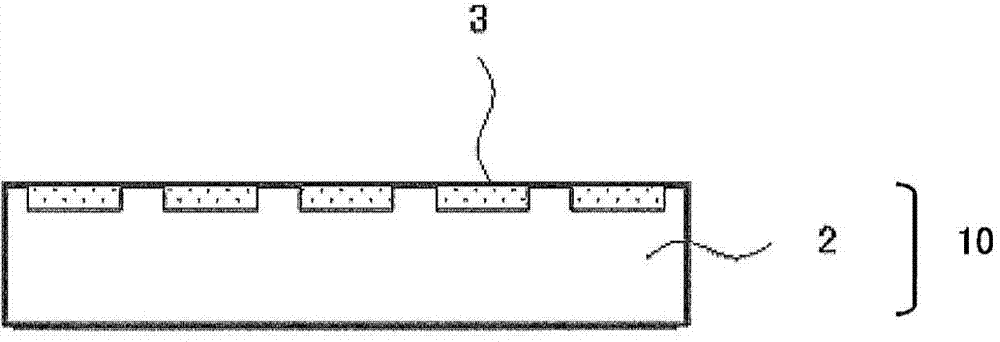
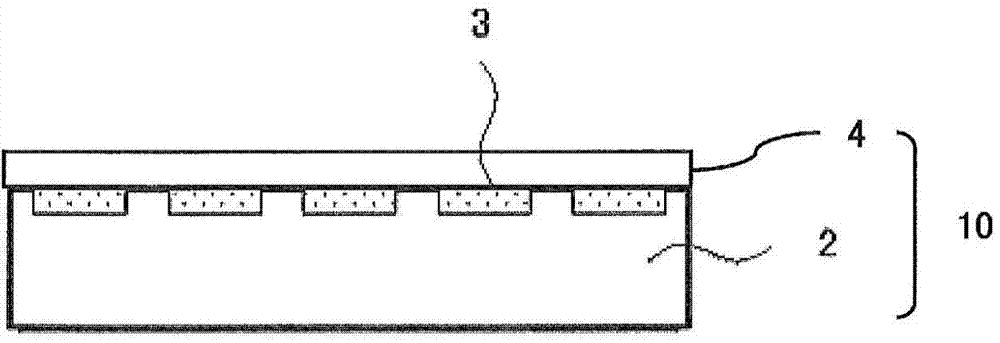
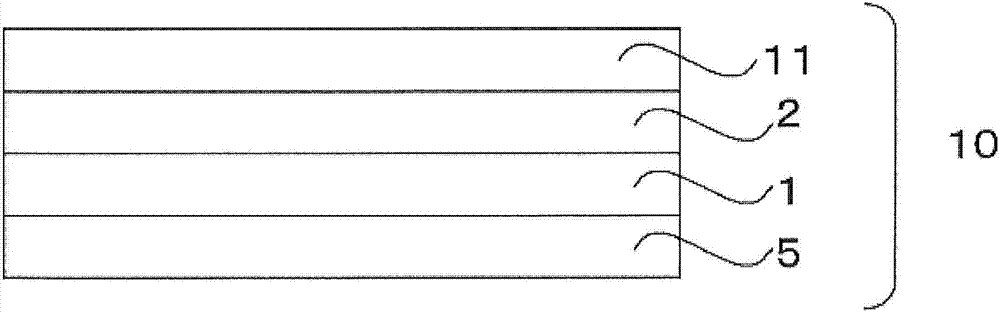
Heat ray shielding material
A technology of heat ray shielding and metal particles, applied in the direction of thin material processing, instruments, coatings, etc., to achieve the effect of good visible light transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0190] Features of the present invention will be described more specifically with reference to Examples given below.
[0191] In the following examples, materials used, their amounts and ratios, processing details, and processing procedures can be appropriately modified or changed without exceeding the scope of the present invention. Therefore, the scope of the present invention should not be limitedly interpreted by the Examples mentioned below.
manufacture example 1
[0192] (Manufacturing Example 1: Preparation of silver plate particle dispersion B1)
[0193] -Synthesis of silver plate particles (preparation of silver plate particle dispersion A)-
[0194] --Synthesis steps of flat core particles-
[0195] 2.5 ml of a 0.5 g / l polystyrene sulfonic acid aqueous solution was added to 50 ml of a 2.5 mM sodium citrate aqueous solution, and heated to 35°C. 3 ml of a 10 mM aqueous solution of sodium borohydride was added to the above solution, and 50 mL of a 0.5 mM aqueous solution of silver nitrate was added thereto at a rate of 20 mL / minute under stirring. The resulting solution was stirred for 30 minutes to prepare a seed solution.
[0196] --FIRST GROWTH STEP OF PLATE PELLETS-
[0197] Next, 2 mL of an aqueous 10 mM ascorbic acid solution was added to 250 mL of the seed solution and heated to 35°C. Under stirring, 79.6 mL of 0.5 mM silver nitrate aqueous solution was added to this solution at a rate of 10 mL / minute.
[0198] --Second Gro...
Embodiment 1
[0217] -Preparation of Coating Solution 1-
[0218] Coating liquid 1 having the composition shown below was prepared.
[0219] Composition of Coating Solution 1:
[0220]
[0221]
[0222] -Formation of Metal Particle Containing Layer-
[0223] Coating liquid 1 was applied onto the surface of a PET film (Cosmoshine A4300, Toyobo, thickness 75 μm) using a wire-wound bar so that the average thickness after drying could be 0.08 μm (80 nm). Subsequently, it was heated at 150° C. for 10 minutes, dried, and cured to form a metal particle-containing layer, whereby the heat ray shielding material of Example 1 was produced.
[0224] The average thickness of the metal particle-containing layer after drying was determined as follows: Using a laser microscope (VK-8510, Keyence), the thickness of the PET film that was not coated with the coating solution 1 was measured and the thickness of the PET film was measured after coating the coating solution 1, heating, The thickness of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com