Method for allocating bandwidth in an optical network
An optical network and bandwidth technology, applied in the direction of electromagnetic network arrangement, multiplexing communication, wavelength division multiplexing system, etc., can solve the problems of difficult price/energy consumption growth control, waste of non-congested link transparent bandwidth, etc. To achieve the effect of low complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] Specific non-limiting technical examples of the invention will now be described.
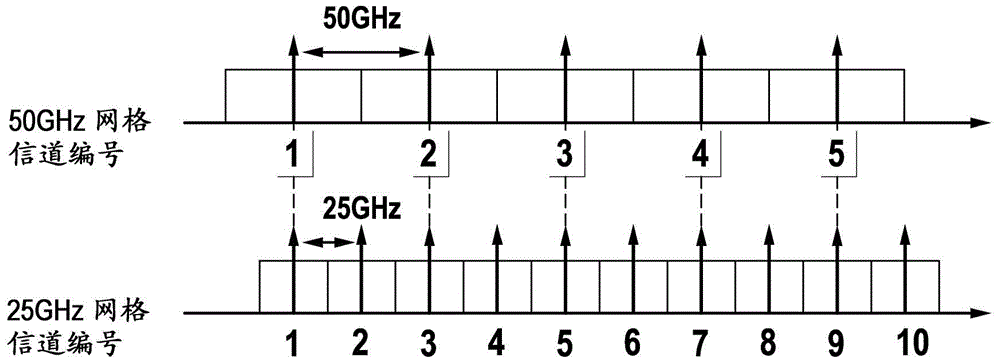
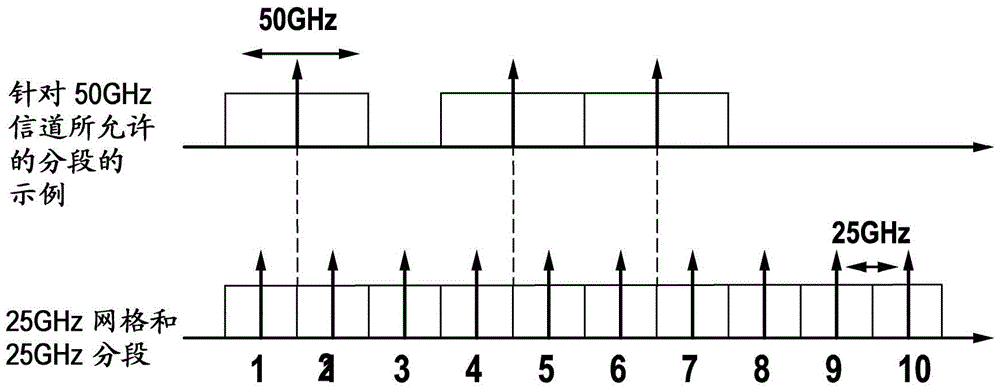
[0026] figure 1 is a diagram representing the relationship between the 50GHz grid and the 25GHz grid as defined by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), and figure 2 is an example showing a 25GHz grid and the allowed spectrum allocation for channels of 50GHz width according to the present invention.
[0027] The bandwidth grid as defined by the ITU is such that the center frequency of the nth 50GHz bandwidth segment corresponds to the center frequency of the (2*n-1)th 25GHz bandwidth segment. Thus, the 50GHz bandwidth segment at least partially overlaps with three other 25GHz bandwidth segments.
[0028] The bandwidth grid as proposed herein is such that the center frequency of a 50GHz bandwidth segment lies between the center frequencies of two other 25GHz bandwidth segments. Thus, the 50GHz bandwidth segment overlaps, preferably completely overlaps, two other 25GHz bandwi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com