Method for preparing rice starch acetate through supported heteropoly acid catalyst
A technology for immobilizing heteropolyacid and starch acetate, applied in the field of starch deep processing, can solve the problems of high environmental harm, low economic benefit, equipment damage, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
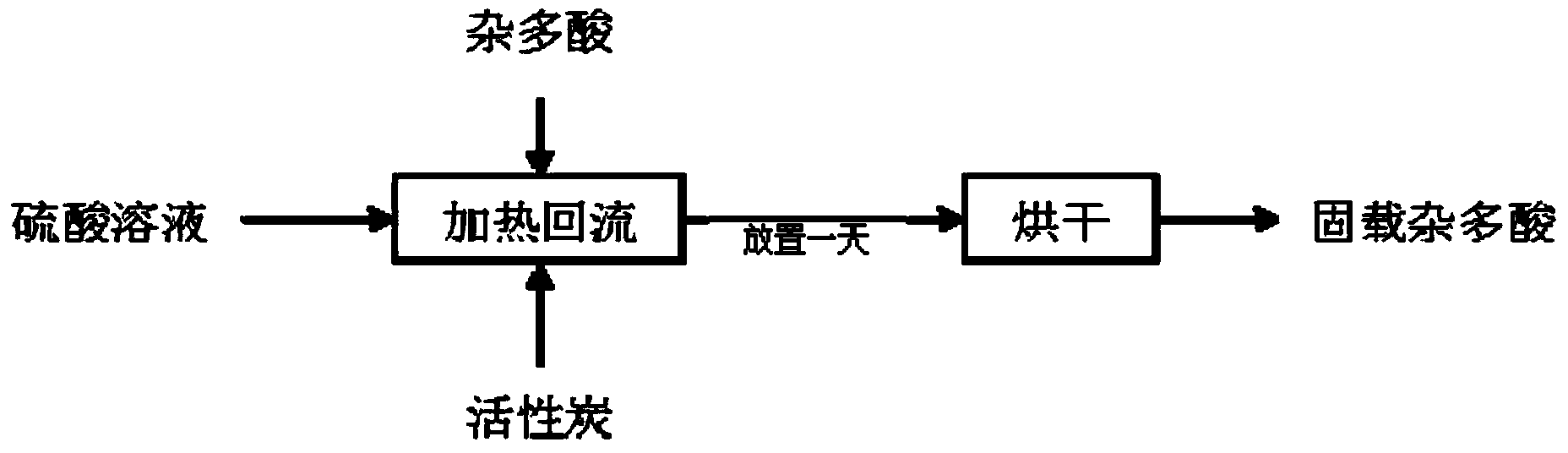
[0023] Use activated carbon with Keggin structure as a carrier, take 9 parts of activated carbon, mix 3 parts of phosphotungstic acid with 60 parts of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, heat the activated carbon with it and reflux for 12 hours, place it for one day, and bake it at 140°C dry to obtain the desired solid-supported catalyst.
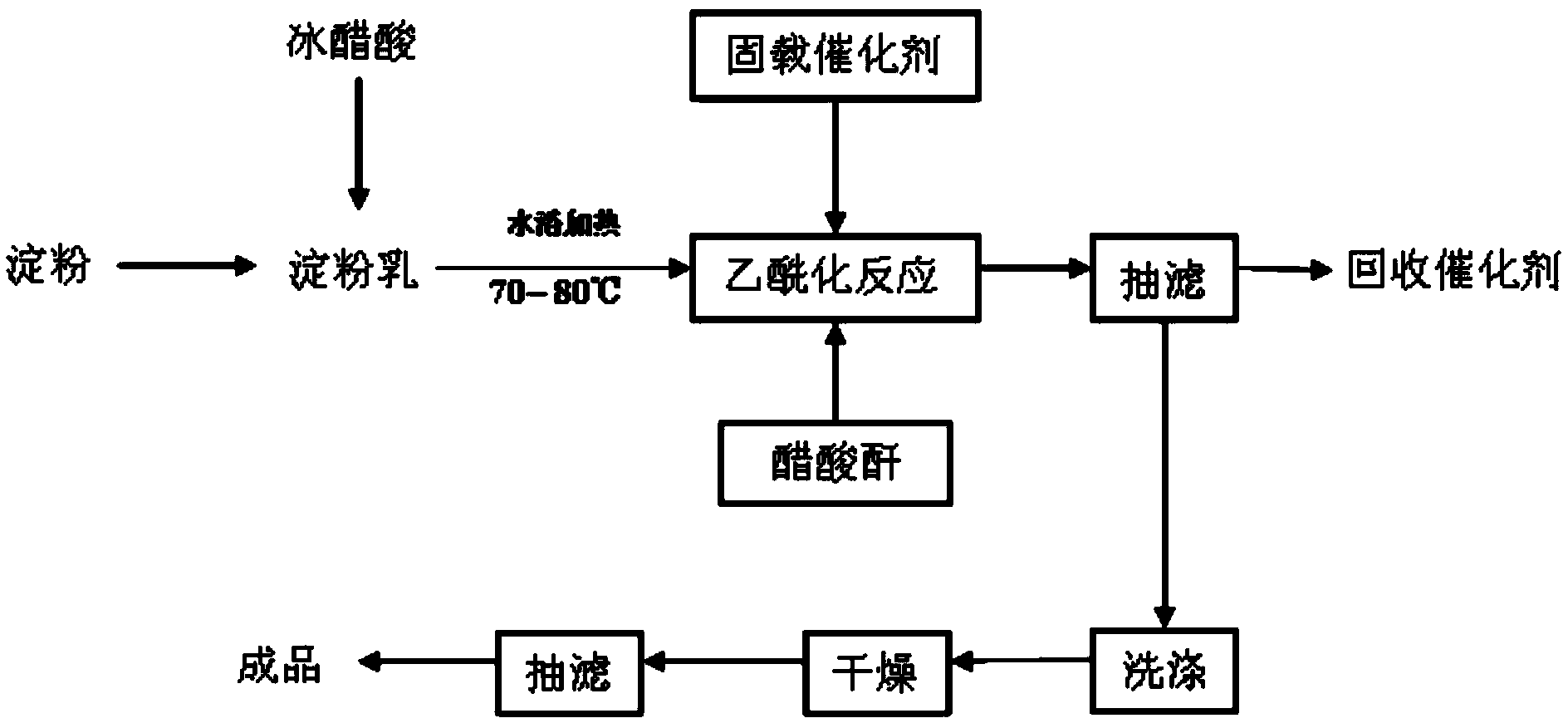
[0024] Weigh 10 parts of rice starch, add 25 parts of glacial acetic acid, stir at room temperature for 3 minutes to make it evenly mixed, add 3 parts of solid-loaded heteropolyacid and 25 parts of acetic anhydride in a constant temperature water bath at 75°C, and react for 2 hours , suction filtration, the filtrate was poured into 1L distilled water, a large amount of starch was separated out, washed, extracted, vacuum-dried at 40°C, ground and sieved to obtain rice starch acetate with a degree of substitution of 2.51.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Use activated carbon with a Keggin structure as a carrier, take 11 parts of activated carbon, mix 4 parts of phosphomolybdic acid with 50 parts of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 0.5mol / L, and heat the activated carbon with it for 12 hours and then place it for one day at 140°C drying to obtain the desired solid-supported catalyst.
[0027] Weigh 10 parts of rice starch, add 27 parts of glacial acetic acid, stir at room temperature for 3 minutes to make it evenly mixed, and add 4 parts of solid-loaded heteropoly acid and 30 parts of acetic anhydride in an environment of constant temperature water bath at 80°C, and react for 2.5 hours , suction filtration, the filtrate was poured into 1L distilled water, a large amount of starch was separated out, washed, extracted, vacuum-dried at 40°C, ground and sieved to obtain rice starch acetate with a degree of substitution of 2.65.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Use activated carbon with a Keggin structure as a carrier, take 12 parts of activated carbon, mix 5 parts of phosphovanadic acid with 60 parts of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, heat the activated carbon with it for 12 hours, place it for one day, and bake it at 140°C dry to obtain the desired solid-supported catalyst.
[0030] Weigh 10 parts of rice starch, add 20 parts of glacial acetic acid, stir at room temperature for 3 minutes to make it evenly mixed, and add 3 parts of recovered solid-loaded heteropolyacid and 25 parts of acetic anhydride in an environment of constant temperature water bath at 70°C, and react After 2 hours, filter with suction, pour the filtrate into 1L of distilled water, precipitate a large amount of starch, wash, extract, vacuum-dry at 40°C, grind and sieve to obtain rice starch acetate with a substitution degree of 2.50.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com