Method for detecting storage condition of lonicera macranthoides bud medicinal material
A technique for detecting Lonicera saponin B and a detection method is applied in the storage field of traditional Chinese medicine Shan Yinhua, which can solve the problem of vague requirements, uneven quality of medicinal materials, inconsistent storage factors such as illumination, temperature, humidity, oxygen, time, etc. 1. Carry out research and control issues to achieve the effect of convenient practical operation and scientific method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Purchased 4 copies of Sanyinhua medicinal materials from 4 different stalls in the Chongqing Traditional Chinese Medicinal Materials Market, each 500g, all of which were identified as genuine Sanyinhua specified in the "Chinese Pharmacopoeia", marked as medicinal material 1, medicinal material 2, medicinal material 3 and medicinal material 4; Take another 1000g of Lonicerae pilosula flower buds collected in Xiushan County, Chongqing, steam them and dry them in a high-temperature dryer, and mark them as medicinal material 5.
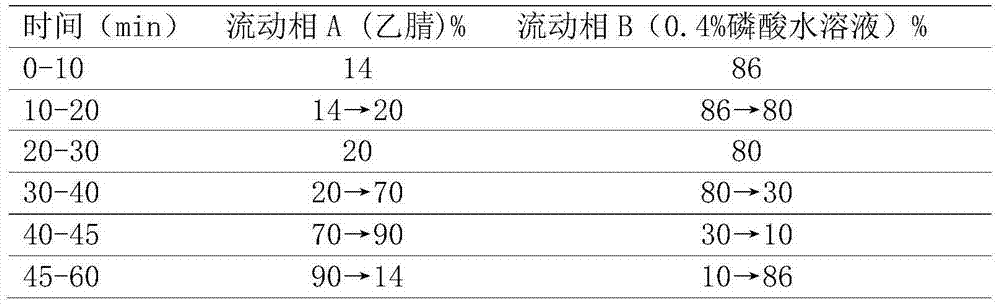
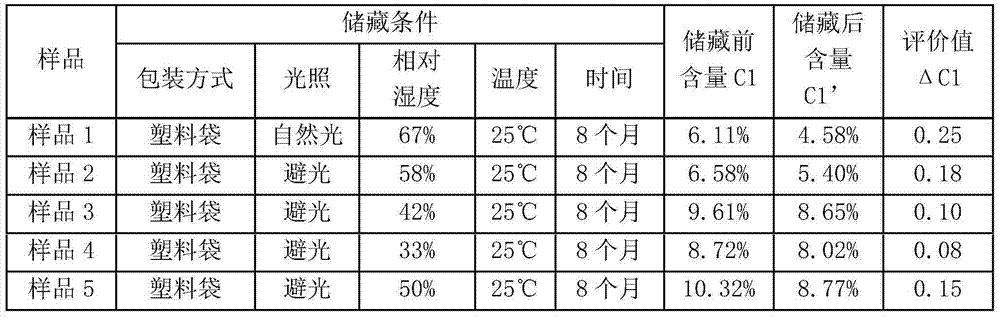
[0060] Take 10 g of each portion of medicinal materials 1-5 as samples 1-5, and measure the content C1 of chlorogenic acid therein by HPLC method. The above samples were stored under different conditions. After storage, the content C1' of chlorogenic acid was measured respectively, and the evaluation value ΔC1 was calculated according to the formula ΔC1=1-C1' / C1. The storage conditions and measurement results are shown in Table 3 :
[0061] Table ...
Embodiment 2
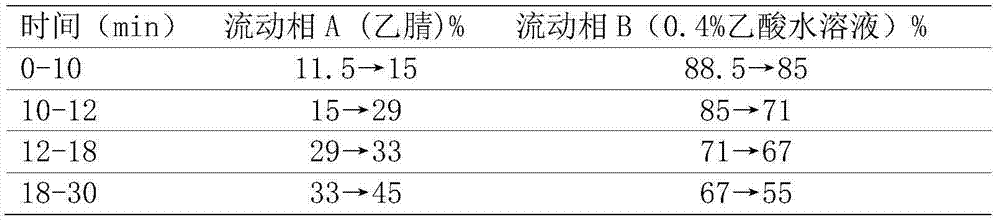
[0066] Take 10 g of medicinal materials 1-5 in Example 1 as samples 6-10, and measure the content C2 of caffeic acid in them by HPLC method. The above samples were stored under different conditions. After storage, the content C2' of caffeic acid was measured respectively, and the evaluation value ΔC2 was calculated according to the formula ΔC2=1-C2 / C2'. The storage conditions and results are shown in Table 4:
[0067] Table 4 The content change of caffeic acid in L. japonicus under different temperatures
[0068]
[0069] It can be seen that the change of the content of caffeic acid can better evaluate the influence of temperature during storage on L. japonicus. When the evaluation value ΔC2≤0.20, it can be considered that the medicinal material is stored in a "shady place", such as storage below 20°C.
Embodiment 3
[0071] 10 g of medicinal materials 1 to 5 in Example 1 were taken as samples 11 to 15, and the content C3 of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid was determined by HPLC. The above samples were stored under different conditions. After storage, the content C3' of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid was measured respectively, and the evaluation value ΔC3 was calculated according to the formula ΔC3=1-C3' / C3. Storage conditions and results are shown in Table 5:
[0072] Table 5 Changes in the content of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid in Flos Japonica under different vacuum conditions
[0073]
[0074] It can be seen that the change in the content of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid can better evaluate the effect of oxygen on Linica japonica during storage. When the evaluation value ΔC3≤0.15, it can be considered that the medicinal material is stored in vacuum packaging.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com