Method for hydrolyzing vegetable protein
A technology of hydrolyzing plant protein and plant protein, which is applied in the field of step-by-step hydrolyzing plant protein to produce feed raw materials, can solve the problems that cannot meet the production requirements of feed raw materials, and cannot deal with anti-nutritional factors extensively and deeply, so as to achieve thorough hydrolysis and reduce stress. Possibility of irritating reaction, wide adaptability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
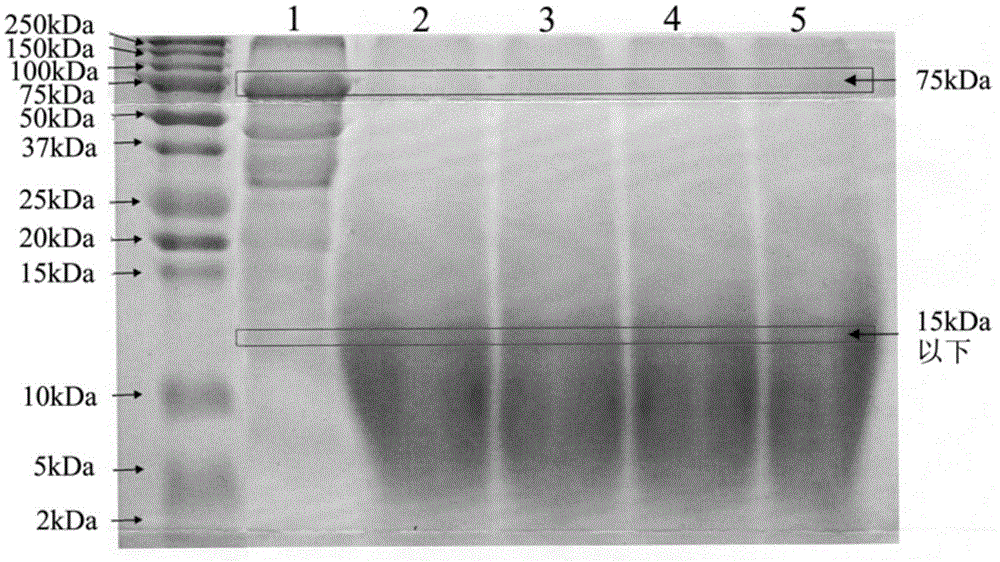
[0054] Weigh 100g of soybean meal powder, add 600ml of boiling water, and keep at 90°C for half an hour. Adjust the temperature to 55°C, pH 4-4.5, add a mixture of α-amylase, cellulase, hemicellulase, pectinase, α-galactosidase, and phytase at a mass ratio of 10:5:5 :2:2:1, a total of 0.65g, hydrolyzed for 4h. Adjust the temperature to 60°C, adjust the pH to 7.0-7.5, add 0.3 g of neutral protease, and hydrolyze for 3 hours. Adjust the temperature to 70°C, adjust the pH to 8.5-9.0, add 0.4 g of alkaline protease, and hydrolyze for 3 hours. Drying and crushing, the degree of proteolysis was determined to be 71.7%. The contents of stachyose and raffinose were determined by HPLC method, and the contents of stachyose and raffinose were 1.0mg / g and 6.2mg / g respectively, compared with Comparative Example 4, the contents were respectively reduced by 90% and 72%. The phytic acid content was measured by GB / T5009.153-2003, and the phytic acid content of the hydrolyzed vegetable protei...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Weigh 1000kg of soybean meal powder and place it in a reaction kettle, add 6000kg of hot water at 90-100°C, and maintain the temperature above 90°C for 30 minutes. The temperature was adjusted to 55° C., and the pH was adjusted to 4-4.5. Add the compound of α-amylase, cellulase, hemicellulase, pectinase, α-galactosidase and phytase, the mass ratio is 10:5:5:2:2:1, a total of 6.5 kg, hydrolyzed for 3h. Adjust the temperature to 60°C, adjust the pH to 7.0-7.5, add 3 kg of neutral protease, and hydrolyze for 3 hours. Adjust the temperature to 70°C, adjust the pH to 8.5-9.0, add 4 kg of alkaline protease, and hydrolyze for 3 hours. The pH is adjusted to 7-8, the homogenate is spray-dried, and the degree of protein hydrolysis is determined to be 67.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0058] Weigh 1000kg of wheat gluten powder and put it in the reaction kettle, add 8000kg of hot water at 90-100℃, and keep the temperature above 90℃ for 30 minutes. The temperature was adjusted to 55°C, pH 4-4.5. Add the compound of α-amylase, cellulase, hemicellulase, pectinase, α-galactosidase and phytase, the mass ratio is 10:5:5:2:2:1, 6kg in total , Hydrolyzed for 3h. Adjust the temperature to 60°C, adjust the pH to 7.0-7.5, add 3 kg of neutral protease, and hydrolyze for 3 hours. Adjust the temperature to 70°C, adjust the pH to 8.5-9.0, add 4 kg of alkaline protease, and hydrolyze for 5 hours. The pH is adjusted to 7-8, the homogenate is spray-dried, and the degree of protein hydrolysis is determined to be 62.4%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com