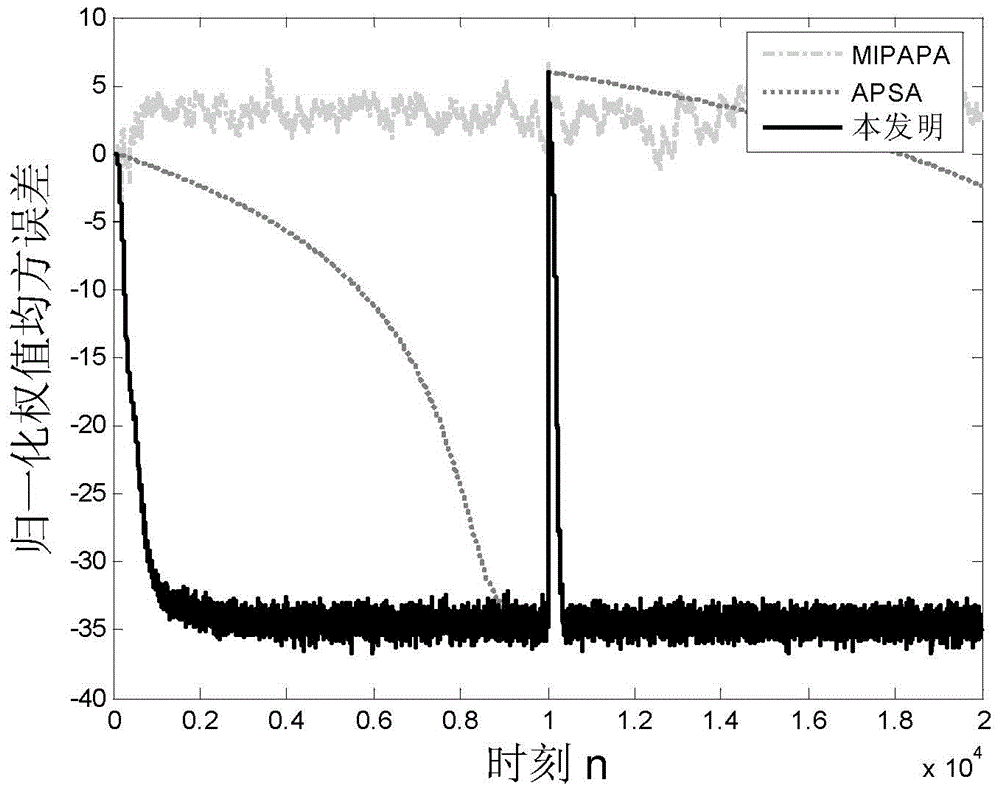
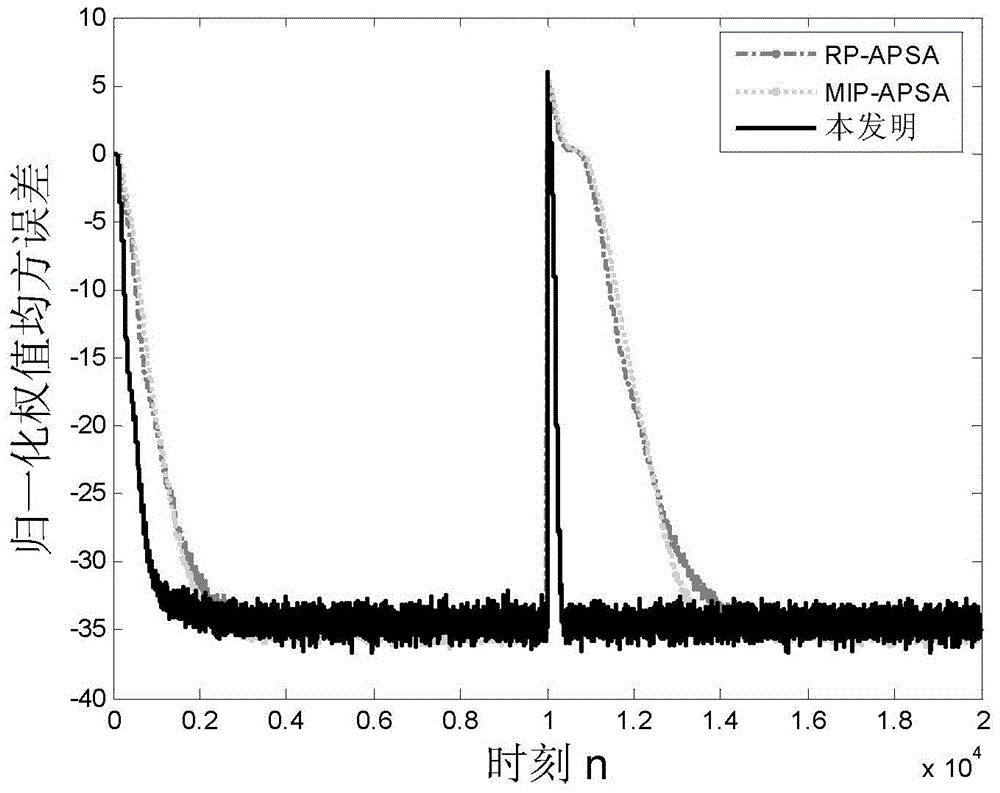
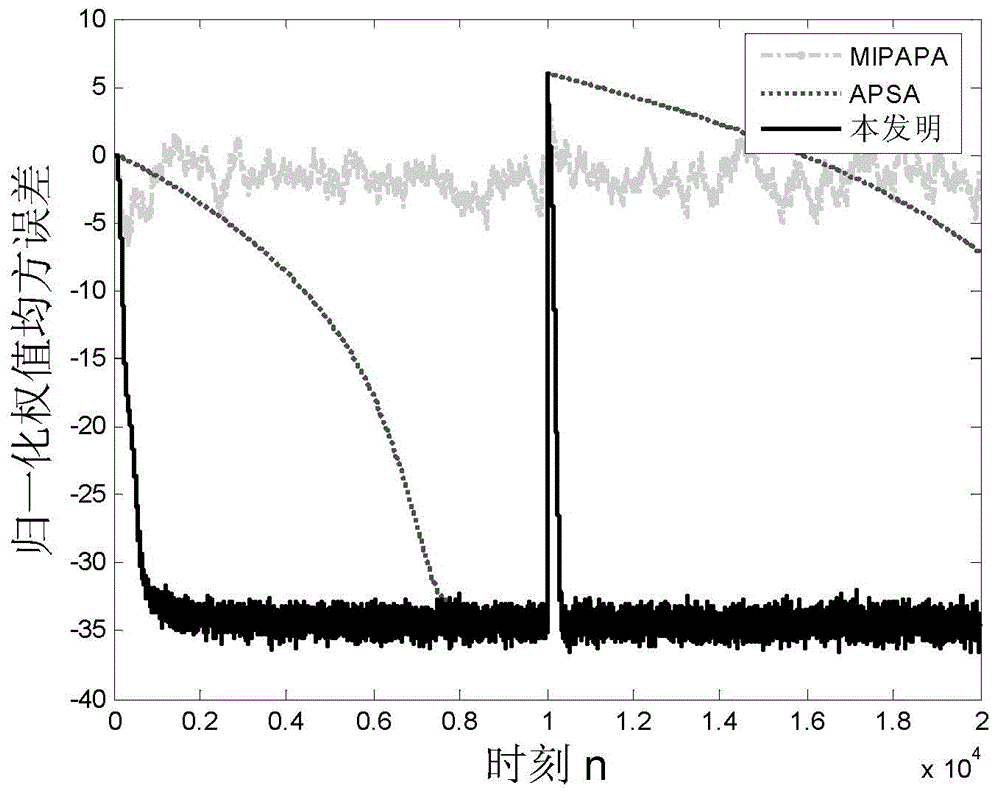
Self-adaptive sparse system identification method based on impact-interference-resistance of independent activity factor
A technology of active factor and system identification, applied in the field of sparse system identification, can solve the problems of slowing down the convergence speed of RP-APSA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0040] An adaptive sparse system identification method based on independent active factors for anti-shock interference, comprising the following steps:
[0041] A. Obtain the desired signal and output signal of the filter
[0042] Send the input signal x(n) to the sparse system w o , get the sparse system w o The output signal d(n) of the adaptive FIR filter is the desired signal; at the same time, the input signal x(n) is sent to the adaptive FIR filter to obtain the output signal of the adaptive FIR filter in:
[0043] n represents the current moment, the superscript T represents the transpose operation, w(n)=[w 1 (n),w 2 (n),...,w i (n),...,w M (n)] T is the weight column vector of the adaptive FIR filter at the current moment, that is, the sparse system w o The column vector identification value at the current moment, its length is M; the value of M depends on the situation of the sparse system, the more complex the sparse system, the larger the value, usually u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com