Power transmission line wind-deviation fault intelligent identification method
An identification method and transmission line technology, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring electrical variables, measuring devices, etc., to achieve the effect of clear physical concepts and clear judgment ideas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
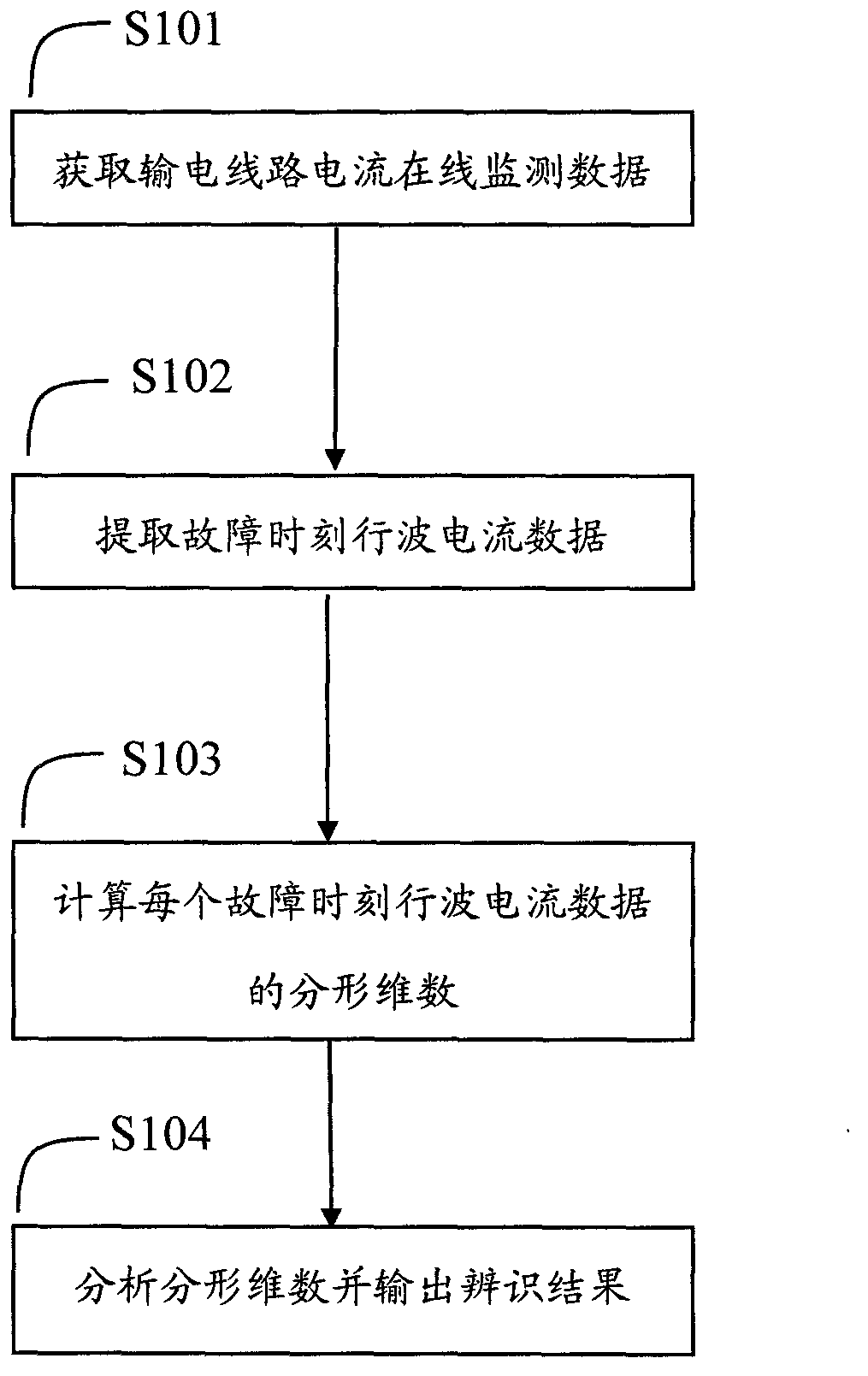
[0014] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a step-by-step flowchart of an identification method for a lightning strike transmission line lightning protection line and a pole tower according to the present invention.
[0015] Described measuring method comprises the following steps:
[0016] Step S101, acquiring online monitoring data of transmission line current.
[0017] In this step, an online current monitoring device is installed on the phase conductors of the three phases A, B, and C of the transmission line. On the one hand, the device can record the traveling wave current propagating on the transmission line and its GPS time stamp when the electromagnetic disturbance occurs in the power system On the other hand, when the transmission line fails and trips, the device can record the power frequency fault current and its GPS time stamp.
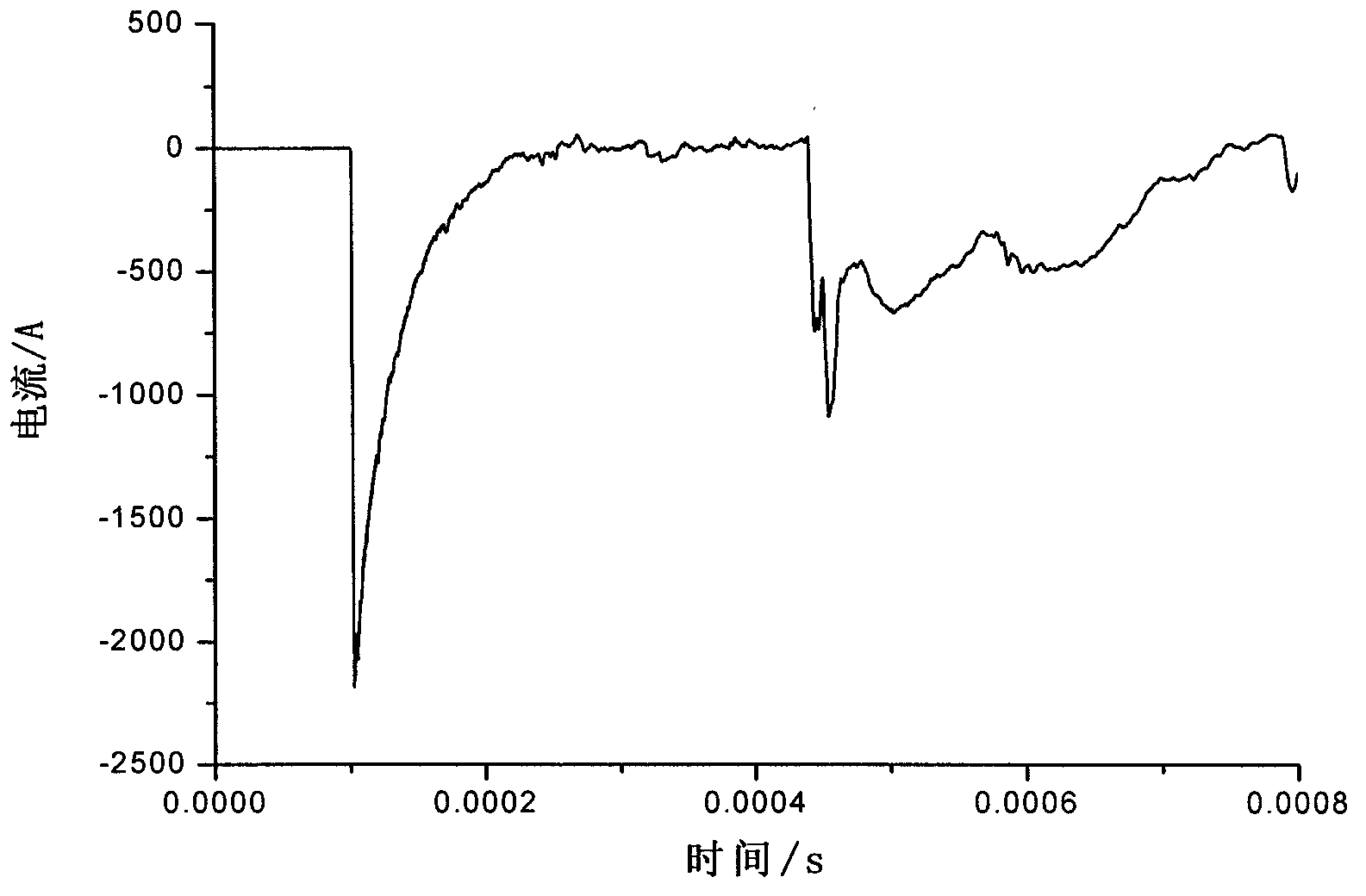
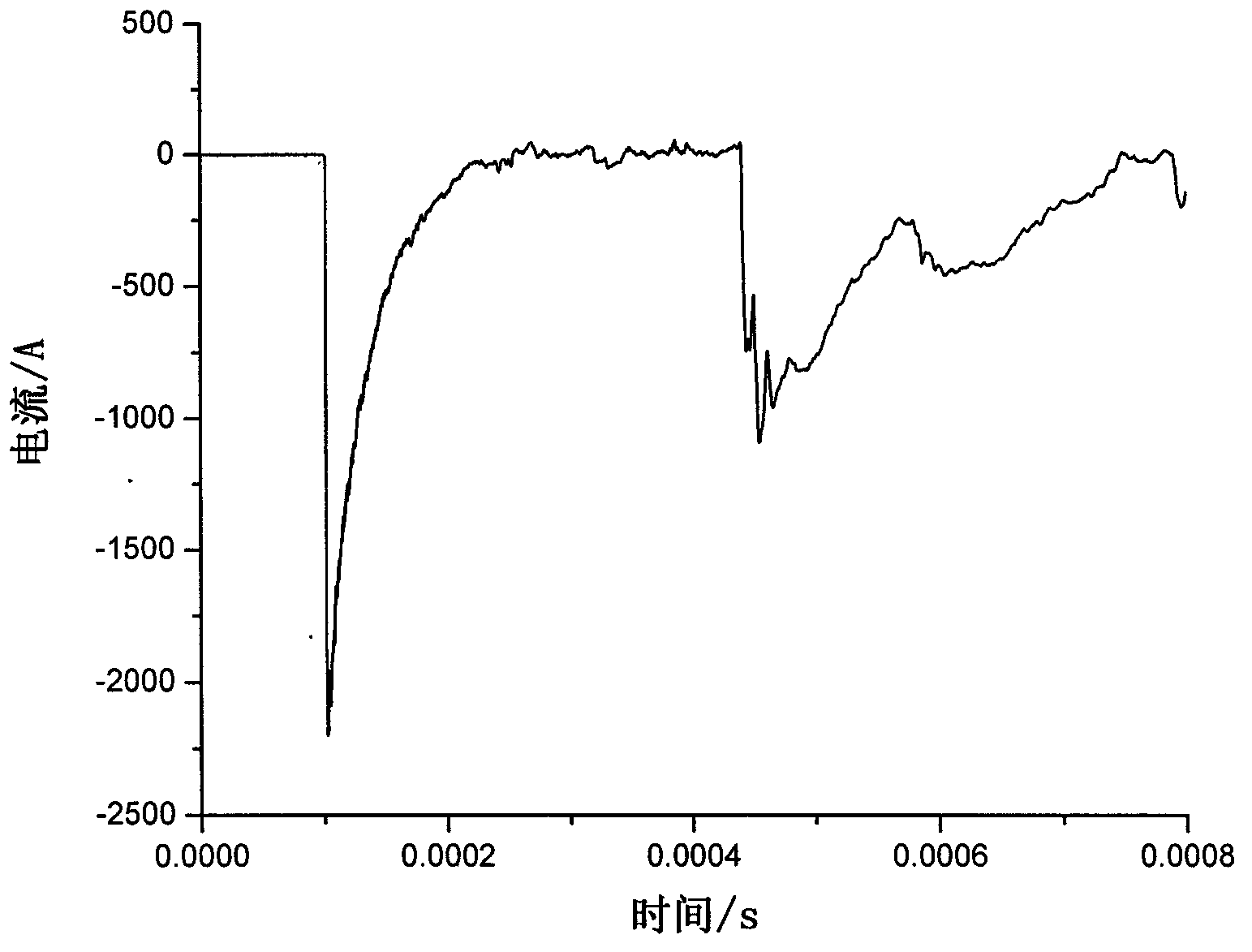
[0018] Step S102, extracting the traveling wave current data at the fault time.
[0019] Preferably, the traveling wave current data with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com