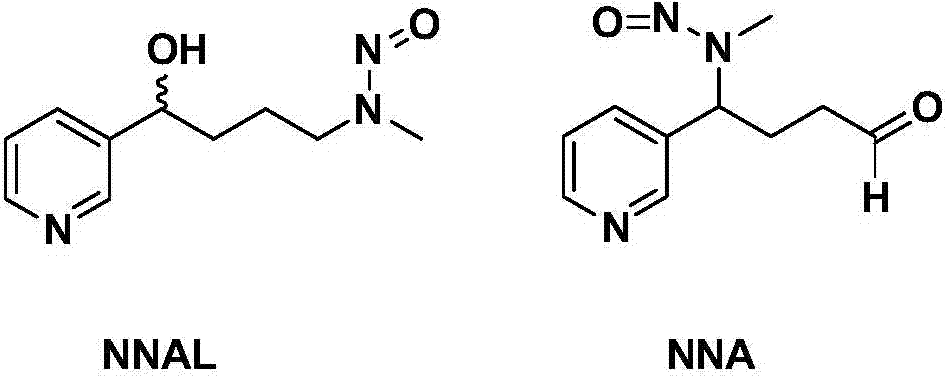
Method for detecting NNAL (4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol) and NNA in cut tobacco and cigarette smoke
A cigarette smoke and shredded tobacco technology, applied in the field of tobacco chemical inspection, can solve the problems of difficult detection, low nitrosamine content, complex tobacco extract and smoke matrix, and achieve easy popularization and application, low detection limit, and stability Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The mensuration of embodiment 1 cigarette sample NNAL and NNA release
[0026] Chemical reagent preparation: 4-(-methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-butanol (NNAL) (racNNAL, CAS No. 76014-81-8), 4-(methylnitrosamino )-4-(3-pyridyl)butyraldehyde (NNA) (CAS No. 64091-90-3), 4-(methyl-d3-nitrosoamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butan Aldehydes (NNA-methyl-d3).
[0027] (1) Standard curve establishment:
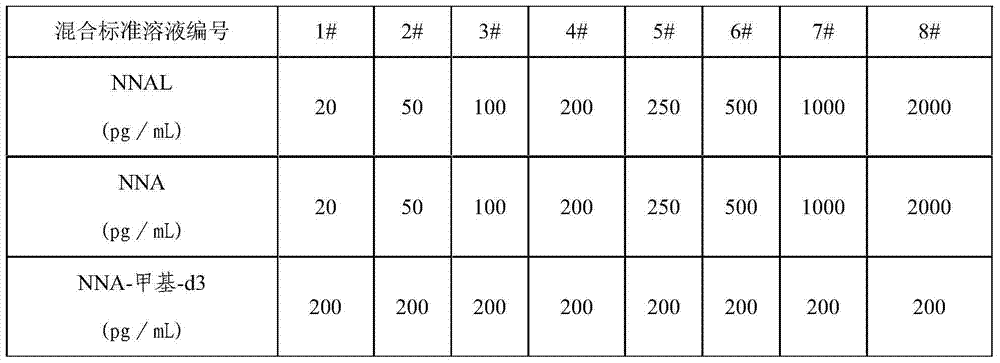
[0028] Using acetonitrile as solvent, prepare NNAL, NNA and NNA-methyl-d3 standard single standard solutions with a concentration of 1 μg / mL, retaining four significant figures; using acetonitrile as solvent, prepare NNAL, NNA and NNA according to Table 2 -The mixed standard solution of methyl-d3; With the ratio of the concentration of NNA in the HPLC-MS-MS chromatogram and the concentration of NNA-methyl-d3 as abscissa, the quantitative ion pair peak area of NNA in the chromatogram and NNA -The ratio of quantitative ion to peak area of methyl-d3 is ordinate, establishes the stan...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The mensuration of NNAL and NNA in the shredded tobacco sample of embodiment 2
[0038] Repeat Example 1 to establish a standard curve and test samples, with the following differences: Accurately weigh 2.0 g of shredded tobacco into a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask with a stopper, add 20 μL (1 ng / mL) of NNA-methyl-d3 solution, add 10 mL Ammonium formate aqueous solution with a concentration of 10mmol / L was shaken at room temperature for 20 minutes, the supernatant was taken, passed through a 0.2μm aqueous phase filter membrane, and detected by HPLC-MS-MS. Using the standard solution working curve of NNAL and the standard solution working curve of NNA to calculate the NNAL and NNA in the shredded tobacco sample, and then convert the contents of NNAL and NNA in the shredded tobacco sample to be 5.78ng / g and 10.46ng / g, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3 Determination of NNAL and NNA in Total Particulate Matter of Cigarette Mainstream Smoke
[0040]Repeat Example 1 to establish a standard curve and sample detection, with the following differences: 20 cigarettes were smoked under standard smoking conditions, and 20 μL (1ng / mL) NNA-methyl-d3 solution, then add 14mL of dichloromethane and shake (45min, 160rpm) to extract. After the extract was evaporated to dryness, it was reconstituted with 500 μL of dichloromethane, and 1 mL of 0.1 mol / L HCl solution was added, vortexed to mix, and then left to separate layers. The upper aqueous phase was transferred to a clean glass bottle, and 120 μL of 1 mol / L NaOH solution was added to The sample was purified on a Waters Oasis HLB solid-phase extraction cartridge activated with 2 mL of methanol and 2 mL of water respectively, rinsed with 2 mL of 5% methanol aqueous solution, and finally eluted with 2 mL of methanol. The eluate was evaporated to dryness and dissolved in 10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com