Image processing apparatus, imaging device, image processing method, and computer-readable recording medium
An image processing device and image technology, applied in image data processing, computing, image enhancement, etc., can solve problems such as large processing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
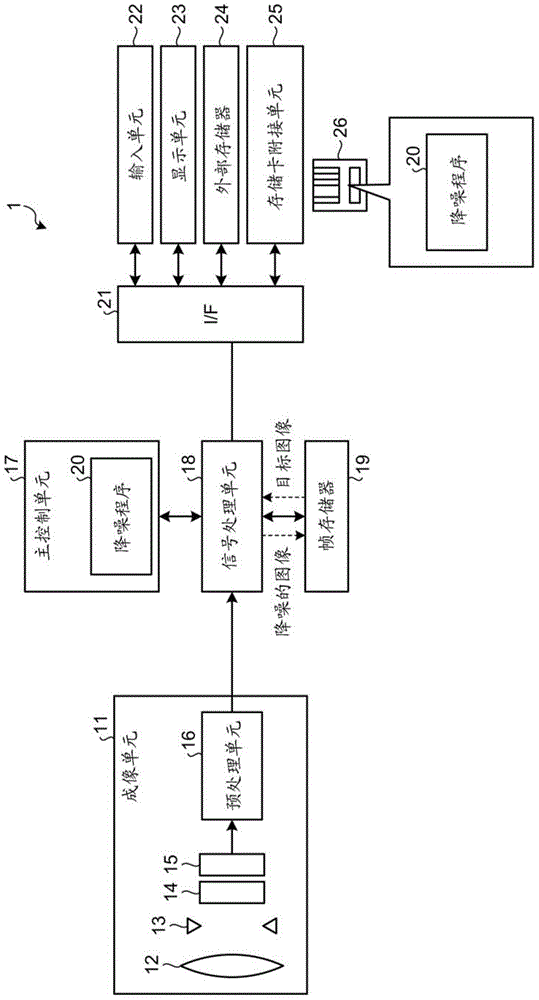
[0031] figure 1 is a block diagram illustrating the overall configuration of the imaging device 1 according to the first embodiment. Specific examples of the imaging device 1 include digital cameras. The imaging device 1 includes an imaging unit 11 that captures an image, a signal processing unit 18 that processes an image signal obtained from the imaging unit 11, a main control unit 17 that controls the entire imaging device 1, a frame memory 19 for storing image data, and a An I / F (Interface) 21 that enables connection with various devices. The I / F 21 is connected to an input unit 22 that receives input from a user, a display unit 23 that displays images and the like, an external memory 24 for storing image data or reading out image data, and a memory card attachment for attaching a storage medium 26 Connect unit 25.
[0032]The imaging unit 11 includes a lens 12 , a diaphragm 13 , an electronic shutter 14 , a photoelectric conversion element 15 , and a preprocessing unit...
no. 2 example
[0089] An image forming apparatus according to a second embodiment will be described below. In the imaging device according to the first embodiment, the weight coefficient is calculated based on the mean value and noise variance value of similar pixel groups of the target image. In contrast, the imaging device according to the second embodiment calculates the weight coefficient based on the variance value (pixel variance value) and the noise variance value of the pixel values of similar pixel groups of the target image.
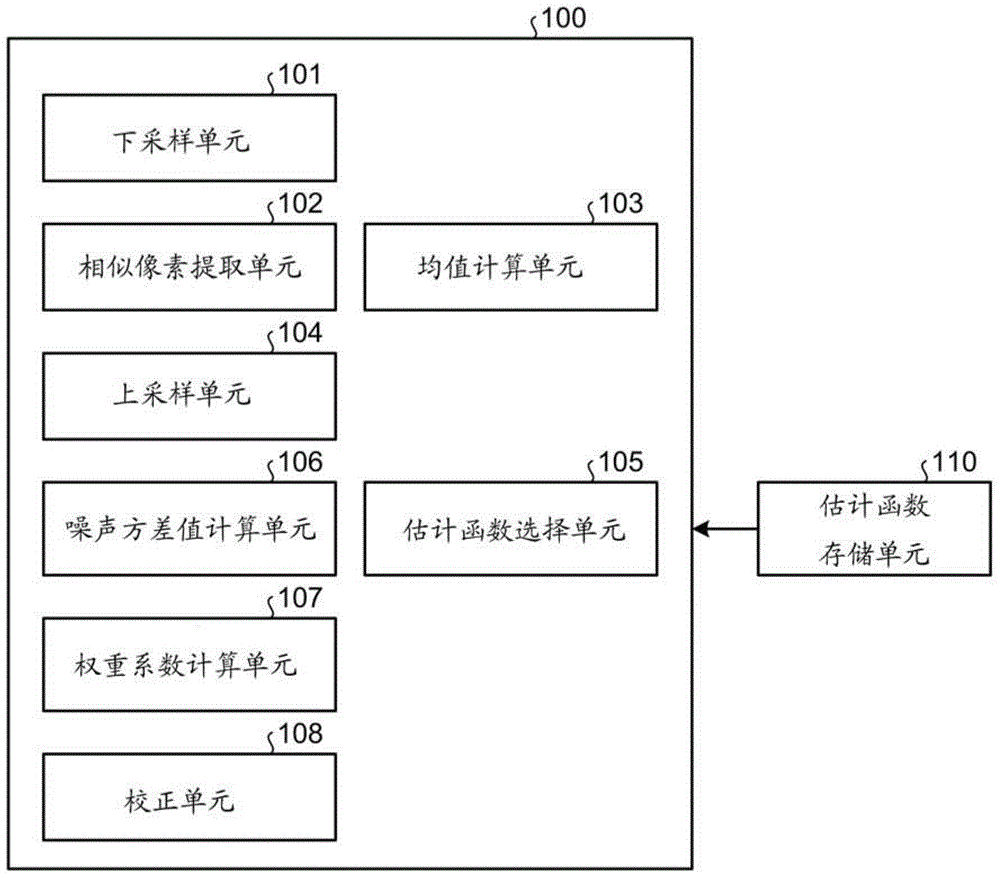
[0090] Hereinafter, differences from the imaging device 1 according to the first embodiment will be described. Figure 10 is a block diagram illustrating the functional configuration of the image processing unit 120 according to the second embodiment. In addition to the functional configuration of the image processing unit 100 of the first embodiment, the image processing unit 120 includes a mean square value calculation unit 121 and a pixel variance value...
no. 3 example
[0108] Similar to the imaging device according to the second embodiment, the imaging device according to the third embodiment calculates weight coefficients based on pixel variance values and noise variance values of similar pixel groups with respect to a target pixel. However, while the imaging device according to the second embodiment calculates the pixel variance value of the pixels of the downsampled image, the imaging device according to the third embodiment does not calculate the pixel variance value of the pixels of the downsampled image. The imaging apparatus according to the third embodiment calculates only the mean square value of the pixels of the downsampled image, and after completing the upsampling, calculates the pixel variance value of the target pixel based on the mean square value.
[0109] The functional configuration of the image processing unit of the imaging device according to the third embodiment is the same as that referred to above Figure 10 The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com