Sub-module layering voltage-sharing method of modularized multi-level current converter
A modular multi-level, sub-module technology, applied in the direction of converting AC power input to DC power output, electrical components, output power conversion devices, etc. Influence and other issues, to reduce the loss and the risk of equipment failure, improve the dynamic response characteristics, reduce the effect of switching frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In order to describe the present invention more specifically, the technical solutions of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
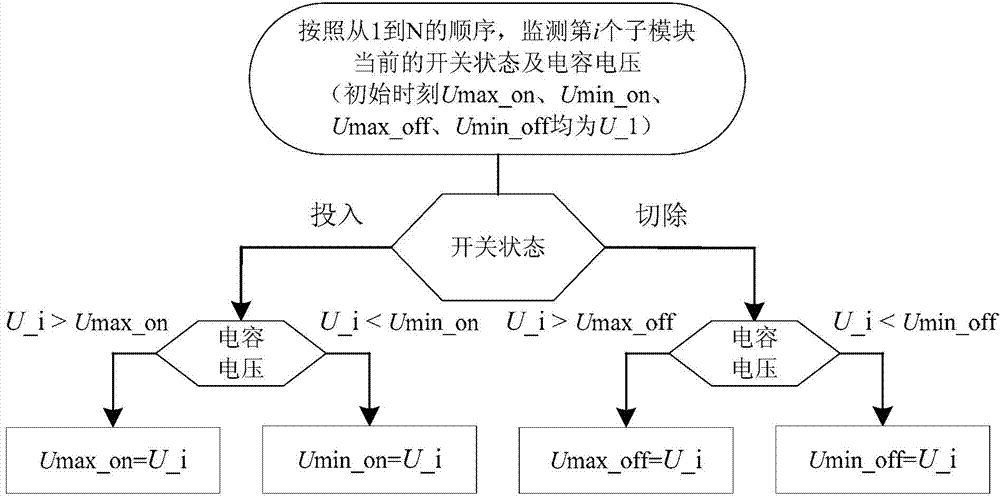
[0033] A sub-module layered voltage equalization method for a modular multilevel converter, the specific steps comprising:
[0034] Step 1: For each bridge arm, monitor the initial switching state of the bridge arm sub-module, record the maximum and minimum values of the capacitor voltage, and monitor the phase θ of the AC voltage of this phase j .
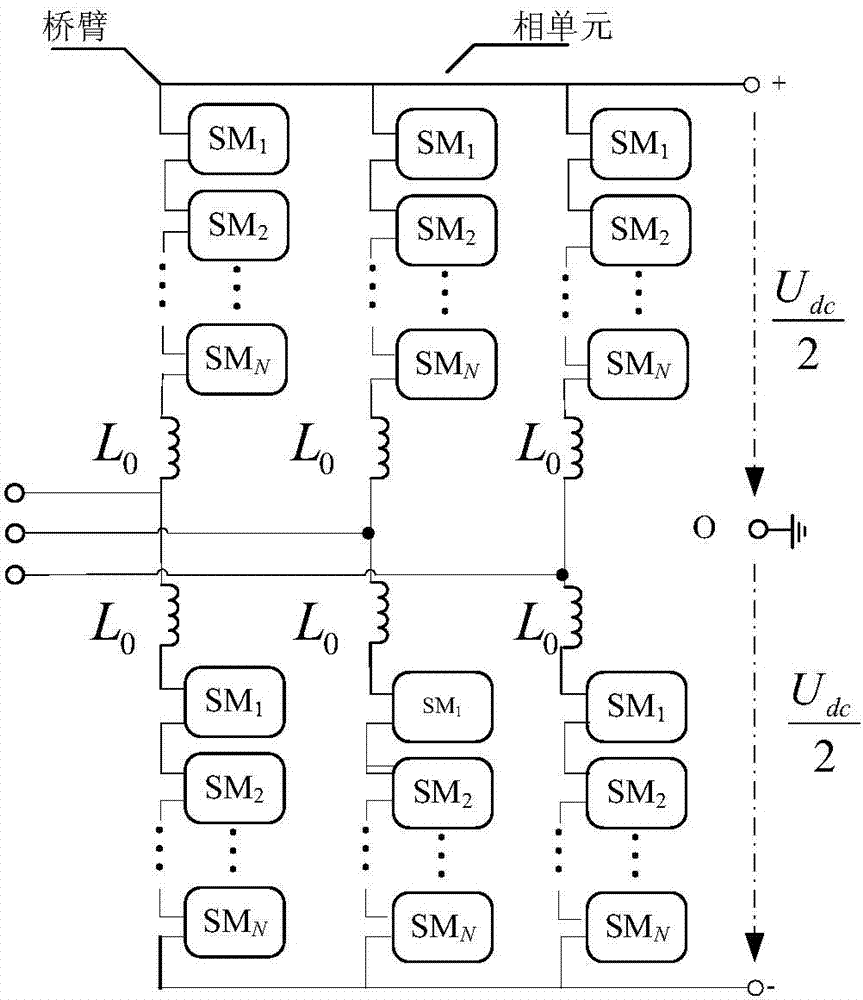
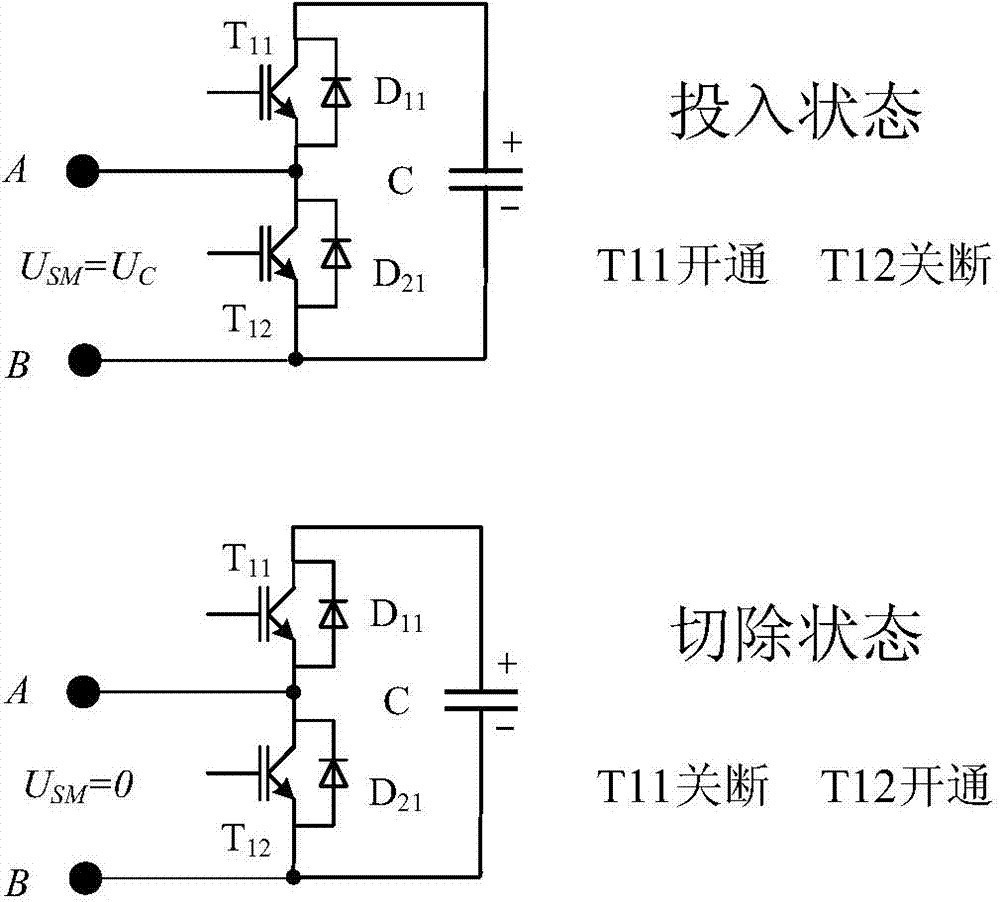
[0035] The MMC topology adopts a three-phase six-leg structure such as figure 1 As shown, each bridge arm is formed by cascading N basic operating power units, and a snubber reactance L is configured at the same time 0 To suppress the rate of rise of circulating current and fault current. udc is the MMC bipolar DC bus voltage difference. Sub-modules in existing projects generally adopt a half-bridge str...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com