Al-Er-Hf alloy and heat treatment process thereof
An al-er-hf, processing technology, applied in the field of aluminum alloy materials and their heat treatment technology, can solve problems such as limited space and limited
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0010] Example 1: An alloy ingot was prepared by melting in a graphite crucible and casting in an iron mold, and the raw materials used were pure aluminum and an intermediate alloy of Al6Er and Al4Hf. At a melting temperature of 790±10°C, first melt the aluminum ingot, then add the master alloy, after the master alloy is melted, degas hexachloroethane, stir, keep warm and let the elements in the melt distribute evenly Perform iron mold casting. Five alloys with different compositions were prepared, and their actual compositions were measured by XRF, as shown in Table 1 below. Among them, samples A1 and A2 are Al-Er and Al-Hf binary alloys, respectively, for comparison.
[0011] Table 1 Experimental alloy composition
[0012] sample
Embodiment 2
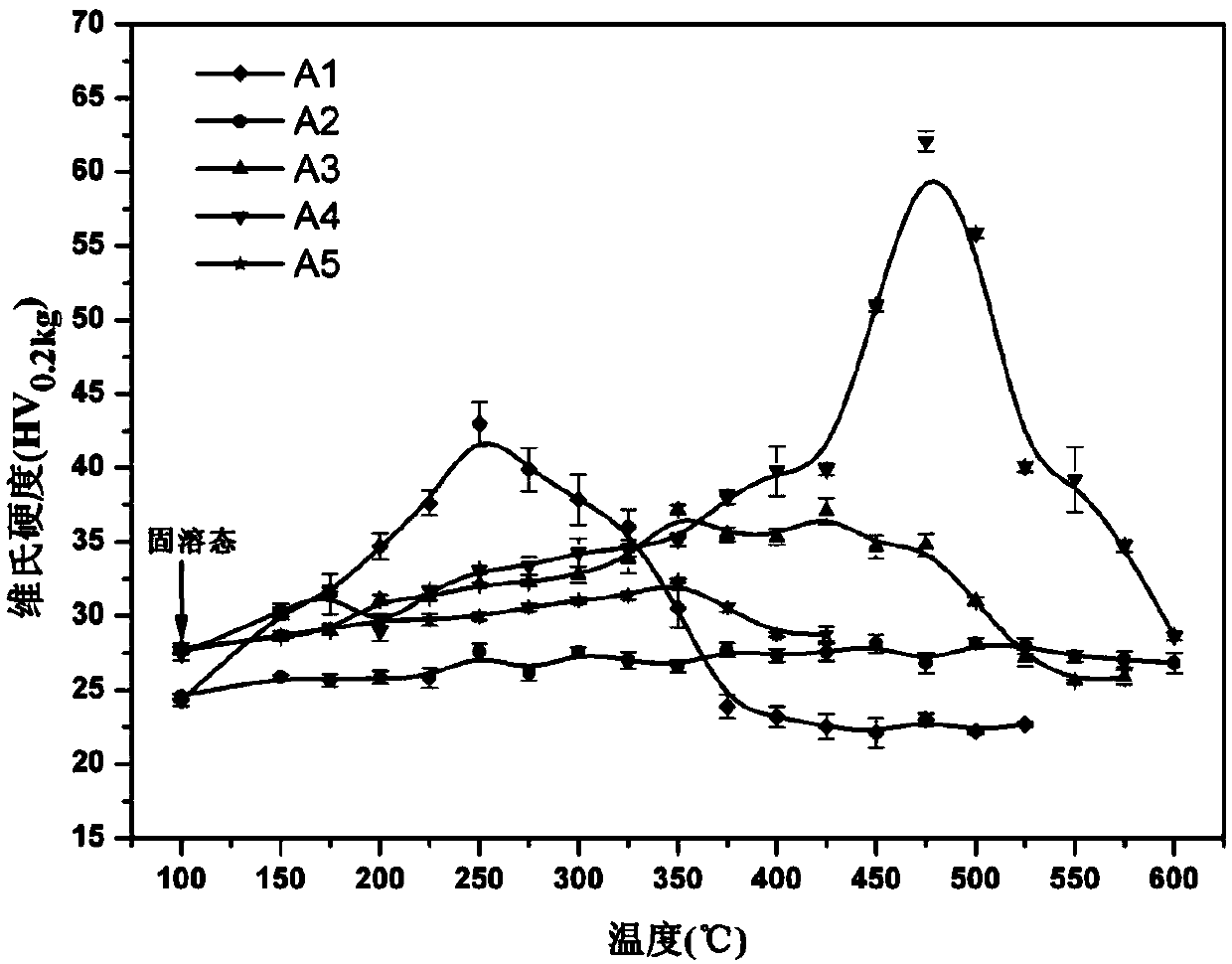
[0013] Example 2: After the alloy in Example 1 was solution treated at 635±10°C for 24 hours, it was water quenched to room temperature; then it was subjected to isochronic aging at 150~(425-600)°C for 3 hours, and samples were taken every 25°C. figure 1 The Vickers hardness of the alloy at different temperatures is given, from which it can be seen that the maximum hardness of the A4 alloy is about 62HV at 475°C, which is much higher than the maximum hardness value of the A1 Al-Er alloy. And with the addition of Hf, the hardness value decreases more slowly than that of Al-Er with the increase of temperature, which shows that the thermal stability of Al-Er-Hf alloy is better than that of Al-Er alloy. In addition, Al-Hf alloy did not show strengthening phenomenon, which is because the precipitation process of Al-Hf alloy is too slow and 3 hours annealing is not enough to make it precipitate.
Embodiment 3
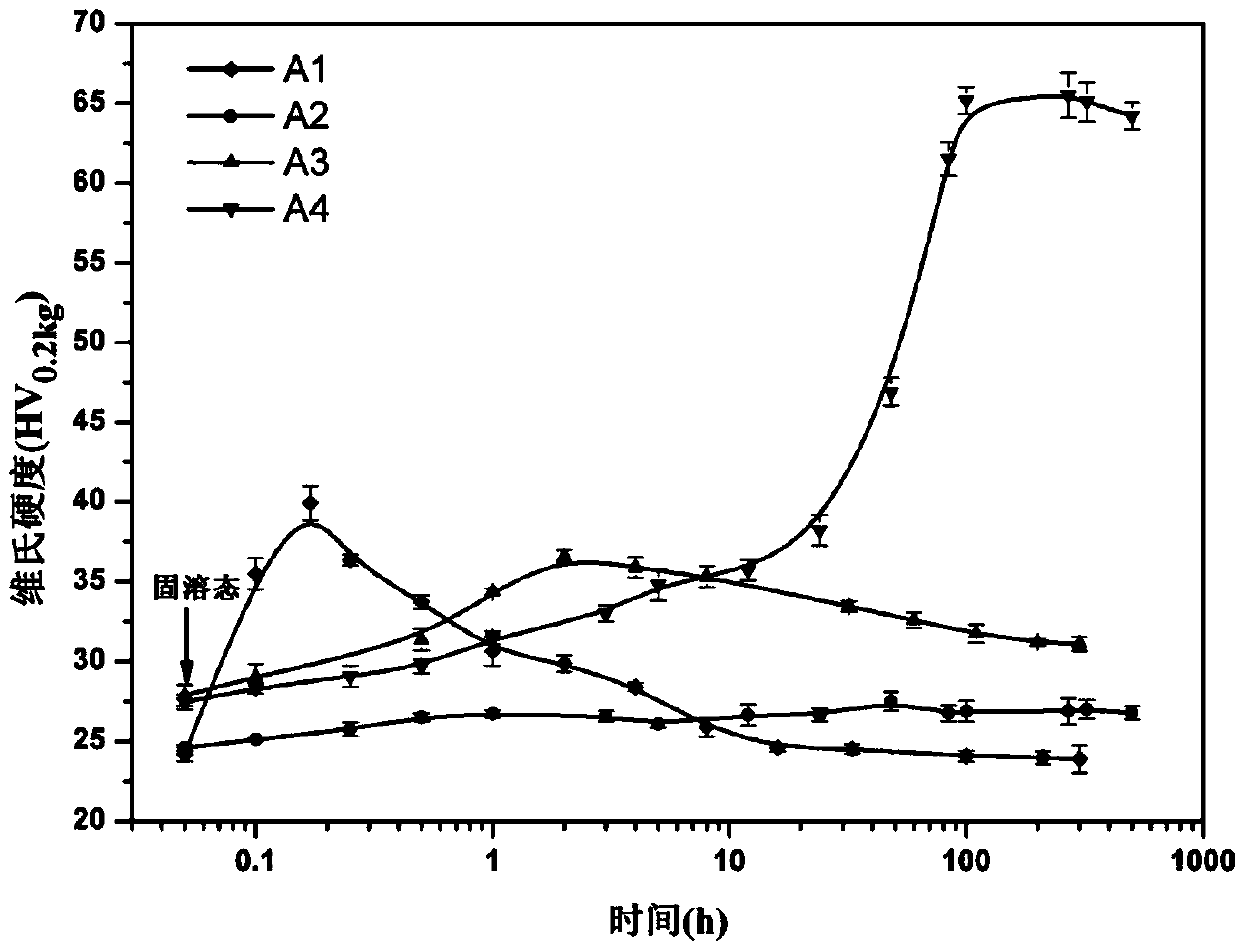
[0014] Example 3: Alloys A1, A2, A3, and A4 in Example 1 were solution treated at 635±10° C. for 24 hours, then water quenched to room temperature; then isothermal aging treatment was performed at 350° C. figure 2 The hardness change curve of the solid solution alloy at 350°C isothermal aging is given. It can be seen from the figure that the hardness of the A4 alloy is the highest, reaching nearly 66HV, which is much higher than the rest of the alloy samples. The hardness value of the alloy added with Hf decreases more slowly than that of the Al-Er binary alloy sample as time goes on, which shows that its thermal stability has been greatly improved. However, the Al-Zr binary alloy aged at this temperature for 500 hours did not show strengthening phenomenon, and the alloy added with Er showed obvious age hardening, indicating that the presence of Er promoted the precipitation of Hf.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com