Dot matrix sandwich structure of wooden engineering composite material
A technology of engineering composite materials and sandwich structures, applied in the field of building materials, can solve problems such as low strength and stiffness, competition of building materials, high prices, etc., and achieve the effect of improving strength, broad market prospects, and high specific strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
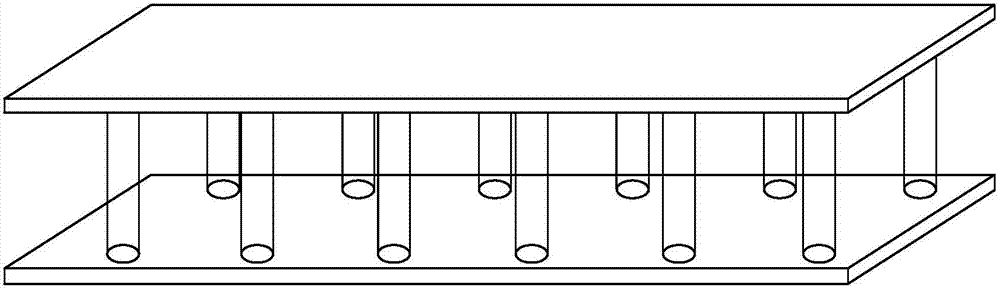
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, a wood engineering composite material straight-column lattice sandwich structure, which includes a first panel, a core layer, and a second panel.
[0036] The core layer includes a straight-column lattice structure and a filler filled with a straight-column lattice structure, and is partially reinforced with a fiber-reinforced material and bonded with an adhesive.
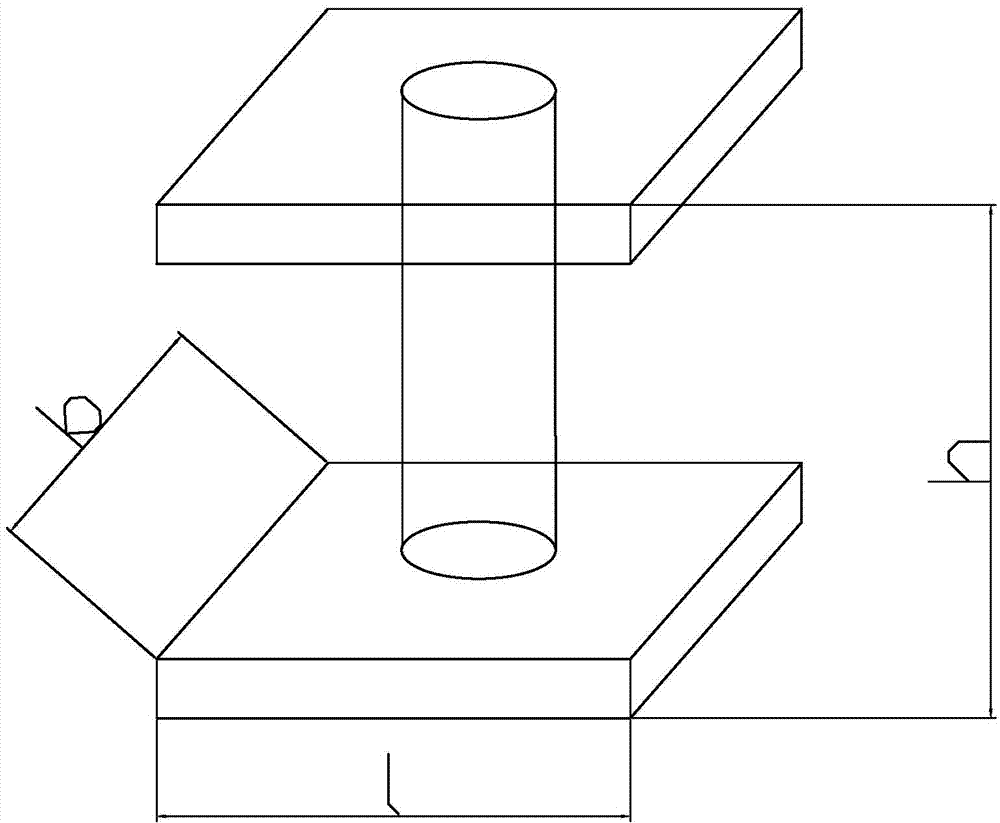
[0037] The straight-column lattice structure is periodically distributed in the core layer according to its unit specification design. Such as figure 2 As shown, the specification design of the straight column unit is: length l=32*n mm, width b=32*n mm, height (h) is 3 to 10 times the thickness of the panel, n=1 to 10. According to the unit specifications of the straight column type, mortise on the panel 1 and panel 2. The diameter of the mortise is 6-50mm, and the depth of the mortise is 1 / 3-2 / 3 times the thickness of the panel. Stick the lattice column with cloth. Insert pane...
Embodiment 2
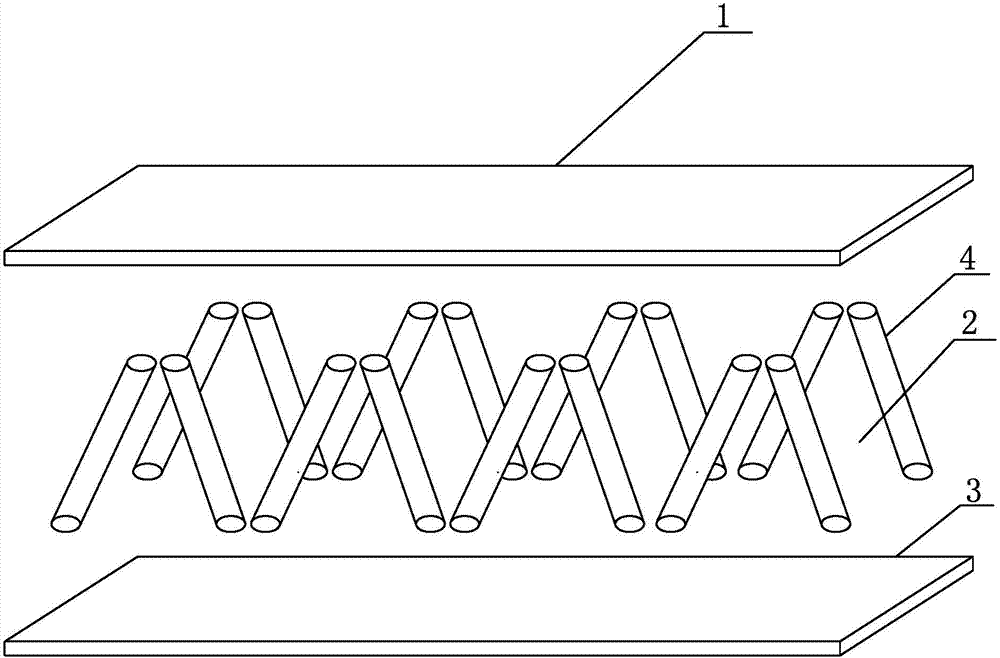
[0040] Such as image 3 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that its lattice structure is oblique column type, such as Figure 4 As shown, the lattice column and the panel form an angle w, w=20°~70°, and the specification design of the oblique column type unit: the height h is 3 to 10 times the panel thickness, and the length l=2*h / sin w+10mm , Width b=32*n mm, n=1~10. There are two ways of mortise joint, one is that half of the mortise is uniform in depth, and the other half is drilled through the panels, and the shorter dot matrix columns are dipped in cloth adhesive and inserted into the corresponding mortise grooves on panels 1 and 2. The longer dot matrix columns are inserted into the corresponding tenon grooves on panels 1 and 2, and the diameter of the dot matrix columns is slightly larger than the tenon grooves; the other is that the tenoning depth is all uniform, and the dot matrix columns coated with adhesive and the panels are 1. P...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the difference between the present embodiment and the second embodiment is that the lattice structure is tetrahedral, and the lattice columns and the second panel form an angle w, w=20°-70°. Such as Figure 8As shown, the specification design of the tetrahedral unit: the height h is 3 to 10 times the panel thickness, the length l=hcos30° / sin w+10mm, and the width b=h / sin w+10mm. The filler of the core layer is carbon black. The tetrahedral lattice sandwich structure further improves the shear performance compared with the inclined column lattice sandwich structure, and the filler-carbon black adds electromagnetic shielding function to it, which can be used in special structures that require electromagnetic shielding function.
[0044] The lattice column is made of glass fiber rods; panels 1 and 2 are made of solid wood sawn timber; the fiber reinforced material is made of carbon fiber mesh cloth; the adhesive is made of phenolic resin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com