Radiation detection device based on soi CMOS process and its preparation method
A radiation detection and process technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve the problems of lack of protection devices, single event effect isolation, low sensitivity response, etc., and achieve the effects of extending the detection range, reducing the threshold voltage, and high storage capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
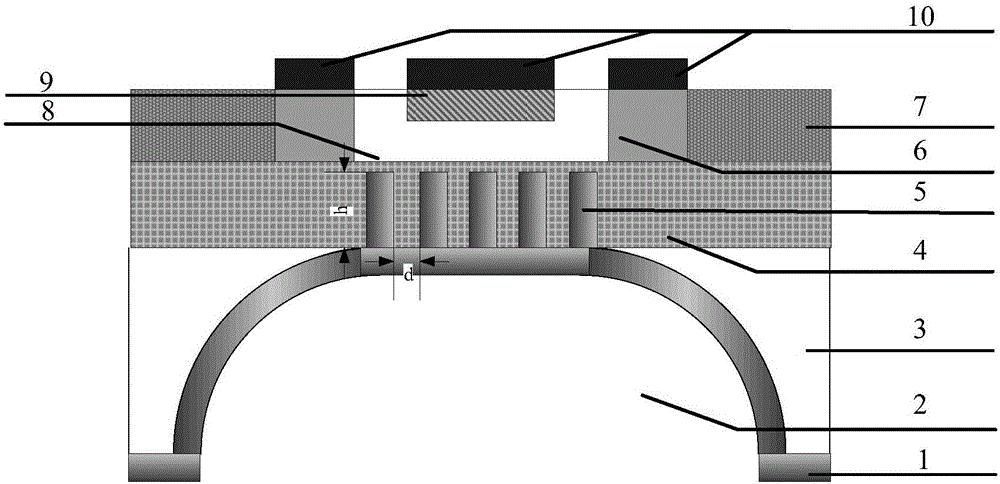
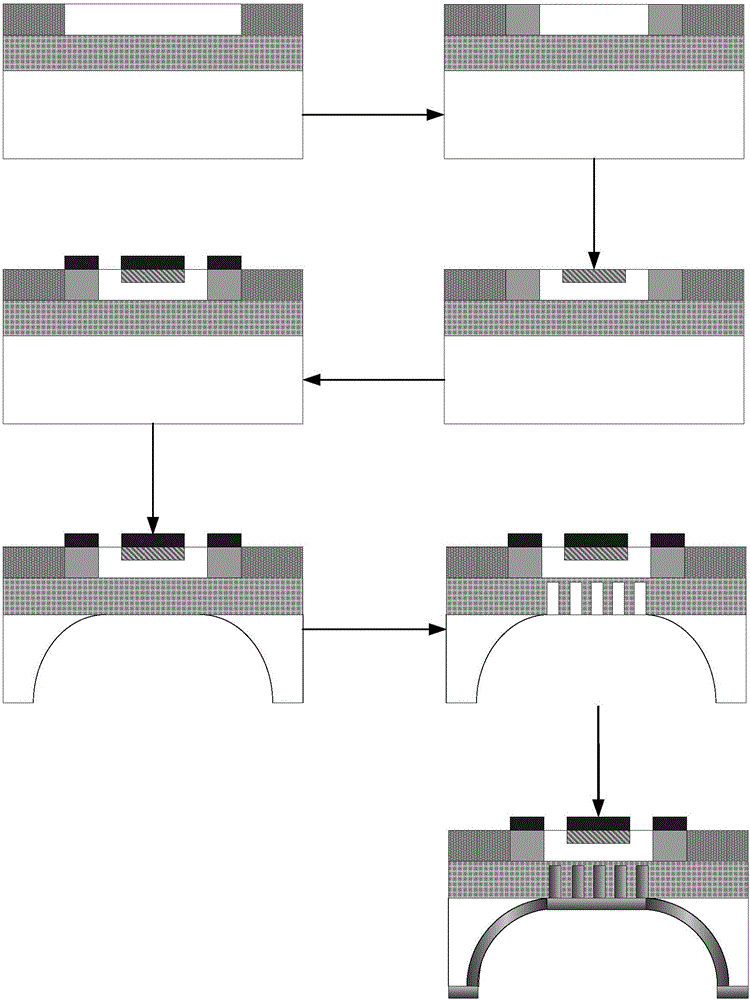
[0042] 1) On the front side of the SOICMOS substrate, use the LOCOS process to grow a dielectric isolation region, wherein the SOICMOS substrate includes a Si substrate, a buried oxide layer above the Si substrate, and a Si thin film region above the buried oxide layer.
[0043] The specific steps are: remove all oxide layers on the SOICMOS substrate, clean, and grow SiO with a thickness of 50nm by dry oxygen oxidation. 2 Oxygen pad layer, in which the temperature of the oxidation furnace used is 900°C, the temperature of the oxidation bottle is 85°C, and the oxidation time is 5min; then the Si with a thickness of 190nm is grown by low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD). 3 N 4 Masking layer, wherein the deposition pressure is 25Pa, the deposition time is 30min, and the deposition temperature is 600°C; the pattern of the dielectric isolation region is photoetched by photolithography, and the dry oxidation, wet oxidation and dry oxidation are used in sequence The method...
Embodiment 2
[0053] 1) On the front side of the SOICMOS substrate, use the LOCOS process to grow a dielectric isolation region, wherein the SOICMOS substrate includes a Si substrate, a buried oxide layer above the Si substrate, and a Si thin film region above the buried oxide layer.
[0054] The specific steps are: remove all oxide layers on the SOICMOS substrate, clean, and grow SiO with a thickness of 125nm by dry oxygen oxidation. 2 Oxygen pad layer, in which the temperature of the oxidation furnace used is 950°C, the temperature of the oxidation bottle is 88°C, and the oxidation time is 9min; then the Si with a thickness of 210nm is grown by low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD). 3 N 4 The masking layer, wherein the deposition pressure is 33Pa, the deposition time is 45min, and the deposition temperature is 700°C; the pattern of the dielectric isolation region is photoetched by photolithography, and the dry oxidation, wet oxidation and dry oxidation are used in sequence The m...
Embodiment 3
[0064] 1) On the front side of the SOICMOS substrate, use the LOCOS process to grow a dielectric isolation region, wherein the SOICMOS substrate includes a Si substrate, a buried oxide layer above the Si substrate, and a Si thin film region above the buried oxide layer.
[0065] The specific steps are: remove all oxide layers on the SOICMOS substrate, clean, and grow SiO with a thickness of 100nm by dry oxygen oxidation. 2 Oxygen pad layer, in which the temperature of the oxidation furnace used is 1000°C, the temperature of the oxidation bottle is 90°C, and the oxidation time is 8 minutes; then the Si layer with a thickness of 205nm is grown by low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD). 3 N 4 The masking layer, wherein the deposition pressure is 27Pa, the deposition time is 55min, and the deposition temperature is 750°C; the pattern of the dielectric isolation region is photoetched by photolithography, and the dry oxidation, wet oxidation and dry oxidation are used in seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com