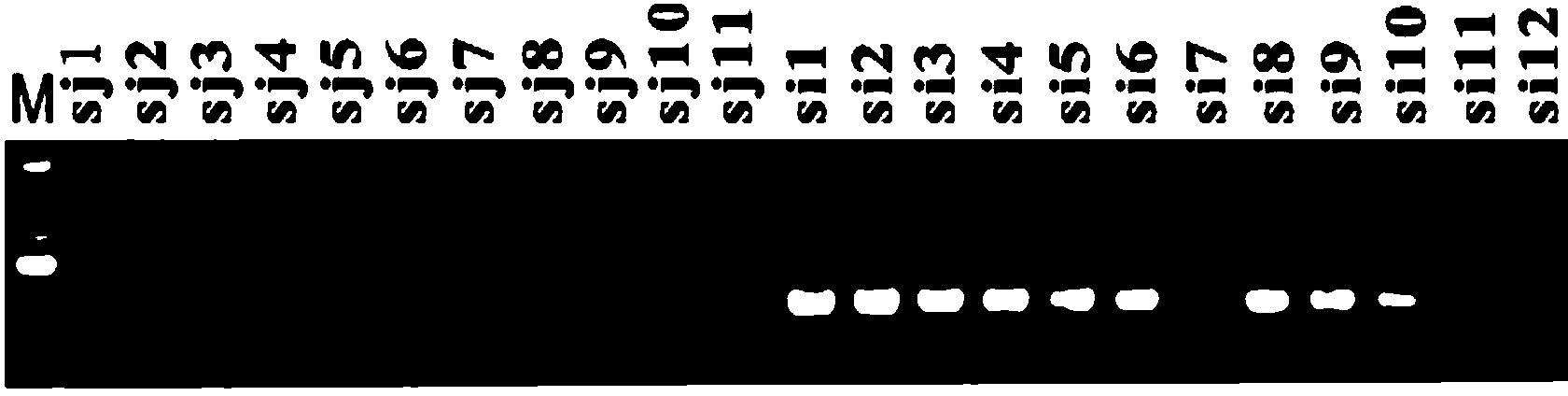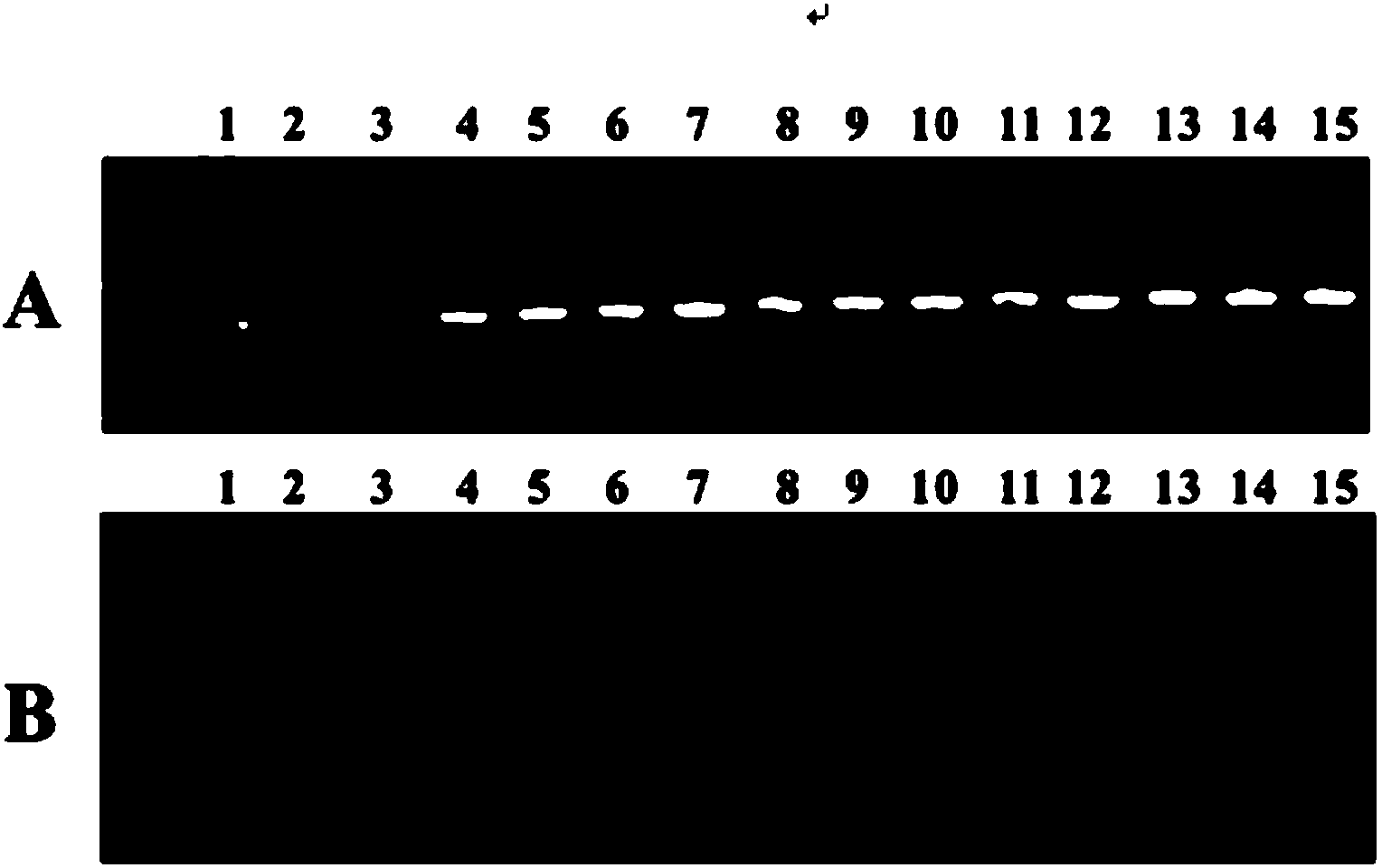Molecular marking method used for rice cytoplasm identification
A molecular marker and cytoplasmic technology, applied in the field of molecular markers for rice cytoplasmic identification, can solve the problems of cumbersome and complicated operations, time-consuming and labor-intensive operations, and achieve the effect of overcoming cumbersome and complicated operations, simple equipment, and reliable and stable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
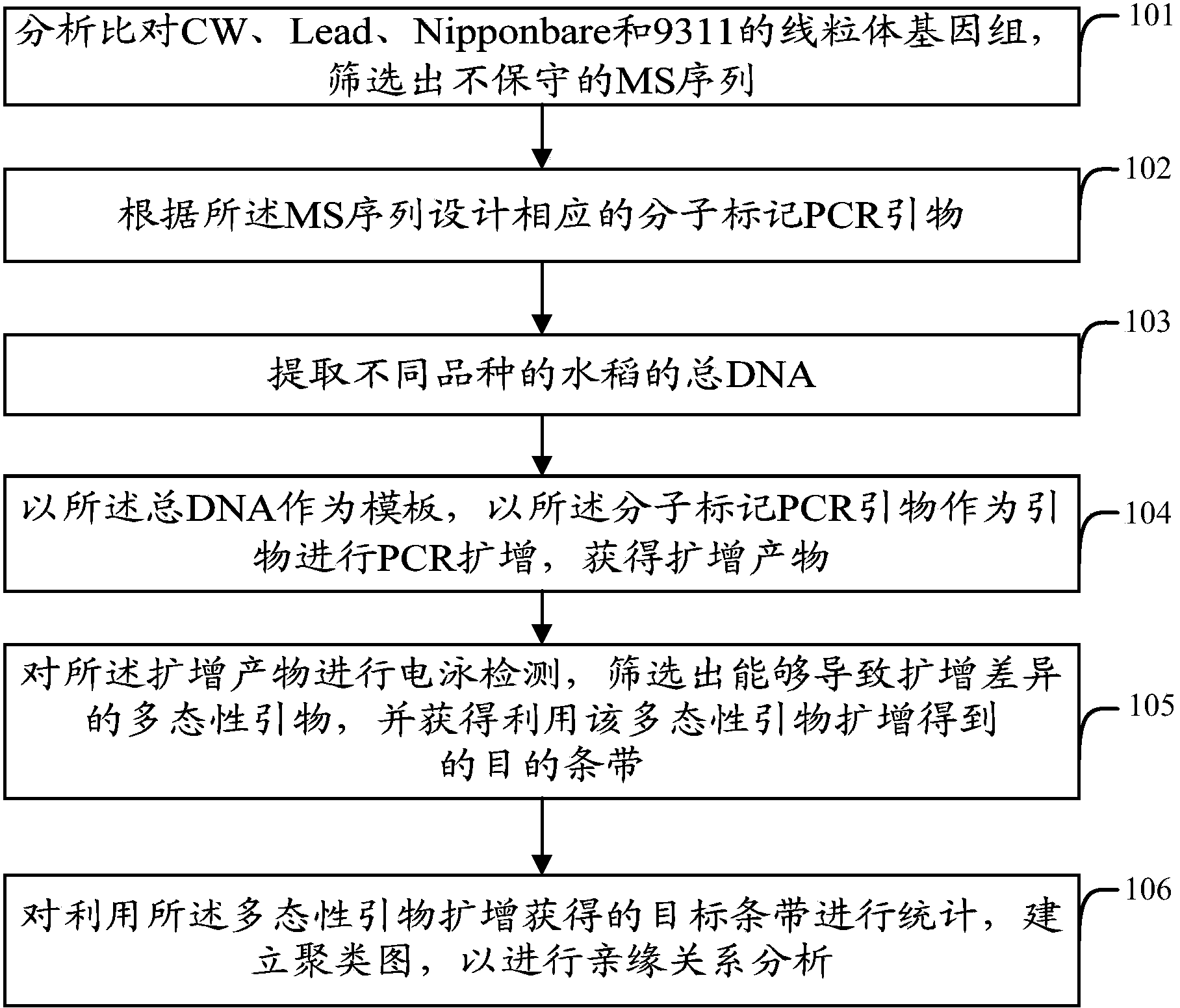
[0039] In the embodiment of the present invention, a molecular marker method for identification of rice cytoplasm is provided, including the following steps, please refer to figure 1 :
[0040] Step 101: analyze and compare the mitochondrial genomes of CW, Lead, Nipponbare and 9311, and screen out non-conserved MS sequences;
[0041] CW, Lead, Nipponbare and 9311 are the four rice varieties whose mitochondrial genome sequencing has been completed so far. 9311 is a typical indica rice variety. The CW cytoplasm is derived from Chinese common wild rice W1 (Oryza rufipogon), and the LD cytoplasm is derived from the indica rice variety Lead in Myanmar. In rice, the largest mitochondrial genome is CW (559,045bp), while LD is only 434,745bp. Synteny analysis shows that Nipponbare and 9311 are relatively conservative, while CW and LD differ from the other two sequenced rice genomes in sequence composition and arrangement Therefore, there are a large number of specific sequences (MS) ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The molecular marker method for rice cytoplasmic identification of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0058] 1. Analyze and compare the mitochondrial genomes of CW, Lead, Nipponbare and 9311, and screen out non-conserved MS sequences;
[0059] In this step, specifically, the mitochondrial genomes of CW, Lead, Nipponbare and 9311 were analyzed and compared using BLAST2 software, and 55 non-conserved MS sequences were screened out.
[0060] BLAST2 software is accurate for the comparison of mitochondrial genomes of different varieties of rice, and 55 non-conserved MS sequences can ensure the number of corresponding primers, thereby increasing the probability of high polymorphism in subsequent amplification.
[0061] 2. Design corresponding molecular marker PCR primers according to the MS sequence;
[0062] The above-mentioned steps are the same as steps 101-102 of the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
[0063] 3. Extract the total DNA ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com