Silicon wafer cleaning process
A silicon wafer cleaning and process technology, applied in cleaning methods and utensils, cleaning methods using liquids, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective removal of metals, weak reaction ability, easy adsorption of particle impurities, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0012] The silicon wafer cleaning process of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
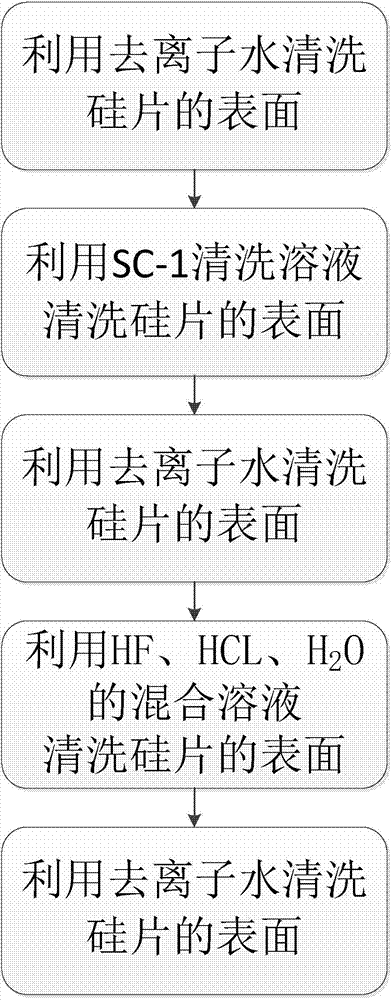
[0013] Such as figure 1 As shown, in the silicon wafer cleaning process of the present invention, the first step is to clean the surface of the silicon wafer with deionized water. The second step is to use SC-1 cleaning solution to clean the surface of the silicon wafer to remove particulate organic matter, etc. In order to improve the cleaning effect and enhance the removal ability, a multi-tank cleaning method is adopted. The third step is to use deionized water to clean the surface of the silicon wafer to remove the liquid medicine in the previous tank. In order to improve the cleaning effect and enhance the removal ability, a multi-tank cleaning method is adopted. The fourth step, using HF, HCL, H 2 The mixed solution of O cleans the surface of the silicon wafer, in which HF, HCL, H 2 The ratio of O mixed solution ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com