Quasi-sinusoidal winding linear motor
A linear motor and quasi-sine technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of high manufacturing cost, large motor thrust fluctuations, and increased copper consumption, and achieve low manufacturing costs, reduce thrust fluctuations, The effect that insulation is easy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
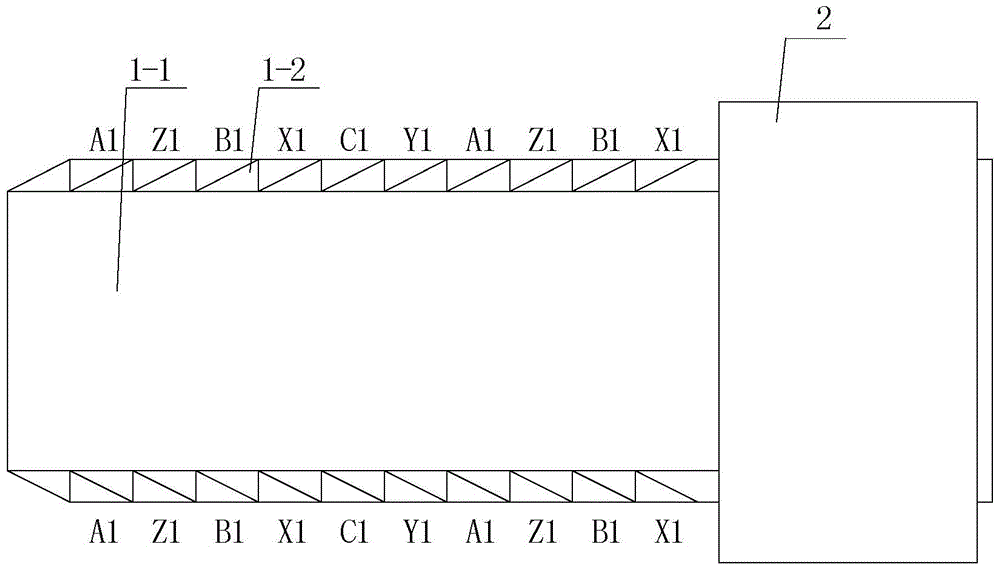
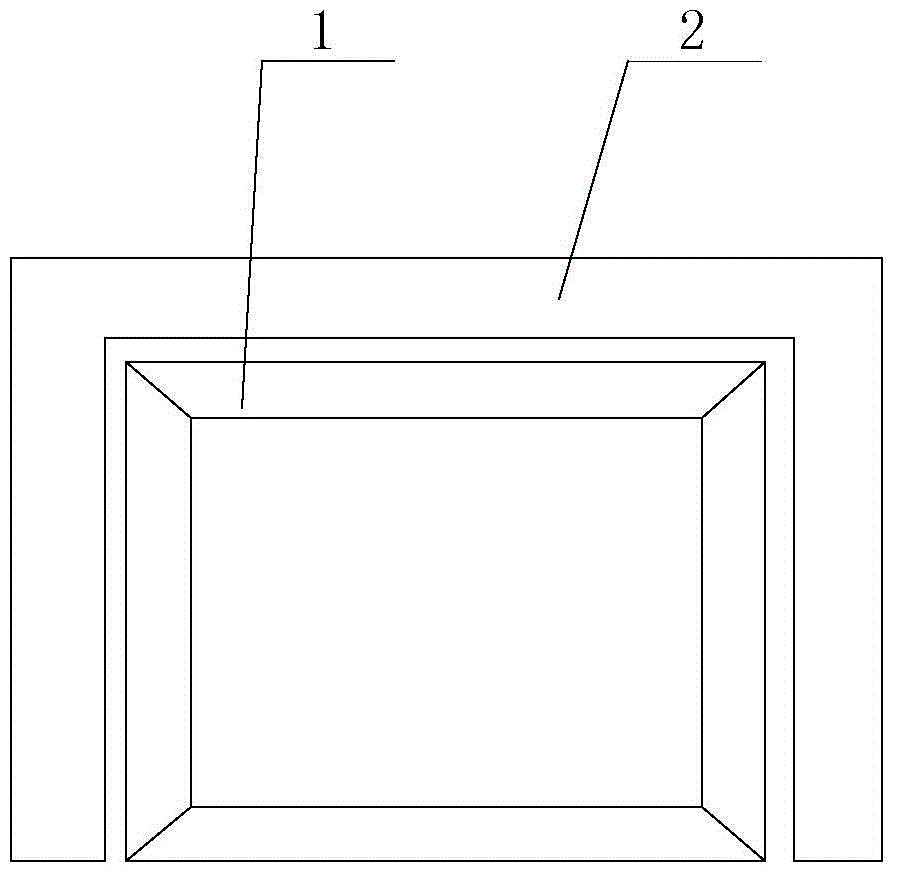
[0020] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 , figure 2 , Figure 5 and Figure 6 Describe this embodiment, the quasi-sinusoidal winding linear motor described in this embodiment includes a primary 1 and a secondary 2, the secondary 2 is a single-sided, double-sided, three-sided or four-sided structure, the opposite surfaces of the primary 1 and the secondary 2 An air gap is formed between them; the primary 1 includes a primary iron core 1-1 and a primary winding 1-2, the cross section of the primary iron core 1-1 along the direction of relative movement is rectangular, and the side surface of the air gap of the primary iron core 1-1 is a smooth plane;
[0021] The primary winding 1-2 is an m-phase winding, and m is the number of phases of the motor; within the range of each pole pitch of the primary core 1-1, m winding coils are closely arranged in sequence along their relative motion direction, and each winding coil is rectangular. Surroun...
specific Embodiment approach 2
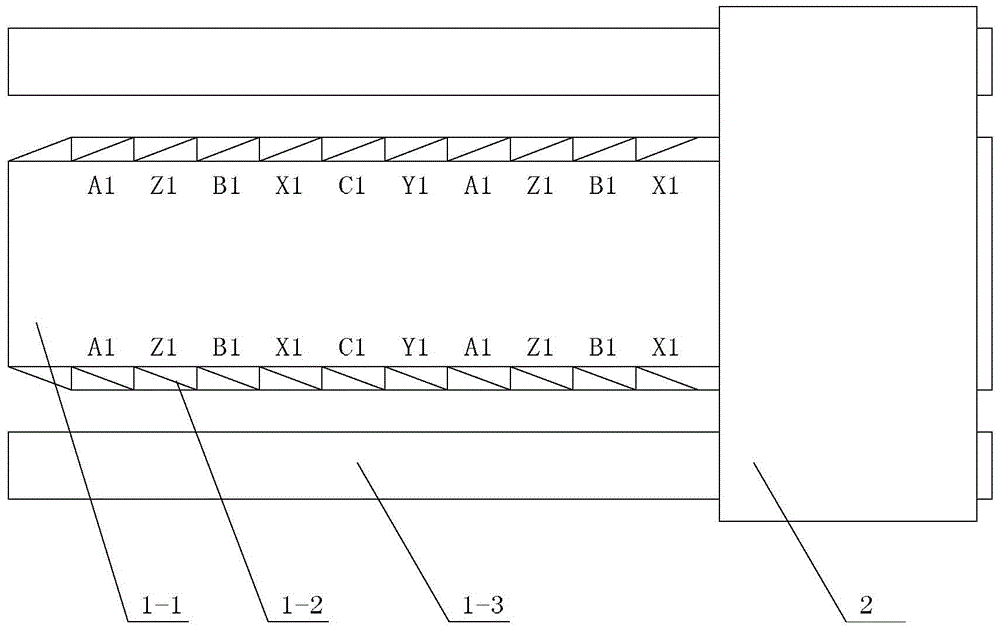
[0023] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1. The secondary 2 in this embodiment has a double-sided, three-sided or four-sided structure. The primary 1 also includes two auxiliary primary cores 1-3, two auxiliary primary cores 1-3 is symmetrically arranged on both sides of the primary core 1-1, placed in parallel with the primary core 1-1, and the two symmetrical secondary sides of the secondary 2 are respectively located on the primary core 1-1 and the corresponding auxiliary primary core 1 Between -3, air gaps are formed between the primary core 1-1 and the secondary 2 and between the auxiliary primary core 1-3 and the secondary 2, and the cross-section of the auxiliary primary core 1-3 along the direction of relative movement is rectangular.
[0024] In this embodiment, the auxiliary primary core 1-3 forms a part of the main magnetic circuit of the motor...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0025] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1. The secondary 2 in this embodiment has a double-sided, three-sided or four-sided structure. The real wire motor also includes two auxiliary primary, and the two auxiliary primary mirrors are symmetrical Set on both sides of the primary core 1-1, placed in parallel with the primary core 1-1, the two symmetrical secondary sides of the secondary 2 are respectively located between the primary core 1-1 and the corresponding auxiliary primary, the primary core 1- Air gaps are formed between 1 and secondary 2 and secondary 2 and auxiliary primary; auxiliary primary includes auxiliary primary core and auxiliary primary winding, the cross-sections of auxiliary primary core and auxiliary primary winding are rectangular along their relative movement direction, auxiliary The arrangement of the auxiliary primary winding on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com