Robot-assisted no-coupling fast-changing titanium clamp surgical device for minimally invasive surgery
A robot-assisted, minimally invasive surgery technology, used in surgery, wound clips, applications, etc., can solve problems such as the lack of titanium clip surgical devices, and achieve the effect of rapid replacement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
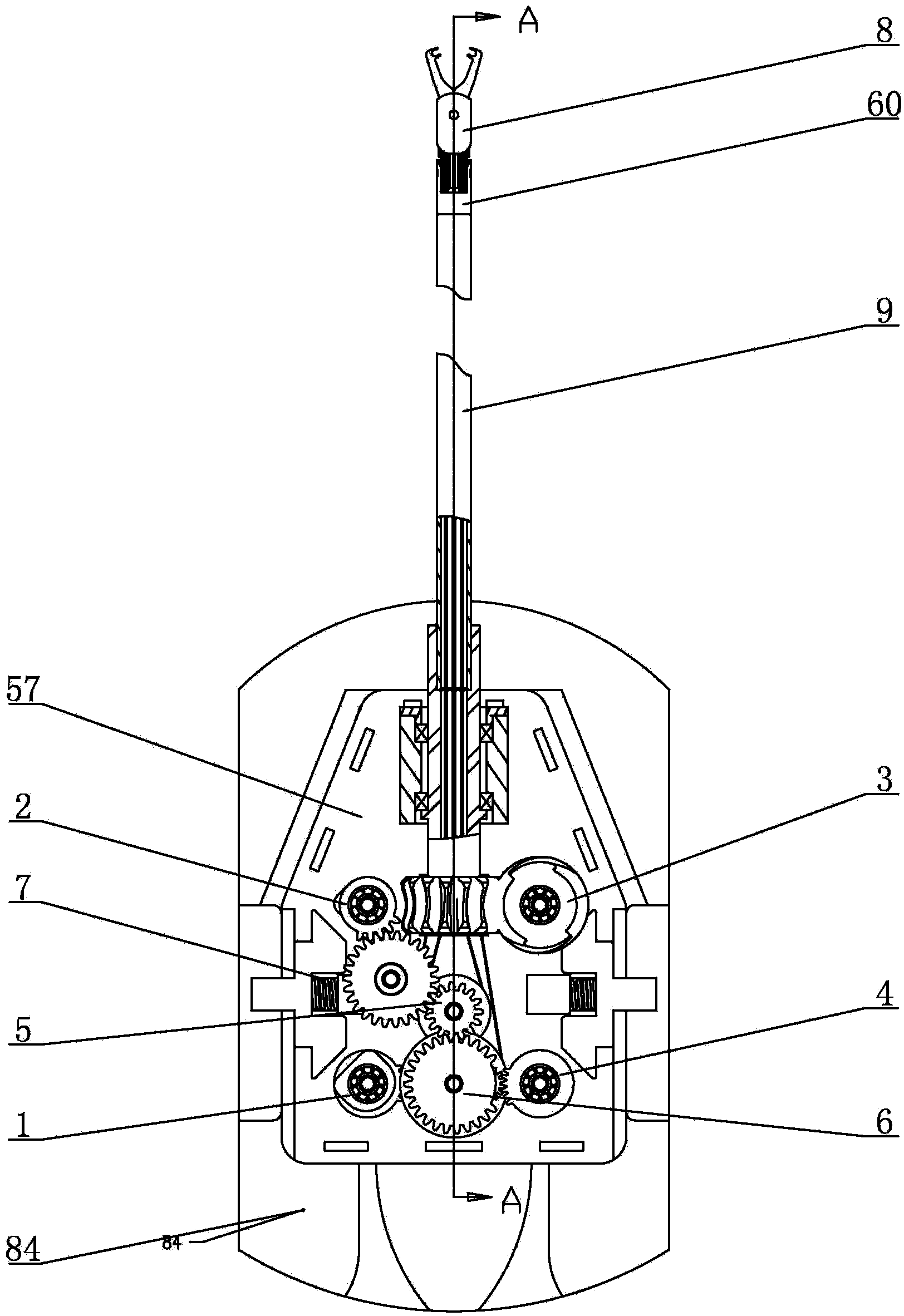
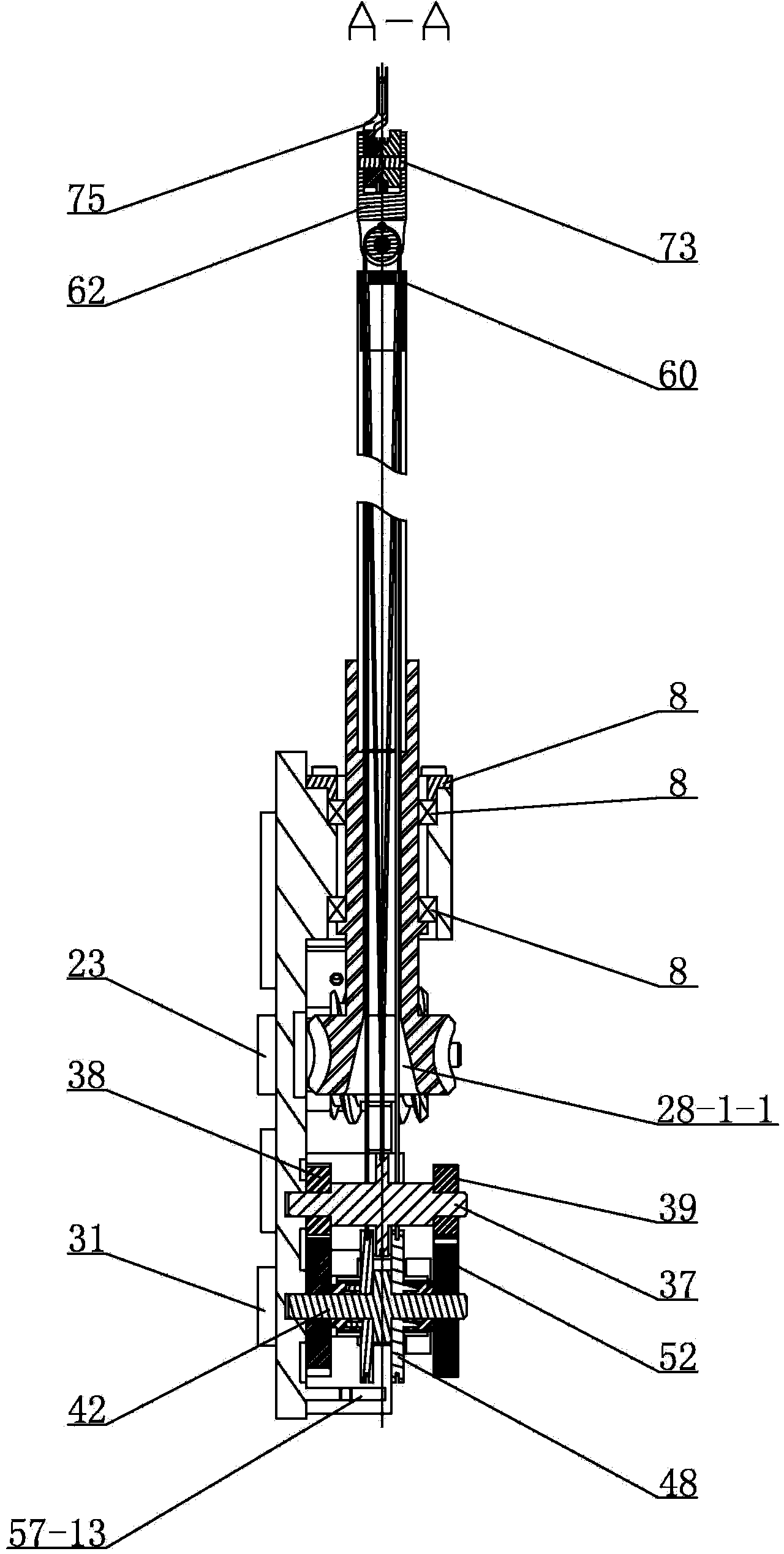
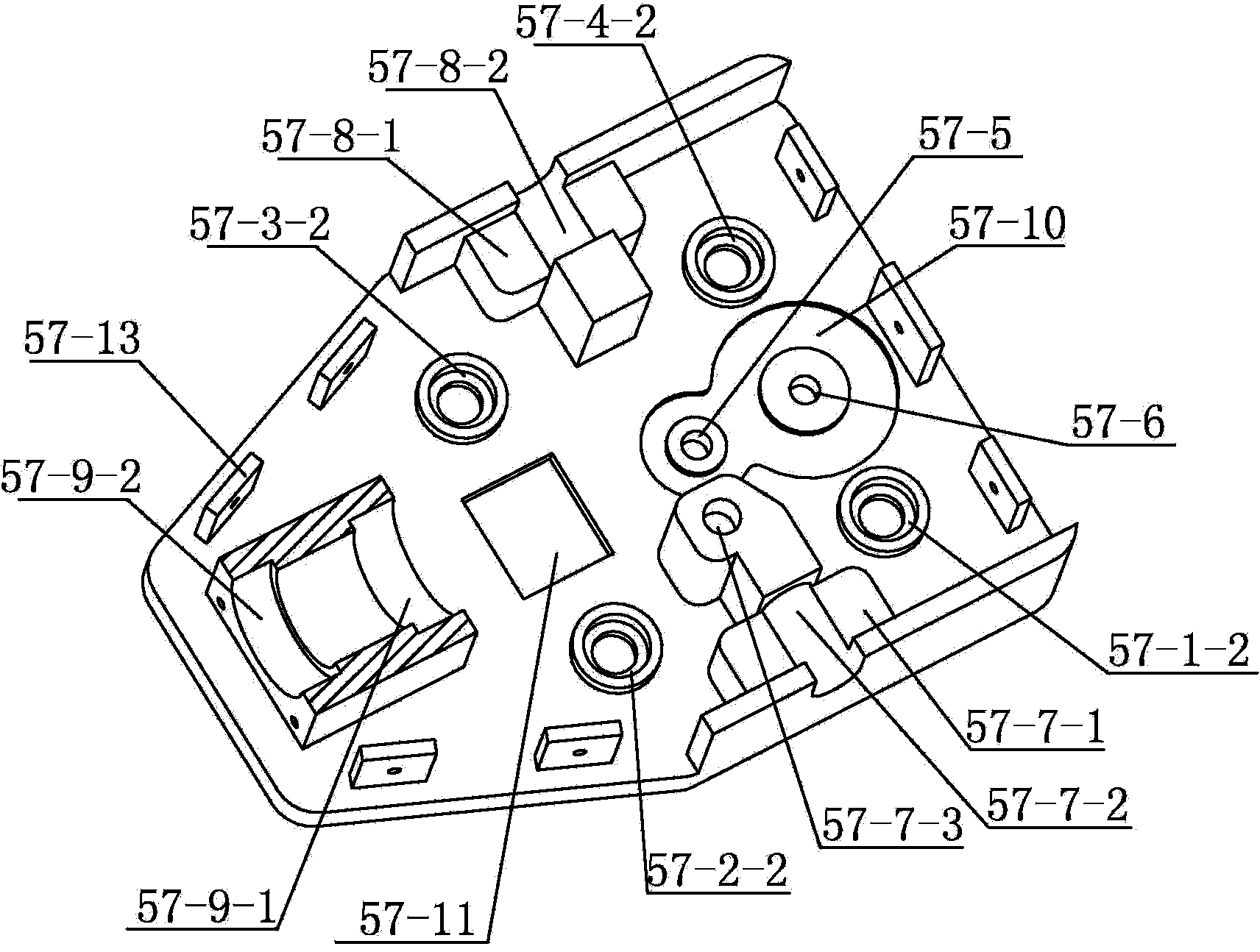
[0007] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 with figure 2 Describe this embodiment. The non-coupling quick-change titanium clamp surgical device for robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery in this embodiment includes a left small claw transmission mechanism 1, a wrist transmission mechanism 2, a sleeve transmission mechanism 3, and a right small claw transmission mechanism. Mechanism 4, first guiding mechanism 5, second guiding mechanism 6, transmission reset mechanism 7, end effector 8, bushing 9, adapter base 57, adapter upper cover 58, bearing seat baffle 59, wrist connector 60, Wrist traction lower steel wire 76, wrist traction upper steel wire 77, left small claw traction left steel wire 78, left small paw traction right steel wire 79, right small paw traction left steel wire 80, right small paw traction right steel wire 81, drive interface base 84 , four baffle screws 82 and seven assembly screws 83, the end effector 8 is connected to one end of the cas...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0008] Specific implementation mode two: combination Figure 7 with Figure 8 Describe this embodiment, the left small claw transmission mechanism 1 of the non-coupling quick-change titanium clamp surgical device for robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery described in this embodiment includes a left small claw transmission clutch disc 10, a left small claw transmission rear bearing 11, The left small claw transmission shaft 12, the left small claw transmission gear 13, the left small claw transmission reset wheel 14, the left small claw transmission bushing 15 and the left small claw transmission front bearing 16, the left small claw transmission shaft 12 is divided in sequence from back to front One section 12-1 of the left small claw transmission shaft, two sections 12-2 of the left small claw transmission shaft, three sections 12-3 of the left small claw transmission shaft, four sections 12-4 of the left small claw transmission shaft, and the rear bearing of the left sma...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0011] Specific implementation mode three: combination image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Image 6 , Figure 9 with Figure 10Describe this embodiment, the wrist transmission mechanism 2 of the non-coupling quick-change titanium clip surgical device for robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery described in this embodiment includes a wrist transmission clutch disc 17, a wrist transmission rear bearing 18, a wrist transmission Shaft 19, wrist drive reset wheel 20, wrist drive gear 21 and wrist drive front bearing 22, wrist drive shaft 19 is divided into wrist drive shaft section 19-1 and wrist drive shaft two sections from back to front in turn 19-2, the third section 19-3 of the wrist transmission shaft and the fourth section 19-4 of the wrist transmission shaft. The inner ring of the bearing 18 after the wrist transmission is set on the outer wall of the second section 19-2 of the wrist transmission shaft. The outer ring of the rear bearing 18 of the internal transmissio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com