Interference coordination method, interference coordination system and network node
A network node and interference coordination technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as uplink/downlink cross-interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
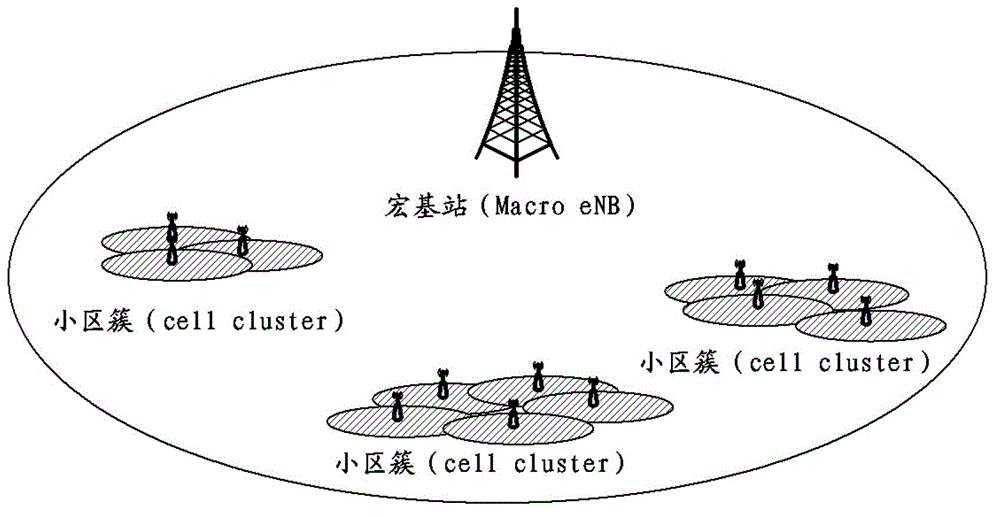
[0078] Assumption: Macro eNB and Small Cells within its coverage form a cell group, and Small Cells can be divided into several Small Cell clusters.
[0079] Embodiment steps are as follows:
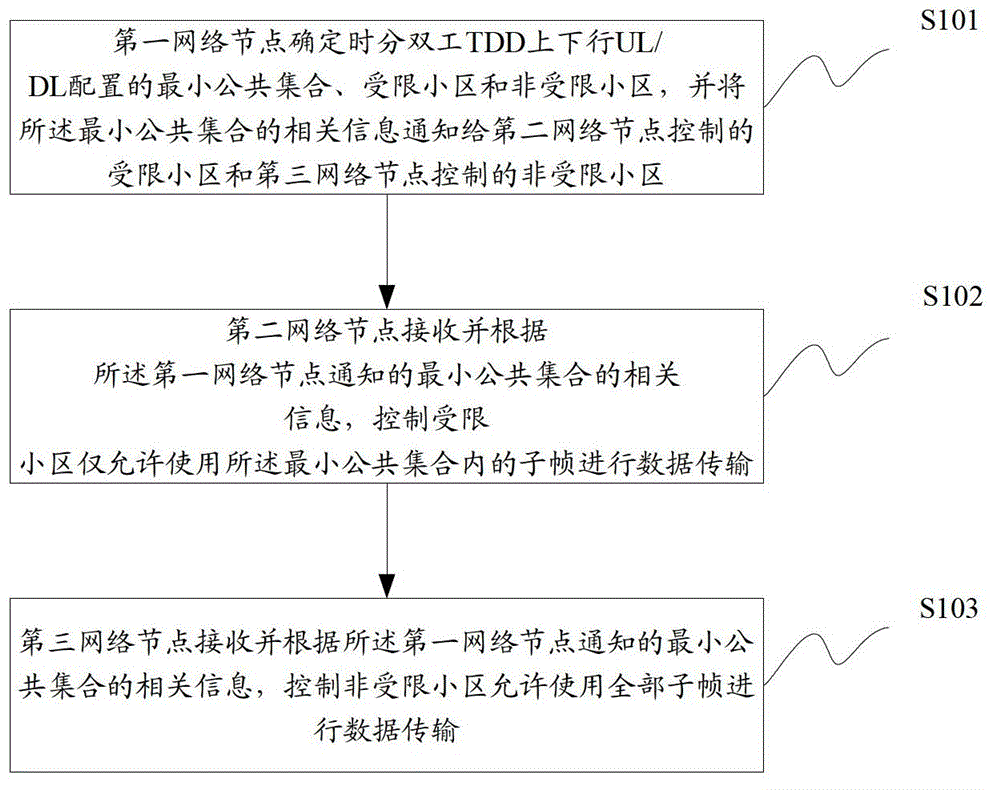
[0080] Step 1: Determine the central management node and the restricted and unrestricted cells
[0081]Since the Macro eNB provides a wide range of coverage, the Macro eNB can be selected as the central management node.
[0082] Considering the interference situation, the Macro eNB may interfere with any cell within its coverage area, so the cells under the Macro eNB can be selected as restricted cells, and other Small Cells as unrestricted cells. In this case, the Macro eNB can know whether the Macro cell supports dynamic TDD configuration information and the indication information of whether dynamic TDD configuration needs to be enabled, so the embodiment only introduces the interaction between the Macro eNB and the Small Cell (or Small Cell Cluster) .
[0083] Step 2: The central m...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Embodiment 2 is assumed to be the same as Embodiment 1. The main difference is that in Embodiment 1, the central management node notifies the restricted cell and the unrestricted cell, and the restricted cell notifies the UE it serves is the minimum common TDD UL / DL configuration. set, while the embodiment 2 notifies the subframe set outside the minimum common set of TDD UL / DL configuration.
[0106] Embodiment 2 except step five, six, seven, other steps are all the same as embodiment 1, only introduce different steps here:
[0107] 1) The difference between Step 5 and Example 1 is:
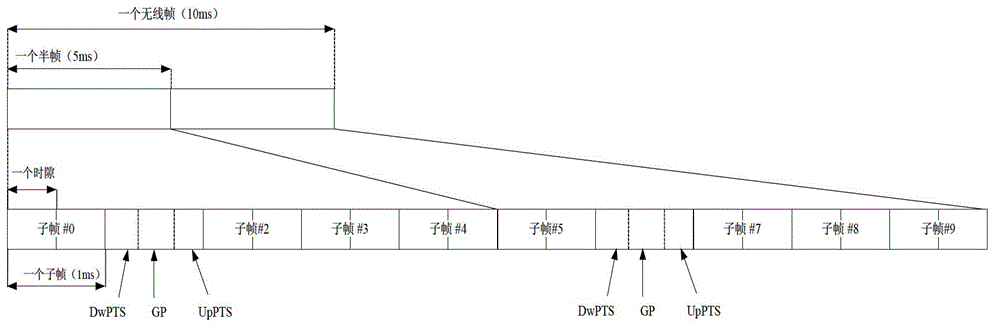
[0108] In Step 5 of Embodiment 1, the Macro eNB notifies the Small Cell (or Small Cell Cluster) and the UE of the minimum common set of TDD UL / DL configurations, while in Embodiment 2 it notifies the minimum common set of TDD UL / DL configurations Other subframes, that is, assuming that the minimum common set of TDD UL / DL configuration determined by Macro eNB is subframe {0,1,2,5}, then th...
Embodiment 3
[0116] Embodiment 3 is assumed to be the same as Embodiment 1. The main difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 1 is that the central management node notifies the unrestricted cell / cell cluster of the TDD UL / Cell specifically used by the cell / cell cluster. DL configuration. The difference between this embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 mainly lies in steps five and six, and other steps are identical.
[0117] In Step 5 of Embodiment 1, what the Macro eNB indicates to the Small Cell (or Small Cell Cluster) is the minimum common set of TDD UL / DL configurations, and here, what the Macro eNB indicates to the Small Cell (or Small Cell Cluster) is the Small Cell ( or Small Cell Cluster) specific TDD UL / DL configurations that can be used.
[0118] For this embodiment 3, step 6 in embodiment 1 can be omitted.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com