A method for screening and domesticating polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing bacteria utilizing xylose
A technology of polyhydroxyalkanoate and xylose, which is applied in the field of screening and domestication of polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing bacteria by efficient utilization of xylose, can solve the problems of lack of domestication screening pressure and long domestication period of PHA synthetic strains, and achieves Avoid cumbersome, short acclimation time effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The basic steps are as follows:
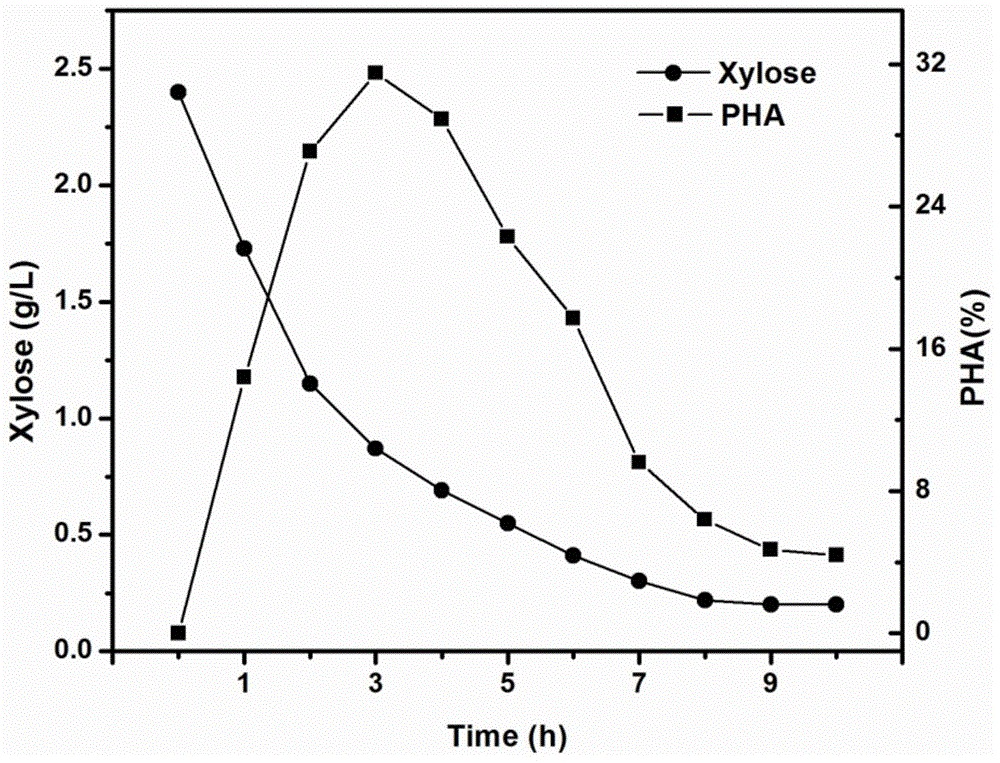
[0023] a) Based on the activated sludge rich in mixed flora, domestication is carried out by referring to the satiety and starvation acclimation model of PHA produced by the mixed flora. A culture cycle includes four steps: feeding, aeration, sedimentation, and drainage. Feeding refers to the addition of fresh xylose acclimation medium at the beginning of each cycle, and drainage refers to the discharge of part of the mixed culture solution after the end of each cycle;
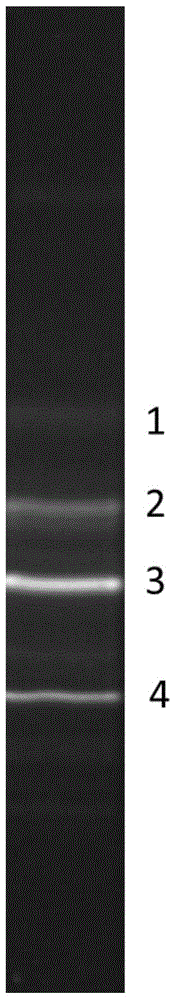
[0024] b) Sampling during the acclimation process, using Nile blue staining method to screen the PHA synthetic flora: Take the cell suspension diluted to a suitable concentration gradient and spread it evenly on the screening medium plate, culture in the dark, and then place it under ultraviolet light Irradiate, select a plate with many fluorescent particles to wash the plate, and inoculate it into the acclimatization system after enrichment culture;
[0025] c) The s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com