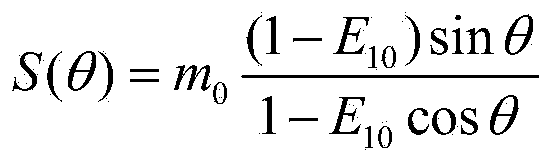Temperature measuring method based on magnetic resonance imaging for in-vivo fat
A magnetic resonance imaging and body fat technology, which is applied in application, diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of inability to guarantee accuracy, low precision, inability to take into account the accuracy and real-time of in-body measurement, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] The magnetic resonance imaging-based temperature measurement method for in-body fat of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
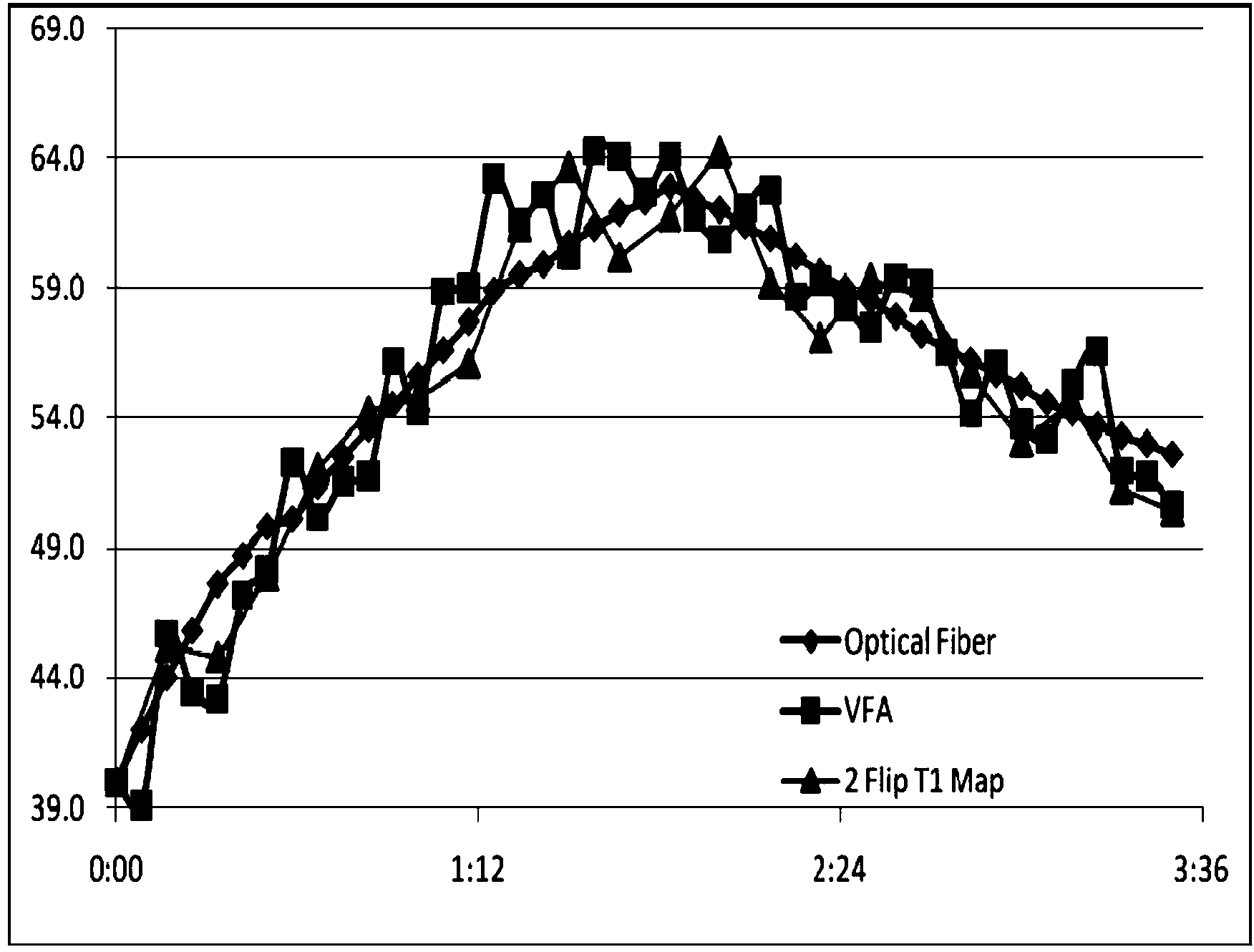
[0062] like figure 1 As shown, a magnetic resonance imaging-based temperature measurement method for body fat includes a non-real-time parameter determination stage and a real-time temperature measurement stage, wherein:
[0063] The non-real-time parameter determination phase includes the following steps:
[0064] 1-1. In the constant body temperature stage, several sets of {θ, S(θ)} data are obtained by scanning, where θ is the flip angle, and S(θ) is the signal intensity corresponding to the flip angle θ;
[0065] 1-2. Use the obtained sets of {θ, S(θ)} data, and the formula Using the least squares method to fit, the equilibrium magnetization vector m is calculated. 0 and the longitudinal relaxation rate R1 0 .
[0066] The number of groups of {θ, S(θ)} is selected according...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com