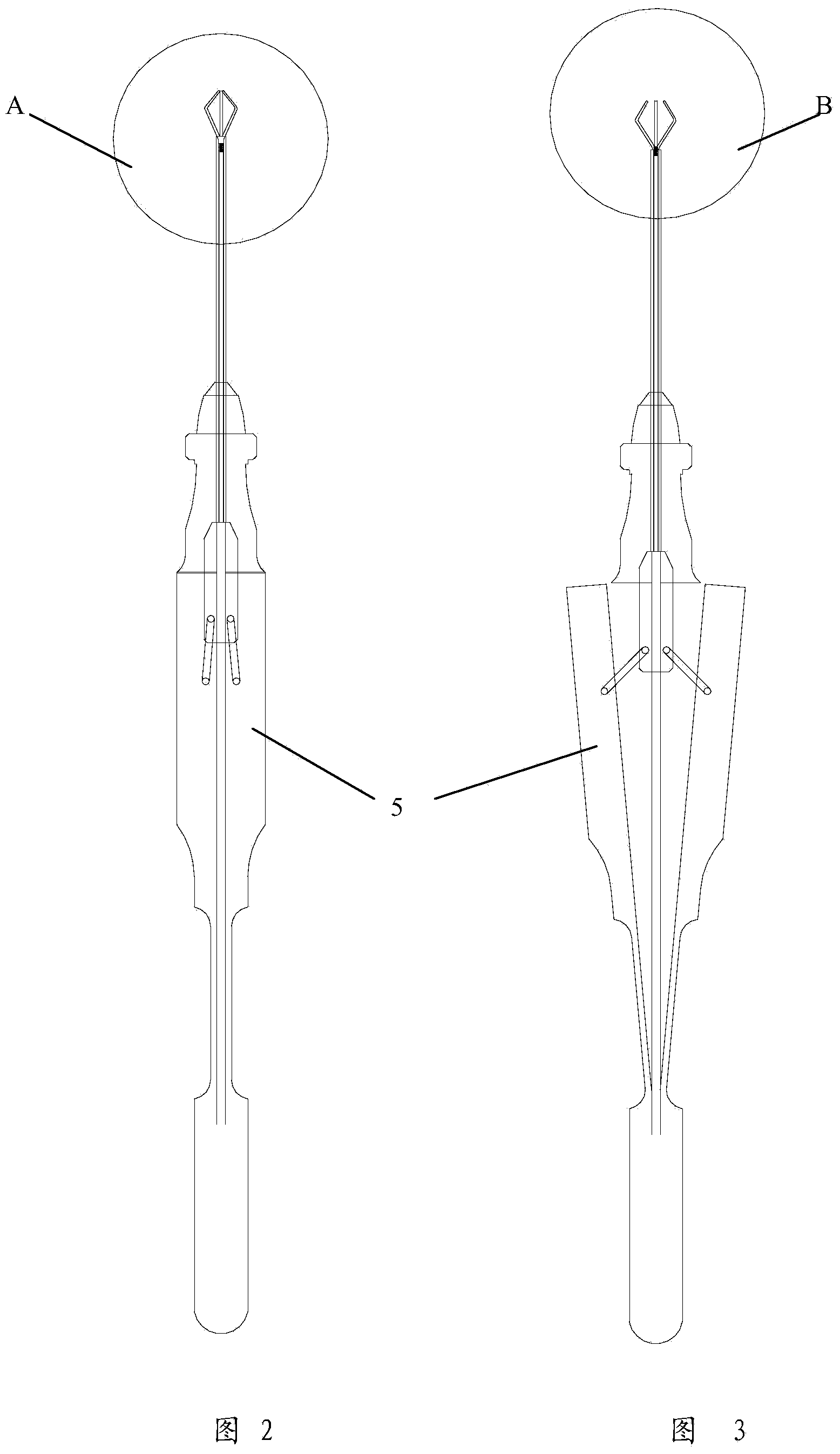
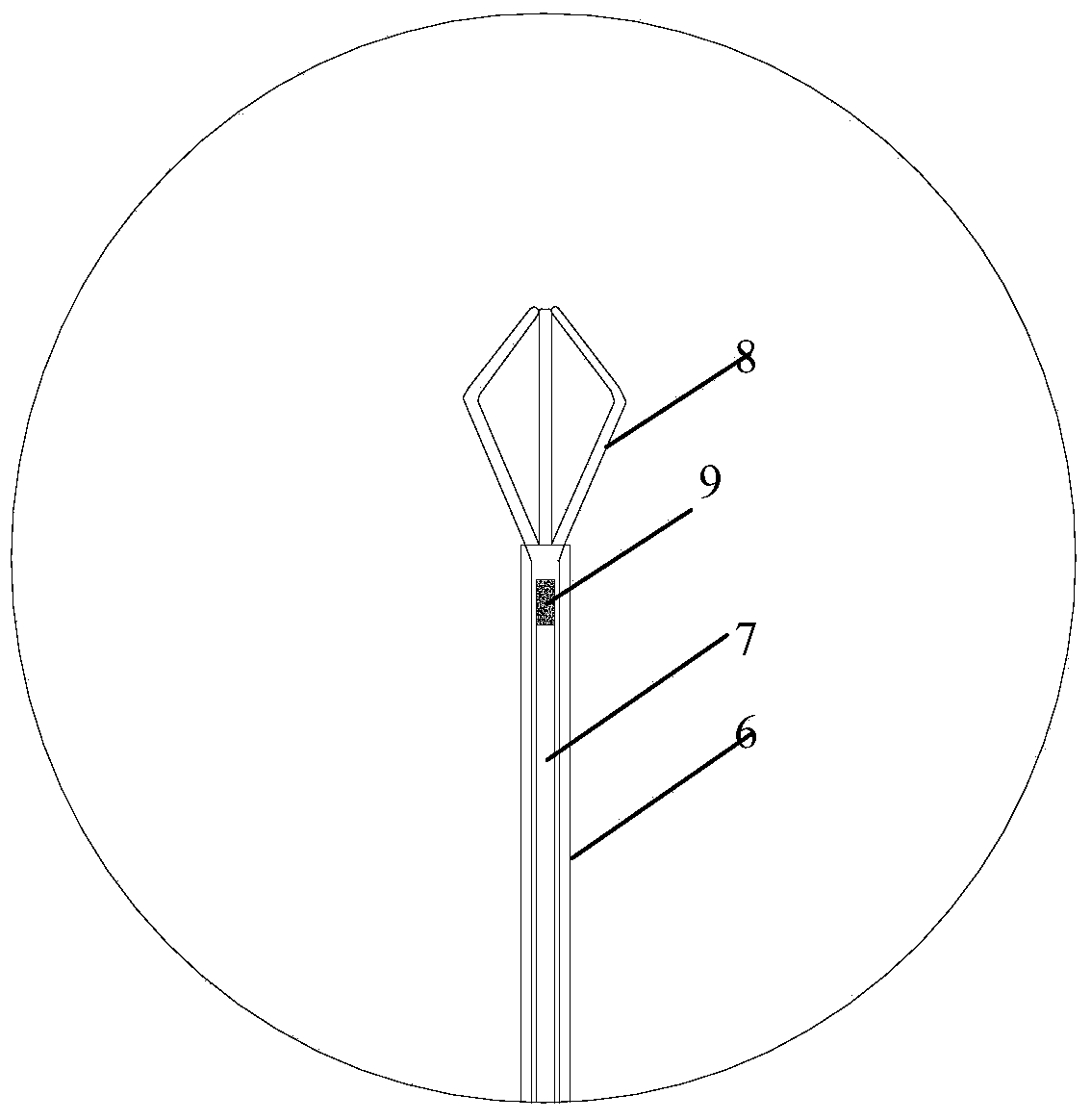
[0023] Such as Figure 2-5 As shown, the intraocular foreign body tweezers of the present invention include a handle 5, a tweezer claw portion and an outer sleeve 6, and the tweezer claw portion includes a fixed tube 7 fixedly connected to the handle and a non-magnetic tweezer claw 8 positioned at the front end of the fixed tube. The outer sleeve 6 is set on the outside of the fixed tube and can be driven to slide back and forth to control the tweezers to draw close together or open away from each other. A magnetic component 9 is fixedly arranged at the front end of the fixed tube, preferably the magnetic The component is a magnetic column or a magnetic block. When the outer sleeve d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com